Neurointervention.
2017 Mar;12(1):11-19. 10.5469/neuroint.2017.12.1.11.
Treatment of Intracranial Aneurysms with Flow Re-direction Endoluminal Device - A Single Centre Experience with Short-term Follow-up Results
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Tuen Mun Hospital, Hong Kong.
- 2Department of Radiology, Princess Margaret Hospital, Hong Kong. neeraj.mahboobani@gmail.com
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Tuen Mun Hospital, Hong Kong.
- KMID: 2371754
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5469/neuroint.2017.12.1.11
Abstract
- PURPOSE
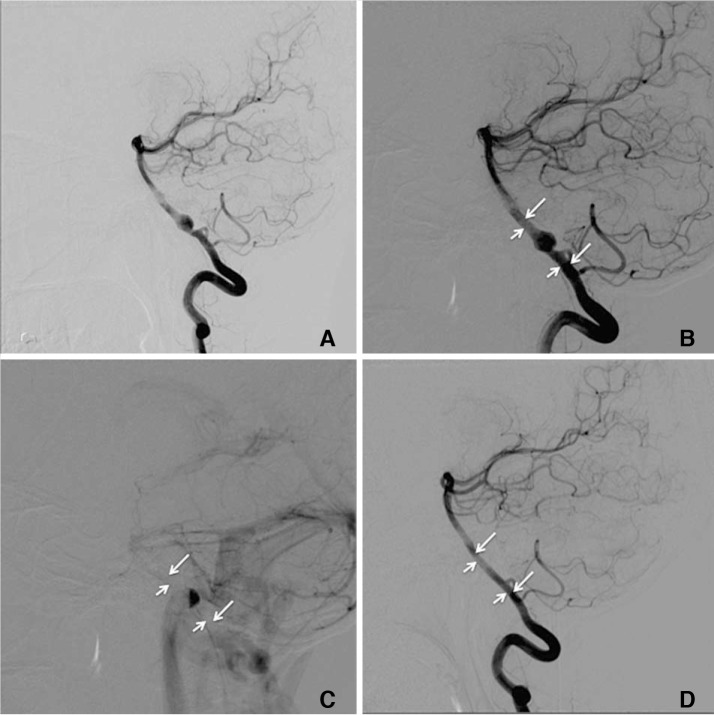
A flow diverter (FD) is an effective treatment option for intracranial aneurysms. The Flow Re-direction Endoluminal Device (FRED) is a relatively new flow diverter with a unique dual-layer design. We report our experience and short-term results with the FRED.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We did a retrospective review of all consecutive cases in which the FRED was used to treat intracranial aneurysms at a single institution from March 2014 till December 2015. Clinical parameters, aneurysm characteristics, technical results and short-term outcomes were reviewed.
RESULTS
Eleven intracranial aneurysms were treated with the FRED in 11 patients. The technical device deployment success rate was 100%. Immediate reduction in intra-aneurysmal flow after deployment was noted in 10 cases. The aneurysm occlusion rate at 6 months was 75%. There was 1 complication of in-stent thrombosis immediately after deployment. There was no side branch occlusion, delayed aneurysm rupture, stroke, or intraparenchymal haemorrhage. There was no neurological deficit, morbidity, or mortality.
CONCLUSION
The FRED is a new FD. It has shown to be safe and effective in our series. The unique dual-layer design of the device renders it to have technical advantages over other FDs. The 6-month aneurysm occlusion rate and complication profile of FRED are similar to other FDs.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Evolution of Flow-Diverting Stents for Cerebral Aneurysms; Historical Review, Modern Application, Complications, and Future Direction
Dong-Seong Shin, Christopher P. Carroll, Mohammed Elghareeb, Brian L. Hoh, Bum-Tae Kim
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2020;63(2):137-152. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2020.0034.
Reference
-
1. Brinjikji W, Murad MH, Lanzino G, Cloft HJ, Kallmes DF. Endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms with flow diverters: a meta-analysis. Stroke. 2013; 44:442–447. PMID: 23321438.
