J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2024 Mar;26(1):58-64. 10.7461/jcen.2023.E2023.04.001.
Flow diverter stenting for intracranial aneurysms in the pediatric population: Two case reports and literature review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Medical College of Wisconsin, WI, USA
- 2Department of Neurology, Medical College of Wisconsin, Wauwatosa, WI, USA
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Northwell Health, New York, USA
- KMID: 2554047
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2023.E2023.04.001
Abstract
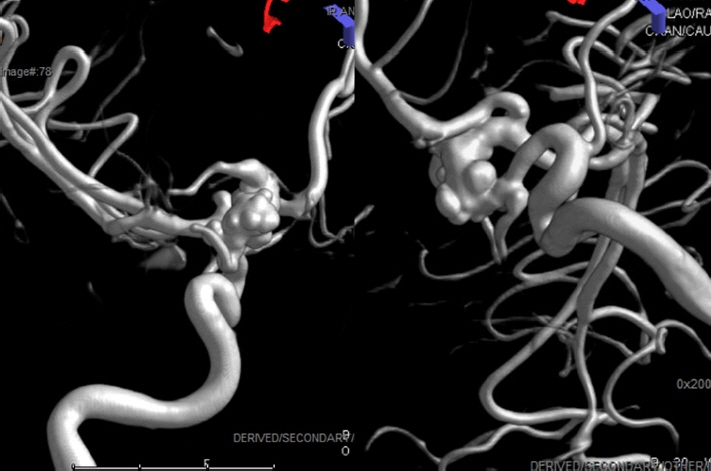
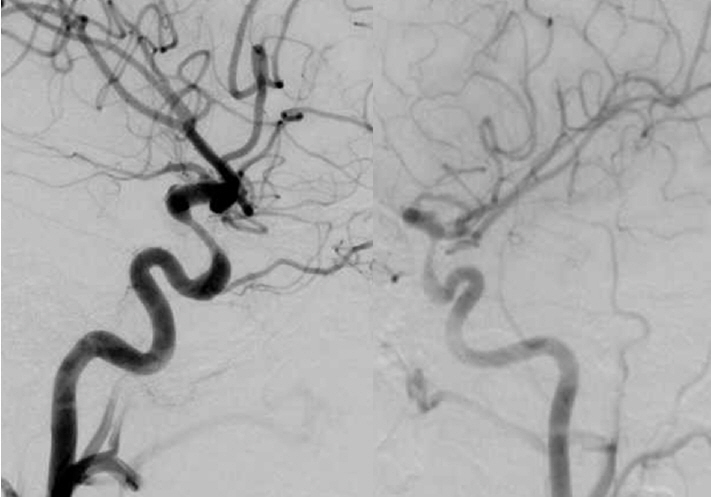
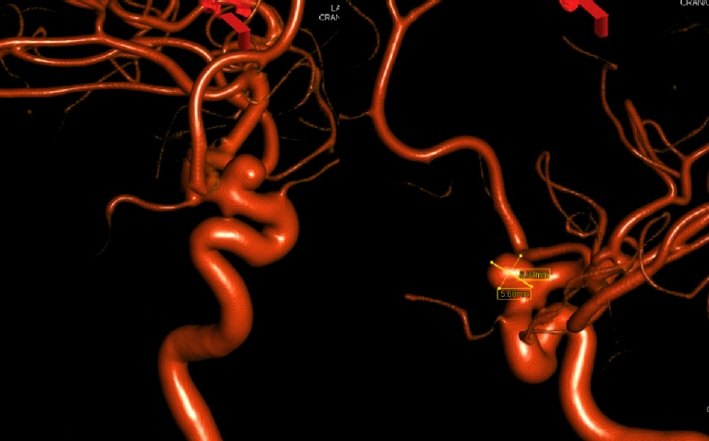
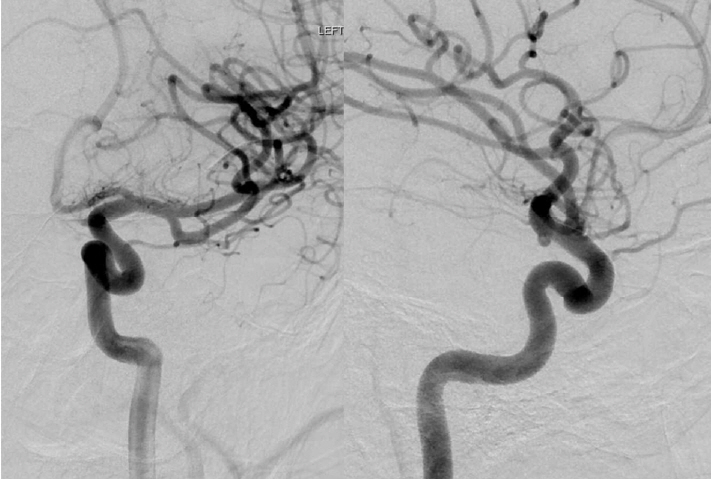
- The Pipeline Embolization Device (PED) is a flow-diverting intraluminal device that is approved for use in adults 18 years or older with internal carotid artery aneurysms. However, it can also be used off-label in pediatric patients with aneurysms that cannot be resolved with traditional endovascular treatments. Herein, we present two cases of flow diversion in the pediatric population with complete obliteration of the aneurysm and excellent outcomes. Flow diversion has been shown to be a safe endovascular option in treating complex aneurysms in children. Larger-sized, multicenter trials are encouraged to compare outcomes between flow diversion and other aneurysm treatment options given the rarity of pediatric aneurysms.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Abla AA, Zaidi HA, Crowley RW, Britz GW, McDougall CG, Albuquerque FC, et al. Optic chiasm compression from mass effect and thrombus formation following unsuccessful treatment of a giant supraclinoid ICA aneurysm with the Pipeline device: Open surgical bailout with STA-MCA bypass and parent vessel occlusion. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2014; Jul. 14(1):31–7.
