Infect Chemother.
2019 Jun;51(2):107-118. 10.3947/ic.2019.51.2.107.
Dissemination of Carbapenem-Resistance among Multidrug Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa carrying Metallo-Beta-Lactamase Genes, including the Novel bla(IMP-65) Gene in Thailand
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand. piyatip.khn@mahidol.edu
- 2Chulabhorn Graduate Institute, Chulabhorn Royal Academy, Bangkok, Thailand.
- KMID: 2450867
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2019.51.2.107
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is considered as one of the most emerging threats in this century. Serious infections caused by this pathogen are often treated by carbapenems which are the last resource of antibiotics. Metallo-beta-lactamases (MBLs) production is one of the most important carbepenem resistance mechanisms and is usually related with nosocomial infections caused by P. aeruginosa. This study was aimed to determine the prevalence of MBL genes and distribution pattern of MBLs producing P. aeruginosa strains in Thailand.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Specific primers were designed to detect MBL genes including IMP-, VIM-, and NDM-type MBL genes. Multilocus sequence typing method was used to determine the dissemination pattern of carbapenem-resistance among multidrug-resistant (CR-MDR) P. aeruginosa.
RESULTS
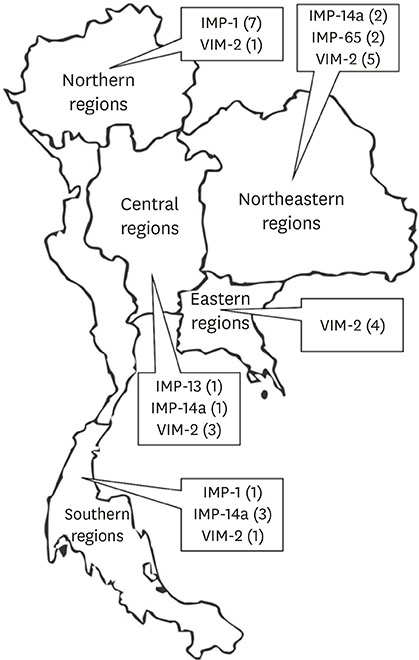
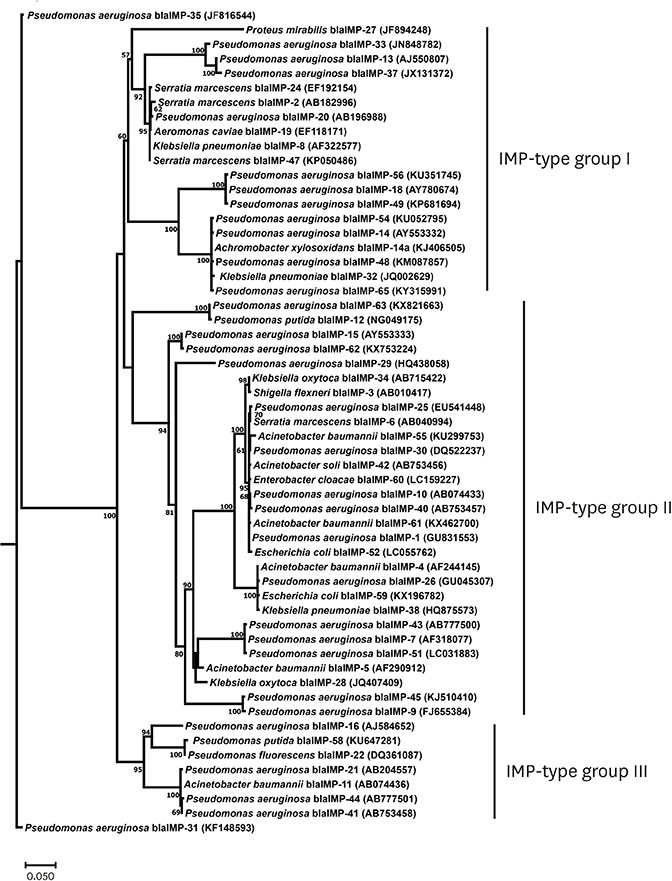
A total of 153 P. aeruginosa clinical isolates were characterized as CR-MDR. Among those, 31 P. aeruginosa clinical isolates (20.3%) presented metallo-beta-lactamase genes which could be divided into VIM-type (14 strains) and IMP-type (17 strains). bla IMP - 1, bla IMP - 13, bla IMP - 14a, and bla VIM - 2 genes were detected. Moreover, a novel IMP-type MBL, bla IMP - 65 was discovered and it was demonstrated to be the unique group of MBLs in Thailand. It was of interest that ST235 was the major ST type in Thailand followed by ST964 and ST111 and ST235 was detected in both MBL harboring and non-MBL harboring strains.
