J Rhinol.
2019 May;26(1):26-31. 10.18787/jr.2019.26.1.26.
Clinical Usefulness of Trasseptal Transsphenoidal Approach for Pituitary Tumors with Septal Cartilage Removal and Replacement via Modified Killian Incision: Review of 42 Cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. fess0101@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2449025
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2019.26.1.26
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
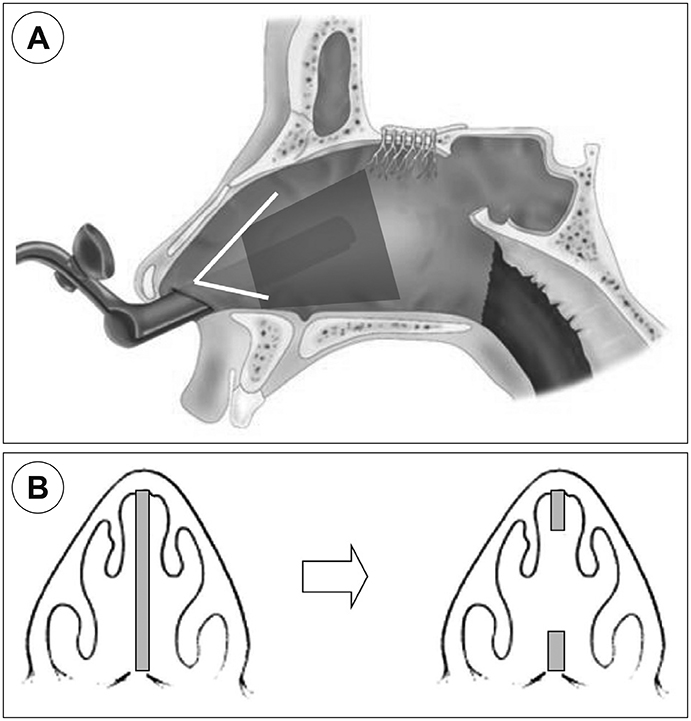
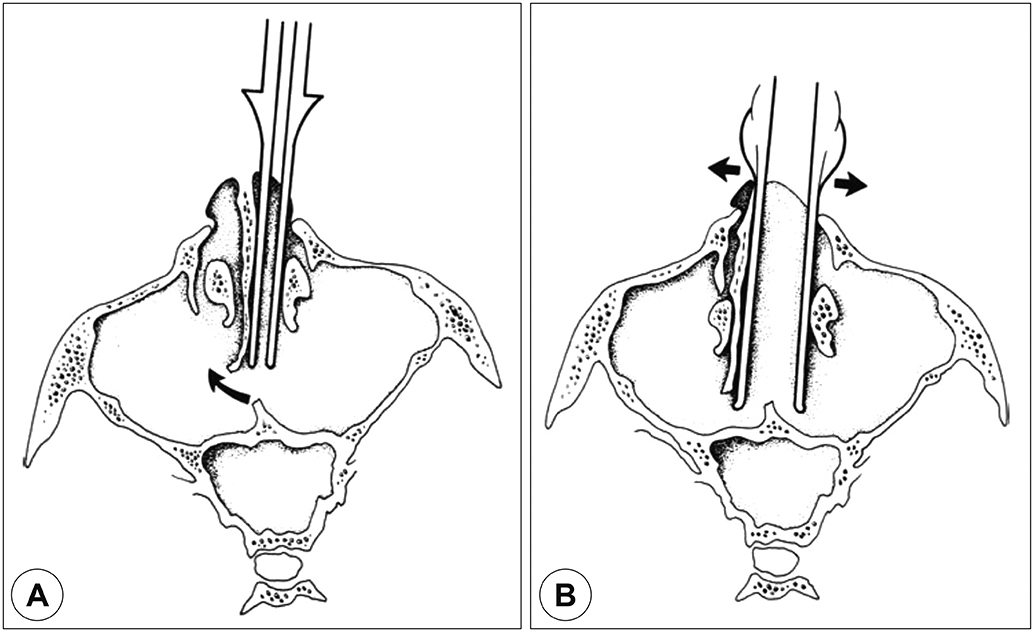
The conventional transseptal transsphenoidal approach can inhibit visualization of the surgical field and may change the shape of external nose. We used the transseptal transsphenoidal technique to remove septal cartilage except the L strut via a modified Killian's incision and preserved the "˜key-stone area.' The aim of this study was to verify the usefulness of this technique.
SUBJECTS AND METHOD
Retrospective analysis was carried out on 42 pituitary tumor patients who received this technique by a single otolaryngologist from March 2005 to March 2012 at Kangbuk Samsung Hospital.
RESULTS
The mean patient age at time of surgery was 52 years, and 41 cases were pituitary adenoma and 1 was Rathke's cleft cyst. Three patients had undergone prior surgery; of which 2 used a pterional approach and 1 a transsphenoidal approach. With regard to complication, there were 2 cases of CSF leakage and 5 cases of septal laceration. There were no cases of meningitis, deformity of external nose, septal perforation, anosmia, or sinusitis. In post operation follow up, 25 cases (59.5%) had no residual tumor, while 17 cases (40.5%) had residual tumor.