Article2. Adeeb N, Griessenauer CJ, Foreman PM, Moore JM, Shallwani H, Motiei-Langroudi R, et al. Use of platelet function testing before pipeline embolization device placement: A multicenter cohort study. Stroke. 2017; May. 48(5):1322–30.
Article3. Appelboom G, Kadri K, Hassan F, Leclerc X. Infectious aneurysm of the cavernous carotid artery in a child treated with a new-generation of flow-diverting stent graft: Case report. Neurosurgery. 2010; Mar. 66(3):e623–4. discussion e624.4. Ares WJ, Tonetti DA, Greene S, Sharma MS, Xavier F, Jankowitz BT, et al. Pipeline embolization of an infectious basilar artery aneurysm in a 2-year-old child: Case report, discussion of the literature and perioperative considerations. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown). 2019; Nov. 17(5):e224–8.
Article5. Barburoglu M, Arat A. Flow diverters in the treatment of pediatric cerebrovascular diseases. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017; Jan. 38(1):113–8.
Article6. Burrows AM, Zipfel G, Lanzino G. Treatment of a pediatric recurrent fusiform middle cerebral artery (MCA) aneurysm with a flow diverter. J Neurointerv Surg. 2013; Nov. 5(6):e47.
Article7. Cherian J, Srinivasan V, Froehler MT, Grossberg JA, Cawley CM, Hanel RA, et al. Flow diversion for treatment of intracranial aneurysms in pediatric patients: Multicenter case series. Neurosurgery. 2020; Jul. 87(1):53–62.
Article8. Cinar C, Bozkaya H, Oran I. Endovascular treatment of cranial aneurysms with the pipeline flow diverting stent: Preliminary midterm results. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2013; MarApr. 19(2):154–64.
Article9. Cobb MIH, Zomorodi AR, Hauck EF, Smith TP, Fernando Gonzalez L. Optimal pediatric dosing of anti-platelet agents for pipeline stent embolization: A case report and review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst. 2017; Apr. 33(4):685–90.