CONCLUSION
This study reported the dissemination of MBL gene including novel MBL, bla IMP-65. This study was also demonstrated major ST of P. aeruginosa which was ST235, followed by ST964 and ST111. Moreover, it is also the first report on many P. aeruginosa STs in Thailand: ST273, ST292, ST621, ST1584, and ST1816 which emphasized the dissemination trait difference of MBLs harboring P. aeruginosa in Thailand.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Boucher HW, Talbot GH, Bradley JS, Edwards JE, Gilbert D, Rice LB, Scheld M, Spellberg B, Bartlett J. Bad bugs, no drugs: no ESKAPE! An update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2009; 48:1–12.
Article2. World Health Organization (WHO). WHO publishes list of bacteria for which new antibiotics are urgently needed. Accessed 24 October 2017. Available at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2017/bacteria-antibiotics-needed/en/.3. Santajit S, Indrawattana N. Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in ESKAPE pathogens. Biomed Res Int. 2016; 2016:2475067.
Article4. Pérez-Losada M, Cabezas P, Castro-Nallar E, Crandall KA. Pathogen typing in the genomics era: MLST and the future of molecular epidemiology. Infect Genet Evol. 2013; 16:38–53.
Article5. Curran B, Jonas D, Grundmann H, Pitt T, Dowson CG. Development of a multilocus sequence typing scheme for the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa . J Clin Microbiol. 2004; 42:5644–5649.
Article6. Oliver A, Mulet X, López-Causapé C, Juan C. The increasing threat of Pseudomonas aeruginosa high-risk clones. Drug Resist Updat. 2015; 21-22:41–59.7. Ji J, Wang J, Zhou Z, Wang H, Jiang Y, Yu Y. Multilocus sequence typing reveals genetic diversity of carbapenem- or ceftazidime-nonsusceptible Pseudomonas aeruginosa in China. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013; 57:5697–5700.
Article8. Feng W, Sun F, Wang Q, Xiong W, Qiu X, Dai X, Xia P. Epidemiology and resistance characteristics of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from the respiratory department of a hospital in China. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2017; 8:142–147.
Article9. Chen Y, Sun M, Wang M, Lu Y, Yan Z. Dissemination of IMP-6-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa ST244 in multiple cities in China. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014; 33:1181–1187.
Article10. Kouda S, Ohara M, Onodera M, Fujiue Y, Sasaki M, Kohara T, Kashiyama S, Hayashida S, Harino T, Tsuji T, Itaha H, Gotoh N, Matsubara A, Usui T, Sugai M. Increased prevalence and clonal dissemination of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa with the blaIMP-1 gene cassette in Hiroshima. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009; 64:46–51.
Article11. Cho HH, Kwon KC, Sung JY, Koo SH. Prevalence and genetic analysis of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa ST235 isolated from a hospital in Korea, 2008-2012. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2013; 43:414–419.12. Kim MJ, Bae IK, Jeong SH, Kim SH, Song JH, Choi JY, Yoon SS, Thamlikitkul V, Hsueh PR, Yasin RM, Lalitha MK, Lee K. Dissemination of metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa of sequence type 235 in Asian countries. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013; 68:2820–2824.
Article13. Falagas ME, Koletsi PK, Bliziotis IA. The diversity of definitions of multidrug-resistant (MDR) and pandrug-resistant (PDR) Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Med Microbiol. 2006; 55:1619–1629.
Article14. Khuntayaporn P, Montakantikul P, Mootsikapun P, Thamlikitkul V, Chomnawang MT. Prevalence and genotypic relatedness of carbapenem resistance among multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa in tertiary hospitals across Thailand. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2012; 11:25.15. Picão RC, Andrade SS, Nicoletti AG, Campana EH, Moraes GC, Mendes RE, Gales AC. Metallo-beta-lactamase detection: comparative evaluation of double-disk synergy versus combined disk tests for IMP-, GIM-, SIM-, SPM-, or VIM-producing isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 2008; 46:2028–2037.
Article16. Cornaglia G, Giamarellou H, Rossolini GM. Metallo-beta-lactamases: a last frontier for beta-lactams? Lancet Infect Dis. 2011; 11:381–393.17. Shibata N, Doi Y, Yamane K, Yagi T, Kurokawa H, Shibayama K, Kato H, Kai K, Arakawa Y. PCR typing of genetic determinants for metallo-beta-lactamases and integrases carried by gram-negative bacteria isolated in Japan, with focus on the class 3 integron. J Clin Microbiol. 2003; 41:5407–5413.
