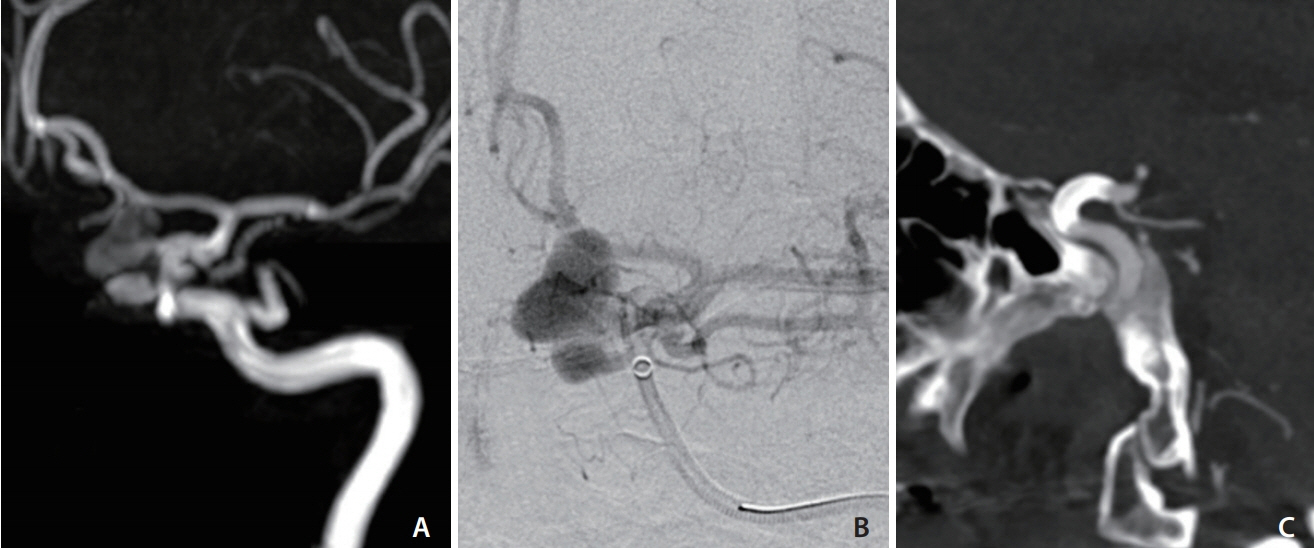
Neurointervention.
2019 Sep;14(2):116-124. 10.5469/neuroint.2019.00073.
Off-Label Application of Pipeline Embolization Device for Intracranial Aneurysms
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Baylor Scott & White Health, Temple, TX, USA. buqing@buqing.org
- 2Texas A&M University HSC-COM, Temple, TX, USA.
- 3Department of Biostatistics, Baylor Scott & White Research Institute, Temple, TX, USA.
- KMID: 2458491
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5469/neuroint.2019.00073
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The Pipeline embolization device (PED) is approved in the USA for treating giant and large aneurysms arising from the petrous to superior hypophyseal segments of the internal carotid artery in patients older than 21 years of age. This study investigates off-label PED results in a large cohort.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Retrospective, single-center review of all patients who had off-label PED surgery.
RESULTS
Sixty-two aneurysms (48 patients) underwent off-label PED treatment from 2012-2017. There were 44 females and four males (age 21 to 75 years; mean/median, 54.3/55.0 years). The most common presenting symptom was headache (47/62, 75.8%). All aneurysms were in the anterior circulation. Aneurysm size ranged from 1.4 to 25.0 mm (mean/median, 7.6/6.9 mm). Fifty-two aneurysms had post-operative imaging with total/near-complete occlusion of 84.6% (44/52). Aneurysm-based operative near-term complication rate was 9.7% while there were no permanent complications. For aneurysms and headache, 86.7% improved/resolved after embo-surgery, and were four times more likely to have a better clinical outcome (resolved or improved symptoms) after surgery (odds ratio [OR], 4.333; P=0.0325). Left-sided aneurysms had a higher occlusion rate (OR, 20; P=0.0073). Hypertension (OR, 4.2; P=0.0332) and smoking (OR, 7; P=0.0155) were more prone towards aneurysm occlusion. Patients without a family history were 14 times more likely to have favorable imaging outcome (P=0.0405). There is no difference of occlusion rates between untreated and previously treated aneurysms (P=0.6894). Overall, occlusion rate decreased by 14% with an increase of aneurysm size by 1 mm (P=0.0283).