Article10. Colby GP, Jiang B, Bender MT, Beaty NB, Westbroek EM, Xu R, et al. Pipeline-assisted coil embolization of a large middle cerebral artery pseudoaneurysm in a 9-month-old infant: Experience from the youngest flow diversion case. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2018; Nov. 22(5):532–40.
Article11. Crowley RW, Evans AJ, Kassell NF, Jensen ME, Dumont AS. Endovascular treatment of a fusiform basilar artery aneurysm using multiple “in-stent stents”: Technical note. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2009; Jun. 3(6):496–500.
Article12. Cunegatto-Braga M, Hogan B, Aguilar-Salinas P, Beier AD, Hanel RA. Pipeline embolization device flow diversion for a dissecting ruptured posterior cerebral artery aneurysm in a pediatric patient. World Neurosurg. 2018; Sep. 117:255–60.
Article13. de Barros Faria M, Castro RN, Lundquist J, Scrivano E, Ceratto R, Ferrario A, et al. The role of the pipeline embolization device for the treatment of dissecting intracranial aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; Dec. 32(11):2192–5.
Article14. Eddleman CS, Surdell D, DiPatri A, Tomita T, Shaibani A. Infectious intracranial aneurysms in the pediatric population: Endovascular treatment with Onyx. Childs Nerv Syst. 2008; Aug. 24(8):909–15.
Article15. Ghali MGZ, Srinivasan VM, Cherian J, Wagner KM, Chen SR, Johnson J, et al. Multimodal treatment of intracranial aneurysms in children: Clinical case series and review of the literature. World Neurosurg. 2018; Mar. 111:e294–307.
Article16. Ikeda DS, Marlin ES, Shaw A, Powers CJ. Successful endovascular reconstruction of a recurrent giant middle cerebral artery aneurysm with multiple telescoping flow diverters in a pediatric patient. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2015; 50(2):88–93.
Article17. Jia L, Wang J, Zhang L, Zhang Y, You W, Yang X, et al. Pediatric patient with a giant vertebrobasilar dissecting aneurysm successfully treated with three pipeline embolization devices. Front Neurol. 2020; Jul. 11:633.
Article18. Kalani MY, Elhadi AM, Ramey W, Nakaji P, Albuquerque FC, McDougall CG, et al. Revascularization and pediatric aneurysm surgery. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2014; Jun. 13(6):641–6.
Article19. Kan P, Mokin M, Puri AS, Wakhloo AK. Successful treatment of a giant pediatric fusiform basilar trunk aneurysm with surpass flow diverter. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016; Jun. 8(6):e23.
Article20. Kim M, Lee HS, Lee S, Park JC, Ahn JS, Kwon DH, et al. Pediatric intracranial aneurysms: Favorable outcomes despite rareness and complexity. World Neurosurg. 2019; May. 125:e1203–16.
Article21. Krings T, Geibprasert S, terBrugge KG. Pathomechanisms and treatment of pediatric aneurysms. Childs Nerv Syst. 2010; Oct. 26(10):1309–18.
Article22. Kumaria A, McConachie NS, Macarthur DC. Successful treatment of giant cavernous carotid artery aneurysm in a child using a flow diverter stent. Br J Neurosurg. 2021; Feb. 35(1):122–4.
Article23. Li JS, Yow E, Berezny KY, Bokesch PM, Takahashi M, Graham TP, et al. Dosing of clopidogrel for platelet inhibition in infants and young children: Primary results of the Platelet Inhibition in Children On cLOpidogrel (PICOLO) trial. Circulation. 2008; Jan. 117(4):553–9.
Article24. Lin N, Lanzino G, Lopes DK, Arthur AS, Ogilvy CS, Ecker RD, et al. Treatment of distal anterior circulation aneurysms with the pipeline embolization device: A US multicenter experience. Neurosurgery. 2016; Jul. 79(1):14–22.