CONCLUSION
This study reveals that transseptal transsphenoidal surgery with septal cartilage removal and a replacement technique for a pituitary tumor are effective, allow easy exposure, and result in a low complication rate.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Black PM, Zervas NT, Candia GL. Incidence and management of complications of transsphenoidal operation for pituitary adenomas. Neurosurgery. 1987; 20:920–924.
Article2. Armengot M, Gallego JM, Gomez MJ, Barcia JA, Basterra J, Barcia C. [Transphenoidal endoscopic approaches for pituitary adenomas: a critical review of our experience]. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp. 2011; 62:25–30.
Article3. Wilson CB. Endocrine-inactive pituitary adenomas. Clin Neurosurg. 1992; 38:10–31.4. Wilson CB. Surgical management of pituitary tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997; 82:2381–2385.
Article5. Youssef AS, Agazzi S, van Loveren HR. Transcranial surgery for pituitary adenomas. Neurosurgery. 2005; 57:168–175. discussion 168-75.
Article6. Cho JH. Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal skull base surgery. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2010; 53:135–142.
Article7. Jho HD, Carrau RL, Ko Y, Daly MA. Endoscopic pituitary surgery: an early experience. Surg Neurol. 1997; 47:213–222. discussion 222-213.
Article8. Nasseri SS, Kasperbauer JL, Strome SE, McCaffrey TV, Atkinson JL, Meyer FB. Endoscopic transnasal pituitary surgery: report on 180 cases. Am J Rhinol. 2001; 15:281–287.
Article9. Kabil M, Eby J, Shahinian H. Fully endoscopic endonasal vs transseptal transsphenoidal pituitary surgery. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2005; 48:348–354.
Article10. Goudakos JK, Markou KD, Georgalas C. Endoscopic versus microscopic trans-sphenoidal pituitary surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Otolaryngol. 2011; 36:212–220.
Article11. Rotenberg B, Tam S, Ryu WHA, Duggal N. Microscopic versus endoscopic pituitary surgery: a systematic review. Laryngoscope. 2010; 120:1292–1297.
Article12. Ammirati M, Wei L, Ciric I. Short-term outcome of endoscopic versus microscopic pituitary adenoma surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2013; 84:843–849.
Article13. Dhong HJ, Park JH, Kim JH. Endoscopic transnasal transsphenoidal pituitary surgery. Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 1999; 42:734–737.14. Pereira EA, Plaha P, Chari A, Paranathala M, Haslam N, Rogers A, et al. Transsphenoidal pituitary surgery in the elderly is safe and effective. Br J Neurosurg. 2013.
Article15. Tao YX, Qu QY, Wang ZL, Zhang QH. Endoscopic transsphenoidal approach to pituitary adenomas invading the cavernous sinus. Chin Med J (Engl). 2010; 123:3519–3523.16. Rotenberg B, Tam S, Ryu WH, Duggal N. Microscopic versus endoscopic pituitary surgery: a systematic review. Laryngoscope. 2010; 120:1292–1297.
Article17. Kahilogullari G, Beton S, Al-Beyati ES, Kantarcioglu O, Bozkurt M, Kantarcioglu E, et al. Olfactory functions after transsphenoidal pituitary surgery: endoscopic versus microscopic approach. Laryngoscope. 2013; 123:2112–2119.
Article18. Griffith HB, Veerapen R. A direct transnasal approach to the sphenoid sinus. J Neurosurg. 1987; 66:140–142.
Article19. Ciric I, Ragin A, Baumgartner C, Pierce D. Complications of transsphenoidal surgery: results of a national survey, review of the literature, and personal experience. Neurosurgery. 1997; 40:225–236. discussion 236-227.
Article20. Kahilogullari G, Beton S, Al-Beyati ES, Kantarcioglu O, Bozkurt M, Kantarcioglu E, et al. Olfactory functions after transsphenoidal pituitary surgery: endoscopic versus microscopic approach. Laryngoscope. 2013; 123:2112–2119.
Article21. Koutourousiou M, Gardner PA, Tormenti MJ, Henry SL, Stefko ST, Kassam AB, et al. Endoscopic endonasal approach for resection of cranial base chordomas: outcomes and learning curve. Neurosurgery. 2012; 71:614–624. discussion 624-615.22. Zhang Y, Wang Z, Liu Y, Zong X, Song M, Pei A, et al. Endoscopic transsphenoidal treatment of pituitary adenomas. Neurol Res. 2008; 30:581–586.
Article23. Hong SD, Nam DH, Seol HJ, Choi NY, Kim HY, Chung SK, et al. Endoscopic binostril versus transnasal transseptal microscopic pituitary surgery: Sinonasal quality of life and olfactory function. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2015; 29:221–225.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Analysis of Pituitary Tumors Treated with Transsphenoidal Approach
- Surgical Experiences of Three Cases of Giant Pituitary Adenoma
- External Rhinoplasty Approach for Transsphenoidal Surgery of Pituitary Tumor
- A Case of Blindness after Transsphenoid Approach for Pituitary Adenoma Removal: Revision Treatment Experience under Local Anesthesia
- Columellar Flap for Transsphenoidal Approach