Article18. Edgar RC. MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004; 32:1792–1797.
Article19. Stamatakis A. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics. 2014; 30:1312–1313.
Article20. Bush K, Jacoby GA. Updated functional classification of beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010; 54:969–976.21. Kazmierczak KM, Rabine S, Hackel M, McLaughlin RE, Biedenbach DJ, Bouchillon SK, Sahm DF, Bradford PA. Multiyear, Multinational survey of the incidence and global distribution of metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015; 60:1067–1078.
Article22. Boonkerd N, Pibalpakdi P, Tiloklurs M, Niumsup PR. Class 1 integron containing metallo beta-lactamase gene blaIMP-1 in carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Thailand. J Infect Chemother. 2009; 15:257–261.
Article23. Piyakul C, Tiyawisutsri R, Boonbumrung K. Emergence of metallo-beta-lactamase IMP-14 and VIM-2 in Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates from a tertiary-level hospital in Thailand. Epidemiol Infect. 2012; 140:539–541.
Article24. Rimrang B, Chanawong A, Lulitanond A, Wilailuckana C, Charoensri N, Sribenjalux P, Phumsrikaew W, Wonglakorn L, Kerdsin A, Chetchotisakd P. Emergence of NDM-1- and IMP-14a-producing Enterobacteriaceae in Thailand. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012; 67:2626–2630.25. Prombhul S, Tribuddharat C, Laikijrung P, Aranya C, Bamrungsri N, Mekviwattanawong S. New variant of an imipenemase, IMP-32, in Klebsiella pneumoniae from a fatal case of a Thai patient. J Med Microbiol. 2016; 65:572–573.
Article26. Zhao WH, Hu ZQ. Acquired metallo-beta-lactamases and their genetic association with class 1 integrons and ISCR elements in Gram-negative bacteria. Future Microbiol. 2015; 10:873–887.
Article27. Zhao WH, Hu ZQ. IMP-type metallo-beta-lactamases in Gram-negative bacilli: distribution, phylogeny, and association with integrons. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2011; 37:214–226.
Article28. Mano Y, Saga T, Ishii Y, Yoshizumi A, Bonomo RA, Yamaguchi K, Tateda K. Molecular analysis of the integrons of metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates collected by nationwide surveillance programs across Japan. BMC Microbiol. 2015; 15:41.29. Samuelsen O, Toleman MA, Sundsfjord A, Rydberg J, Leegaard TM, Walder M, Lia A, Ranheim TE, Rajendra Y, Hermansen NO, Walsh TR, Giske CG. Molecular epidemiology of metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from Norway and Sweden shows import of international clones and local clonal expansion. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010; 54:346–352.
Article30. Koh TH, Khoo CT, Tan TT, Arshad MA, Ang LP, Lau LJ, Hsu LY, Ooi EE. Multilocus sequence types of carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Singapore carrying metallo-beta-lactamase genes, including the novel blaIMP-26 gene. J Clin Microbiol. 2010; 48:2563–2564.
Article31. Wright LL, Turton JF, Hopkins KL, Livermore DM, Woodford N. Genetic environment of metallo-beta-lactamase genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from the UK. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2015; 70:3250–3258.32. Fan X, Wu Y, Xiao M, Xu ZP, Kudinha T, Bazaj A, Kong F, Xu YC. Diverse genetic background of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa from Mainland China, and emergence of an extensively drug-resistant ST292 clone in kunming. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:26522.
Article33. Lee JY, Song JH, Ko KS. Identification of nonclonal Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates with reduced colistin susceptibility in Korea. Microb Drug Resist. 2011; 17:299–304.
Article34. Santella G, Pollini S, Docquier JD, Mereuta AI, Gutkind G, Rossolini GM, Radice M. Intercontinental dissemination of IMP-13-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa belonging in sequence type 621. J Clin Microbiol. 2010; 48:4342–4343.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Epidemiology and Characteristics of Metallo-beta-Lactamase-Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Detection of NDM-1 Metallo-β-Lactamase Genes in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa from Clinical Surveillance Sample: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Clonal Distribution and Its Association With the Carbapenem Resistance Mechanisms of Carbapenem-Non-Susceptible Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates From Korean Hospitals
- Characterization of Class 1 Integrons in Metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Emergence of Acinetobacter pittii Harboring New Delhi Metallo-beta-Lactamase Genes in Daejeon, Korea