CONCLUSION
For anterior circulation aneurysms, the off-label application of PED is as effective and safe as reported for on-label intracranial aneurysms.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Krishna C, Sonig A, Natarajan SK, Siddiqui AH. The expanding realm of endovascular neurosurgery: flow diversion for cerebral aneurysm management. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 2014; 10:214–219.2. US Food and Drug Administration. Instructions for Use (IFU): Pipeline Embolization Device. Silver Spring: US Food and Drug Administration;2011.3. Patel PD, Chalouhi N, Atallah E, Tjoumakaris S, Hasan D, Zarzour H, et al. Off-label uses of the Pipeline embolization device: a review of the literature. Neurosurg Focus. 2017; 42:E4.
Article4. Becske T, Kallmes DF, Saatci I, McDougall CG, Szikora I, Lanzino G, et al. Pipeline for uncoilable or failed aneurysms: results from a multicenter clinical trial. Radiology. 2013; 267:858–868.
Article5. Griessenauer CJ, Ogilvy CS, Foreman PM, Chua MH, Harrigan MR, He L, et al. Pipeline embolization device for small intracranial aneurysms: evaluation of safety and efficacy in a multicenter cohort. Neurosurgery. 2017; 80:579–587.
Article6. Halbach VV, Higashida RT, Dowd CF, Urwin RW, Balousek PA, Lempert TE, et al. Cavernous internal carotid artery aneurysms treated with electrolytically detachable coils. J Neuroophthalmol. 1997; 17:231–239.
Article7. Juvela S, Poussa K, Porras M. Factors affecting formation and growth of intracranial aneurysms: a long-term follow-up study. Stroke. 2001; 32:485–491.8. Qureshi AI, Suarez JI, Parekh PD, Sung G, Geocadin R, Bhardwaj A, et al. Risk factors for multiple intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 1998; 43:22–26. ; discussion 26-27.
Article9. Ellamushi HE, Grieve JP, Jäger HR, Kitchen ND. Risk factors for the formation of multiple intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 2001; 94:728–732.
Article10. Bertakis KD, Azari R, Helms LJ, Callahan EJ, Robbins JA. Gender differences in the utilization of health care services. J Fam Pract. 2000; 49:147–152.11. Arena JE, Hawkes MA, Farez MF, Pertierra L, Kohler AA, Marrodán M, et al. Headache and treatment of unruptured intracranial aneurysms. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017; 26:1098–1103.
Article12. Schwedt TJ, Gereau RW, Frey K, Kharasch ED. Headache outcomes following treatment of unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a prospective analysis. Cephalalgia. 2011; 31:1082–1089.
Article13. Schneider AM, Moore JM, Adeeb N, Gupta R, Griessenauer CJ, Winkler PA, et al. Self-reported headaches in patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms treated with the Pipeline embolization device. World Neurosurg. 2018; 113:e364–e372.
Article14. Kong DS, Hong SC, Jung YJ, Kim JS. Improvement of chronic headache after treatment of unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Headache. 2007; 47:693–697.
Article15. Khan S, Amin FM, Hauerberg J, Holtmannspötter M, Petersen JF, Fakhril-Din Z, et al. Post procedure headache in patients treated for neurovascular arteriovenous malformations and aneurysms using endovascular therapy. J Headache Pain. 2016; 17:73.
Article16. Adeeb N, Moore JM, Wirtz M, Griessenauer CJ, Foreman PM, Shallwani H, et al. Predictors of incomplete occlusion following Pipeline embolization of intracranial aneurysms: is it less effective in older patients? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017; 38:2295–2300.
Article17. Rouchaud A, Brinjikji W, Cloft HJ, Lanzino G, Becske T, Kallmes DF. Smoking does not affect occlusion rates and morbidity-mortality after pipeline embolization for intracranial aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016; 37:1122–1126.
Article18. Chalouhi N, Ali MS, Starke RM, Jabbour PM, Tjoumakaris SI, Gonzalez LF, et al. Cigarette smoke and inflammation: role in cerebral aneurysm formation and rupture. Mediators Inflamm. 2012; 2012:271582.
Article19. Can A, Castro VM, Ozdemir YH, Dagen S, Yu S, Dligach D, et al. Association of intracranial aneurysm rupture with smoking duration, intensity, and cessation. Neurology. 2017; 89:1408–1415.
Article20. Juvela S, Porras M, Poussa K. Natural history of unruptured intracranial aneurysms: probability of and risk factors for aneurysm rupture. J Neurosurg. 2000; 93:379–387.
Article21. Olson JM, Vongpunsawad S, Kuivaniemi H, Ronkainen A, Hernesniemi J, Ryynänen M, et al. Search for intracranial aneurysm susceptibility gene(s) using Finnish families. BMC Med Genet. 2002; 3:7.
