Kosin Med J.
2021 Dec;36(2):193-199. 10.7180/kmj.2021.36.2.193.
Flow Diverter Device for Treatment of Cerebral Aneurysm with Short-Term Follow Up: Two Case Reports
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2524665
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2021.36.2.193
Abstract
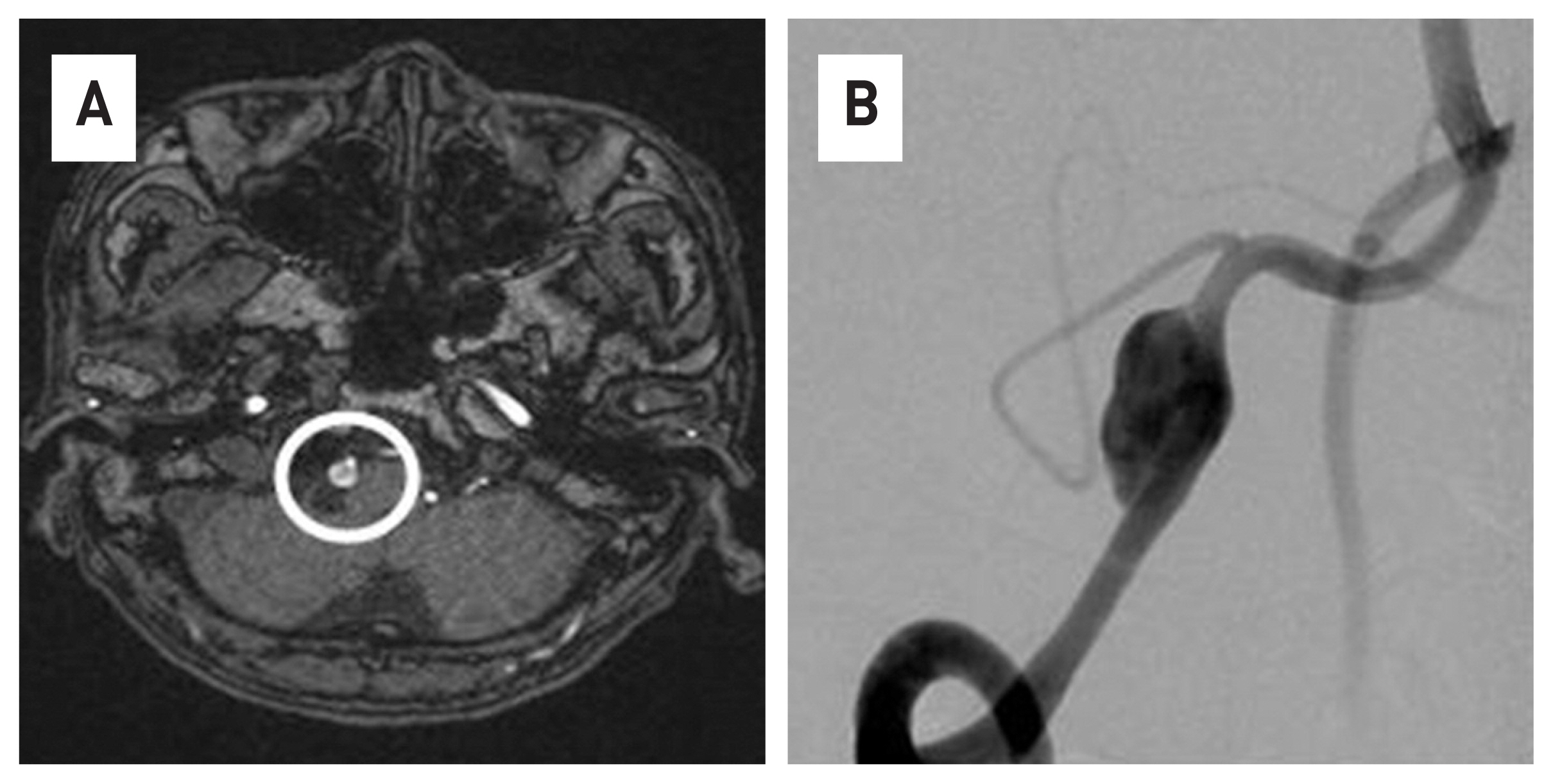
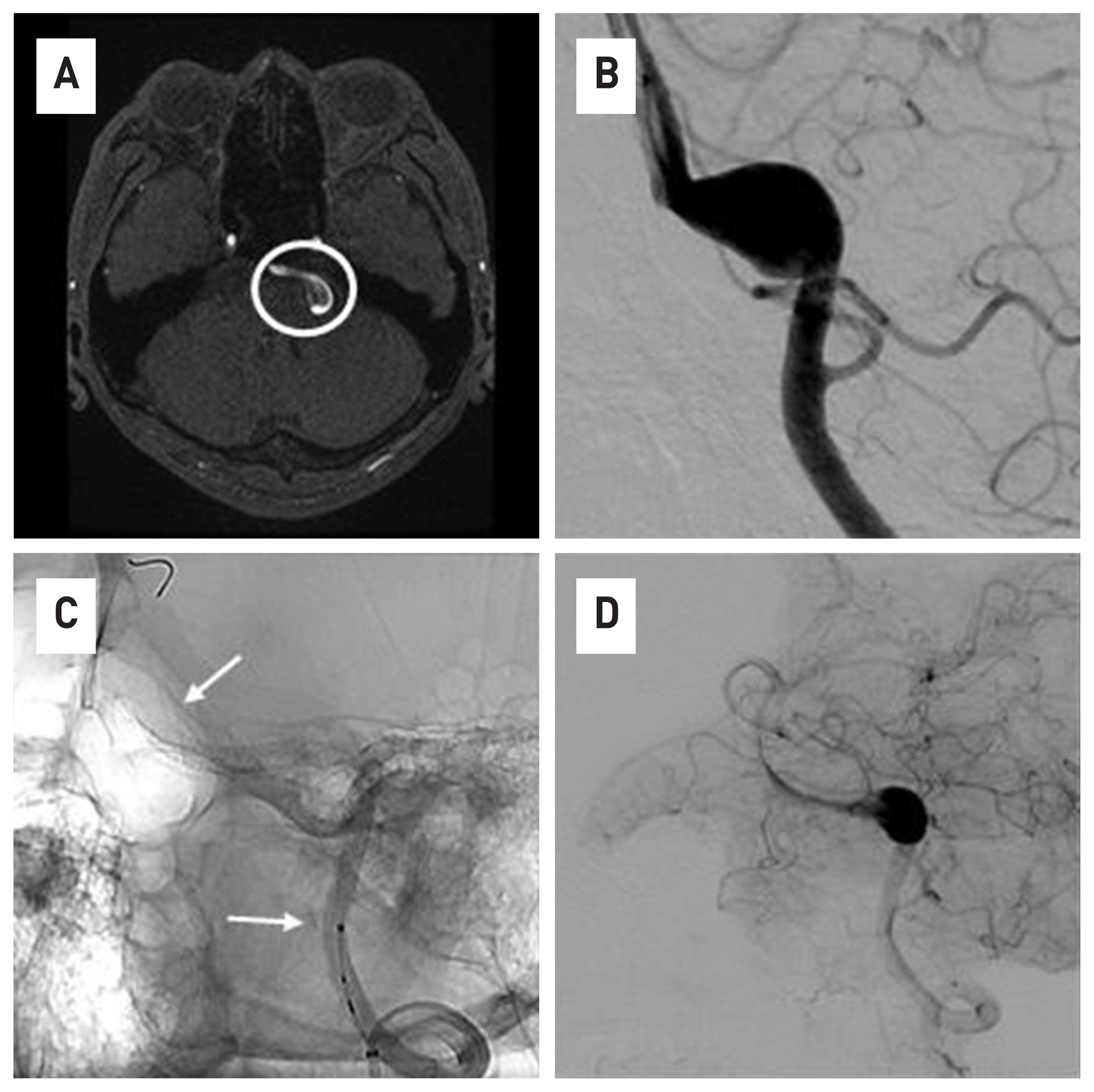
- The flow diverter device (FDD) is an important treatment method for cerebral aneurysms, especially for intracranial dissecting aneurysms. This paper is the result of FDD treatment for two cases of vertebral dissecting aneurysm (VADA) patients and short-term follow-up at 3 months. All two cases were targeted for unruptured cerebral aneurysm, and 4-vessel angiography was performed as a follow-up examination for 3 months after receiving the procedure. As result, it was possible to shorten the period of use of antiplatelet drugs. In the case of VADA, there are limitations in general coiling procedures or conventional surgical treatment methods. In that sense, the FDD treatment method can be a very effective alternative treatment of VADA
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brinjikji W, Murad HM, Lanzino G, Cloft HJ, Kallmes DF. Endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms with flow diverters: a meta-analysis. Stroke. 2013; 44:442–7.
