Neurointervention.
2018 Mar;13(1):54-57. 10.5469/neuroint.2018.13.1.54.
Symptomatic Post Endarterectomy Common Carotid Artery Pseudoaneurysm Treated with Combination of Flow Diverter Implantation and Carotid Stenting
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Advocate Health Care, Normal, IL, USA. michael.young2@advocatehealth.com
- 2Department of Neurointerventional Radiology, Advocate Health Care, Normal, IL, USA.
- KMID: 2424050
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5469/neuroint.2018.13.1.54
Abstract
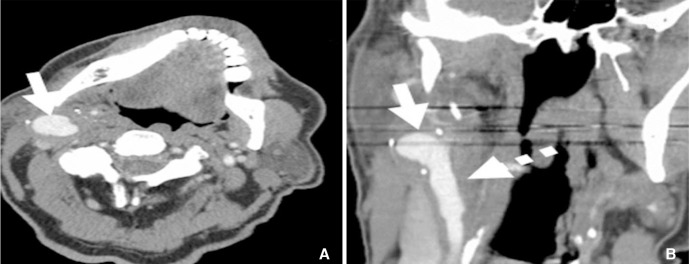
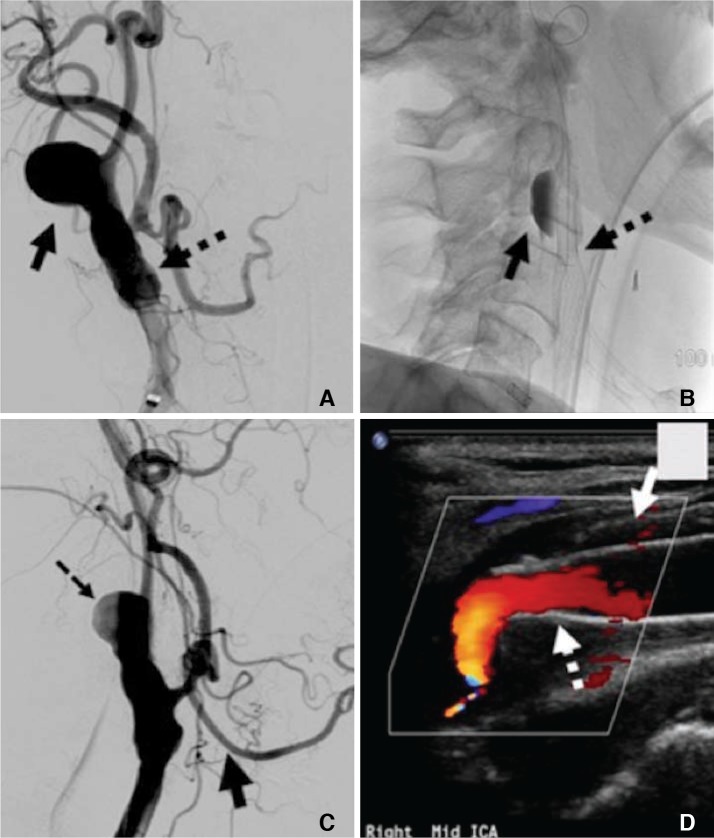
- A 74-year-old male developed cervical carotid artery psuedoaneurysm 8 months after carotid endarterectomy. The patient was successfully managed with dual implantation of flow-diverter and conventional carotid stent. Flow-diverter was placed across the neck of pseudoaneurysm to provide flow diversion while carotid stent was implanted within the lumen of the expanded flow-diverter to approximate and hold the flow diverter proximal and distal to the pseudoaneurysm. Follow-up ultrasonography revealed complete resolution of the pseudoaneurysm.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Branch CL Jr, Davis CH Jr. False aneurysm complicating carotid endarterectomy. Neurosurgery. 1986; 19:421–425. PMID: 3762890.
Article2. Abdelhamid MF, Wall ML, Vohara RK. Carotid artery pseudoaneurysm after carotid endarterectomy: case series and a review of the literature. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2009; 43:571–571. PMID: 19640914.
Article3. Hertzer NR. Extracranial carotid aneurysms: a new look at an old problem. J Vasc Surg. 2000; 31:823–825. PMID: 10753296.
Article4. Varetto G, Gianfranco C, Quaglino S, Garneri P, Benintende E, Gibello L, et al. Successful management with 2 overlapping bare stents for post-carotid endarterectomy carotid pseudoaneurysm secondary to carotid shunt. Ann Vasc Surg. 2015; 29:594.e1–594.e4.
Article5. Troutman DA, Mohan CR, Samhouri FA, Sohn RL. Endovascular repair of carotid artery pseudoaneurysm after carotid endarterectomy with self-expanding covered stents - a long-term follow-up. Ann Vasc Surg. 2010; 24:954.e13–954.e16.6. Holder R, Hilton D, Martin J, Harris PL, Rowlands PC, McWilliams RG. Percutaneous thrombin injection of carotid artery pseudoaneurysm. J Endovasc Ther. 2002; 9:25–28. PMID: 11958321.
Article7. Benndorf G, Campi A, Schneider GH, Wellnhofer E, Unterberg A. Overlapping stents for treatment of a dissecting carotid artery aneurysm. J Endovasc Ther. 2001; 8:566–570. PMID: 11797969.
Article8. Nelson PK, Lylyk P, Szikora I, Wetzel SG, Wanke I, Fiorella D. The pipeline embolization device for the intracranial treatment of aneurysms trial. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; 32:34–40. PMID: 21148256.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fracture of a Flow Diverter in the Cervical Internal Carotid Artery Due to Eagle Syndrome
- Multiple Carotid Artery Occlusive Diseases Treated with Staged Subclavian-carotid Artery bypass and Carotid Endarterectomy: Case Report
- Carotid Artery Stenting
- Microsurgical Endarterectomy for Symptomatic Carotid Artery Stenosis
- Stenting of Extracranial Carotid Artery Stenosis