Article25. Lubicz B, Collignon L, Raphaeli G, Pruvo JP, Bruneau M, De Witte O, et al. Flow-diverter stent for the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms: A prospective study in 29 patients with 34 aneurysms. Stroke. 2010; Oct. 41(10):2247–53.
Article26. Mohammad LM, Coon AL, Carlson AP. Resolution of giant basilar artery aneurysm compression and reversal of sensorineural hearing loss with use of a flow diverter: Case report. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2017; Jul. 20(1):81–5.
Article27. Navarro R, Brown BL, Beier A, Ranalli N, Aldana P, Hanel RA. Flow diversion for complex intracranial aneurysms in young children. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2015; Mar. 15(3):276–81.
Article28. Peters PJ, Harrison T, Lennox JL. A dangerous dilemma: Management of infectious intracranial aneurysms complicating endocarditis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2006; Nov. 6(11):742–8.
Article29. Samples DC, Ravindra VM, Thoms DJ, Tarasiewicz I, Grandhi R. Successful flow diversion treatment of ruptured infectious middle cerebral artery aneurysms with the use of Pipeline Flex with Shield technology. Interv Neuroradiol. 2021; Apr. 27(2):225–9.
Article30. Saraf R, Shrivastava M, Siddhartha W, Limaye U. Intracranial pediatric aneurysms: Endovascular treatment and its outcome. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2012; Sep. 10(3):230–40.
Article31. Sastry RA, Koch MJ, Grannan BL, Stapleton CJ, Butler WE, Patel AB. Flow diversion of a recurrent, iatrogenic basilar tip aneurysm in a pediatric patient: Case report. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2018; Jan. 21(1):90–3.
Article32. Takemoto K, Tateshima S, Golshan A, Gonzalez N, Jahan R, Duckwiler G, et al. Endovascular treatment of pediatric intracranial aneurysms: a retrospective study of 35 aneurysms. J Neurointerv Surg. 2014; Jul. 6(6):432–8.
Article33. Tonetti DA, Casillo SM, Jankowitz BT. Telescoping flow diverters for a pediatric fusiform distal anterior cerebral artery aneurysm: Technical case report. Childs Nerv Syst. 2021; Mar. 37(3):999–1002.
Article34. Trivelato FP, Rezende MTS, Fonseca LV, Bonadio LE, Ulhôa AC, Abud DG. Pipeline embolization device for the treatment of a traumatic intracranial aneurysm in a child. Childs Nerv Syst. 2017; May. 33(5):869–72.
Article35. Vachhani JA, Nickele CM, Elijovich L, Klimo P, Arthur AS. Flow diversion for treatment of growing A2 aneurysm in a child: Case report and review of flow diversion for intracranial aneurysms in pediatric patients. World Neurosurg. 2016; Dec. 96:607.
Article36. Vargas SA, Diaz C, Herrera DA, Dublin AB. Intracranial aneurysms in children: The role of stenting and flow-diversion. J Neuroimaging. 2016; Jan-Feb. 26(1):41–5.
Article37. Zarzecka A, Gory B, Turjman F. Implantation of two flow diverter devices in a child with a giant, fusiform vertebral artery aneurysm: Case report. Pediatr Neurol. 2014; Feb. 50(2):185–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clipping of a persistent middle cerebral artery aneurysm after previous flow diverter placement: An illustrative case and review of the literature
- Flow Diverter Device for Treatment of Cerebral Aneurysm with Short-Term Follow Up: Two Case Reports
- Blood flow in intracranial aneurysms treated with Pipeline embolization devices: computational simulation and verification with Doppler ultrasonography on phantom models
- Symptomatic Post Endarterectomy Common Carotid Artery Pseudoaneurysm Treated with Combination of Flow Diverter Implantation and Carotid Stenting
- Electrothermal Coil Detachment Failure in Flow Diverter-Assisted Coiling of a Small Blister Aneurysm: Technical Considerations and Possible Solutions