Article22. Saatci I, Yavuz K, Ozer C, Geyik S, Cekirge HS. Treatment of intracranial aneurysms using the Pipeline flow-diverter embolization device: a single-center experience with long-term follow-up results. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012; 33:1436–1446.
Article23. Kallmes DF, Brinjikji W, Boccardi E, Ciceri E, Diaz O, Tawk R, et al. Aneurysm Study of Pipeline in an Observational Registry (ASPIRe). Interv Neurol. 2016; 5:89–99.
Article24. Brinjikji W, Murad MH, Lanzino G, Cloft HJ, Kallmes DF. Endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms with flow diverters: a meta-analysis. Stroke. 2013; 44:442–447.
Article25. Chalouhi N, Zanaty M, Whiting A, Yang S, Tjoumakaris S, Hasan D, et al. Safety and efficacy of the Pipeline embolization device in 100 small intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 2015; 122:1498–1502.
Article26. Chalouhi N, Zanaty M, Whiting A, Tjoumakaris S, Hasan D, Ajiboye N, et al. Treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms with the pipeline embolization device. Neurosurgery. 2015; 76:165–172. ; discussion 172.
Article27. Awad AW, Moon Moon, Yoon N, Mazur MD, Kalani MYS, Taussky P, et al. Flow diversion of tandem cerebral aneurysms: a multi-institutional retrospective study. Neurosurg Focus. 2017; 42:E10.
Article28. Cagnazzo F, Mantilla D, Lefevre PH, Dargazanli C, Gascou G, Costalat V. Treatment of middle cerebral artery aneurysms with flow-diverter stents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017; 38:2289–2294.
Article29. Prospective Study on Embolization of Intracranial Aneurysms With Pipeline™ Embolization Device (PREMIER). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02186561. Accessed September 28, 2018.30. American Heart Association. Prospective, Multi-Center Study of Flow Diversion for Small and Medium-Sized Aneurysms: Results of the Premier Trial. https://professional.heart.org/idc/groups/ahamah-public/@wcm/@sop/@scon/documents/downloadable/ucm_492111.pdf. Accessed October 1, 2018.31. Ackroyd N, Gill R, Griffiths K, Kossoff G, Appleberg M. Quantitative common carotid artery blood flow: prediction of internal carotid artery stenosis. J Vasc Surg. 1986; 3:846–853.
Article32. Urbanski P, Lenos A, Lindemann Y, Zacher M, Frank S, Diegeler A. Use of a carotid artery for arterial cannulation: side-related differences. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010; 58:276–279.
Article33. Schneiders JJ, VanBavel E, Majoie CB, Ferns SP, van den Berg R. A flow-diverting stent is not a pressure-diverting stent. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013; 2013:E1–E4.
Article34. Kadirvel R, Ding YH, Dai D, Rezek I, Lewis DA, Kallmes DF. Cellular mechanisms of aneurysm occlusion after treatment with a flow diverter. Radiology. 2014; 270:394–399.
Article35. Kallmes DF, Ding YH, Dai D, Kadirvel R, Lewis DA, Cloft HJ. A new endoluminal, flow-disrupting device for treatment of saccular aneurysms. Stroke. 2007; 38:2346–2352.
Article36. Becske T, Brinjikji W, Potts MB, Kallmes DF, Shapiro M, Moran CJ, et al. Long-term clinical and angiographic outcomes following Pipeline embolization device treatment of complex internal carotid artery aneurysms: fiveyear results of the Pipeline for uncoilable or failed aneurysms trial. Neurosurgery. 2017; 80:40–48.
Article37. Imamura H, Sakai N, Sakai C, Fujinaka T, Ishii A; JR-NET Investigators. Endovascular treatment of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in Japanese Registry of Neuroendovascular Therapy (JR-NET) 1 and 2. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2014; 54:81–90.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Flow diverter stenting for intracranial aneurysms in the pediatric population: Two case reports and literature review
- A Case of Migration of Pipeline Embolization Device Causing Rupture during Treatment of an Unruptured Vertebral Artery Dissecting Aneurysm
- Pipeline Embolization Device for Giant Internal Carotid Artery Aneurysms: 9-Month Follow-Up Results of Two Cases
- Persistent Aneurysm Growth Following Pipeline Embolization Device Assisted Coiling of a Fusiform Vertebral Artery Aneurysm: A Word of Caution!
- Treatment of Intracranial Aneurysms with the Pipeline Embolization Device Only: a Single Center Experience