Article2. Alderazi YJ, Shastri D, Kass-Hout T, Prestigiacomo CJ, Gandhi CD. Flow diverters for intracranial aneurysms. Stroke Res Treat. 2014; 2014:415653. PMID: 24967131.
Article3. Zanaty M, Chalouhi N, Tjoumakaris SI, Rosenwasser RH, Gonzalez LF, Jabbour P. Flow-diversion panacea or poison? Front Neurol. 2014; 5:21. PMID: 24592254.
Article4. Diaz O, Gist TL, Manjarez G, Orozco F, Almeida R. Treatment of 14 intracranial aneurysms with the FRED system. J Neurointerv Surg. 2014; 6:614–617. PMID: 24062251.
Article5. Möhlenbruch MA, Herweh C, Jestaedt L, Stampfl S, Schonenberger S, Ringleb PA, et al. The FRED flow-diverter stent for intracranial aneurysms: clinical study to assess safety and efficacy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015; 36:1155–1161. PMID: 25721079.
Article6. Kocer N, Islak C, Kizilkilic O, Kocak B, Saglam M, Tureci E. Flow Re-direction Endoluminal Device in treatment of cerebral aneurysms: initial experience with short-term follow-up results. J Neurosurg. 2014; 120:1158–1171. PMID: 24628615.
Article7. Poncyljusz W, Sagan L, Safranow K, Rac M. Initial experience with implantation of novel dual layer flow-diverter device FRED. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2013; 8:258–264. PMID: 24130644.
Article8. O'Kelly CJ, Krings T, Fiorella D, Marotta TR. A novel grading scale for the angiographic assessment of intracranial aneurysms treated using flow diverting stents. Interv Neuroradiol. 2010; 16:133–137. PMID: 20642887.9. Joshi MD, O'Kelly CJ, Krings T, Fiorella D, Marotta TR. Observer variability of an angiographic grading scale used for the assessment of intracranial aneurysms treated with flow-diverting stents. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013; 34:1589–1592. PMID: 23449648.
Article10. Delgado Almandoz JE, Crandall BM, Scholz JM, Fease JL, Anderson RE, Kadkhodayan Y, et al. Pre-procedure P2Y12 reaction units value predicts perioperative thromboembolic and hemorrhagic complications in patients with cerebral aneurysms treated with the Pipeline Embolization Device. J Neurointerv Surg. 2013; 5:iii3–iii10. PMID: 23314576.
Article11. Tan LA, Keigher KM, Munich SA, Moftakhar R, Lopes DK. Thromboembolic complications with Pipeline Embolization Device placement: impact of procedure time, number of stents and pre-procedure P2Y12 reaction unit (PRU) value. J Neurointerv Surg. 2015; 7:217–221. PMID: 24553344.
Article12. Heller RS, Dandamudi V, Lanfranchi M, Malek AM. Effect of antiplatelet therapy on thromboembolism after flow diversion with the pipeline embolization device. J Neurosurg. 2013; 119:1603–1610. PMID: 23971953.
Article13. Szikora I, Berentei Z, Kulcsar Z, Marosfoi M, Vajda ZS, Lee W, et al. Treatment of intracranial aneurysms by functional reconstruction of the parent artery: the budapest experience with the pipeline embolization device. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010; 31:1139–1147. PMID: 20150304.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Flow Diverter Device for Treatment of Cerebral Aneurysm with Short-Term Follow Up: Two Case Reports
- A Single Flow Re-direction Endoluminal Device for the Treatment of Large and Giant Anterior Circulation Intracranial Aneurysms
- Flow Diverter Treatment Using a Flow Re-Direction Endoluminal Device for Unruptured Intracranial Vertebral Artery Dissecting Aneurysm: Single-Center Case Series and Technical Considerations
- A Case of Migration of Pipeline Embolization Device Causing Rupture during Treatment of an Unruptured Vertebral Artery Dissecting Aneurysm
- Internal Carotid Artery Reconstruction with a “Mega Flow Diverterâ€: First Experience with the 6×50 mm DERIVO Embolization Device