Article2. Briganti F, Leone G, Marseglia M, Mariniello G, Caranci F, Brunetti A, et al. Endovascular treatment of cerebral aneurysms using flow-diverter devices: a systematic review. Neuroradiol J. 2015; 28:365–75.
Article3. Arrese I, Sarabia R, Pintado R, Delgado-Rodriguez M. Flow-diverter devices for intracranial aneurysms: systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurgery. 2013; 73:193–9. discussion 199–200.4. Kallmes DF, Ding YH, Dai D, Kadirvel R, Lewis DA, Cloft HJ. A new endoluminal, flow-disrupting device for treatment of saccular aneurysms. Stroke. 2007; 38:2346–52.
Article5. Maimon S, Gonen L, Nossek E, Strauss I, Levite R, Ram Z. Treatment of intra-cranial aneurysms with the SILK flow diverter: 2 years’ experience with 28 patients at a single center. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2012; 154:979–87.
Article6. Berge J, Biondi A, Machi P, Brunel H, Pierot L, Gabrillargues J, et al. Flow-diverter Silk stent for the treatment of intracranial aneurysms: 1-year follow-up in a multicenter study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012; 33:1150–5.
Article7. Wagner A, Cortsen M, Hauerberg J, Romner B, Wagner MP. Treatment of intracranial aneurysms. Reconstruction of the parent artery with flow-diverting (Silk) stent. Neuroradiology. 2012; 54:709–18.
Article8. Mpotsaris A, Skalej M, Beuing O, Eckert B, Behme D, Weber W. Long-term occlusion results with SILK flow diversion in 28 aneurysms: do recanalizations occur during follow-up? Interv Neuroradiol. 2015; 21:300–10.
Article9. Shankar JJ, Tampieri D, Iancu D, Cortes M, Agid R, Krings T, et al. SILK flow diverter for complex intracranial aneurysms: a Canadian registry. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016; 8:273–8.
Article10. Brinjikji W, Murad MH, Lanzino G, Cloft HJ, Kallmes DF. Endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms with flow diverters: a meta-analysis. Stroke. 2013; 44:442–7.
Article11. Texakalidis P, Bekelis K, Atallah E, Tjoumakaris S, Rosenwasser RH, Jabbour P. Flow diversion with the pipeline embolization device for patients with intracranial aneurysms and antiplatelet therapy: a systematic literature review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2017; 161:78–87.
Article12. Becske T, Kallmes DF, Saatci I, McDougall CG, Szikora I, Lanzino G, et al. Pipeline for uncoilable or failed aneurysms: results from a multicenter clinical trial. Radiology. 2013; 267:858–68.
Article13. Matsuda Y, Jang DK, Chung JH, Wainwright JM, Lopes D. Preliminary outcomes of single antiplatelet therapy for surface-modified flow diverters in an animal model: analysis of neointimal development and thrombus formation using OCT. J NeuroIntervent Surg. 2019; 11:74–9.
Article14. Marosfoi M, Clarencon F, Langan ET, King RM, Brooks OW, Tamura T, et al. Acute thrombus formation on phosphorilcholine surface modified flow diverters. J Neurointerv Surg. 2018; 10:406–11.
Article15. Hagen MW, Girdhar G, Wainwright J, Hinds MT. Thrombogenicity of flow diverters in an exvivo shunt model: effect of phosphorylcholine surface modification. J Neurointerv Surg. 2017; 9:1006–11.16. Tonetti DA, Jankowitz BT, Gross BA. Antiplatelet therapy in flow diversion. Neurosurgery. 2020; 86:S47–52.
Article17. Matsuda Y, Chung J, Lopes DK. Analysis of neointima development in flow diverters using optical coherence tomography imaging. J Neurointerv Surg. 2018; 10:162–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Kinking of Flow Diverter in a Giant Wide-Necked Supraclinoid Internal Carotid Artery Aneurysm
- Clipping of a persistent middle cerebral artery aneurysm after previous flow diverter placement: An illustrative case and review of the literature
- Treatment of Intracranial Aneurysms with Flow Re-direction Endoluminal Device - A Single Centre Experience with Short-term Follow-up Results
- Delayed Proximal Flow Diverting Stent Migration in a Ruptured Intracranial Aneurysm: A Case Report
- Symptomatic Post Endarterectomy Common Carotid Artery Pseudoaneurysm Treated with Combination of Flow Diverter Implantation and Carotid Stenting