Anesth Pain Med.
2019 Apr;14(2):172-179. 10.17085/apm.2019.14.2.172.
A comparison of clinical performance between i-gel and endotracheal tube in pediatric laparoscopic surgeries
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Dong-A University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. surfy07@gmail.com
- KMID: 2447965
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2019.14.2.172
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The current evidence on the safe use of supraglottic airway for pediatric laparoscopic surgeries is limited. Although i-gel has been successfully used in adult laparoscopic surgeries, to our knowledge, no studies have compared it to the endotracheal tube (ETT) in pediatric laparoscopic surgeries. This study evaluated the effectiveness of i-gel over ETT with regards to the respiratory and hemodynamic parameters during pediatric laparoscopic surgeries.
METHODS
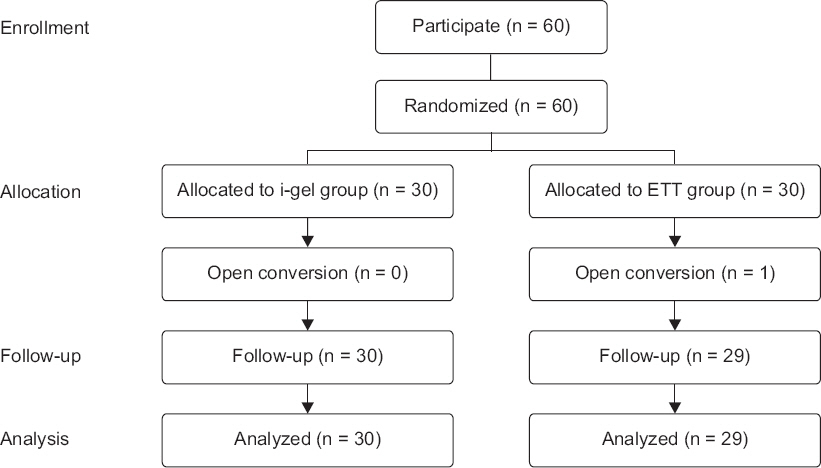
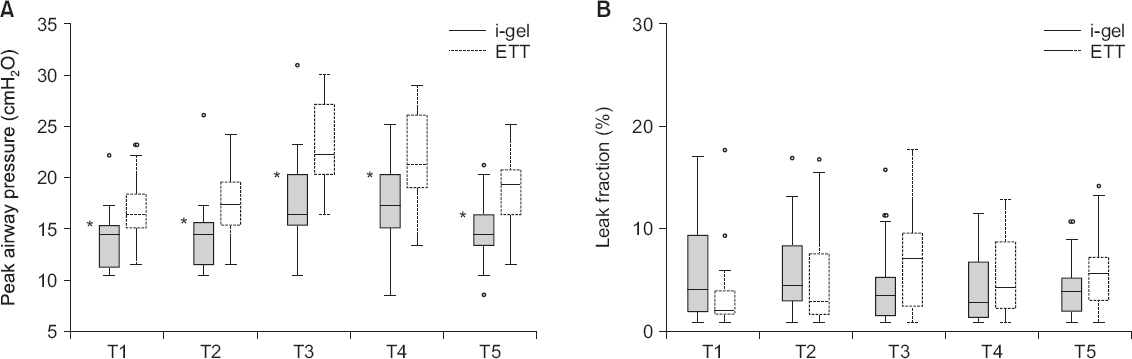
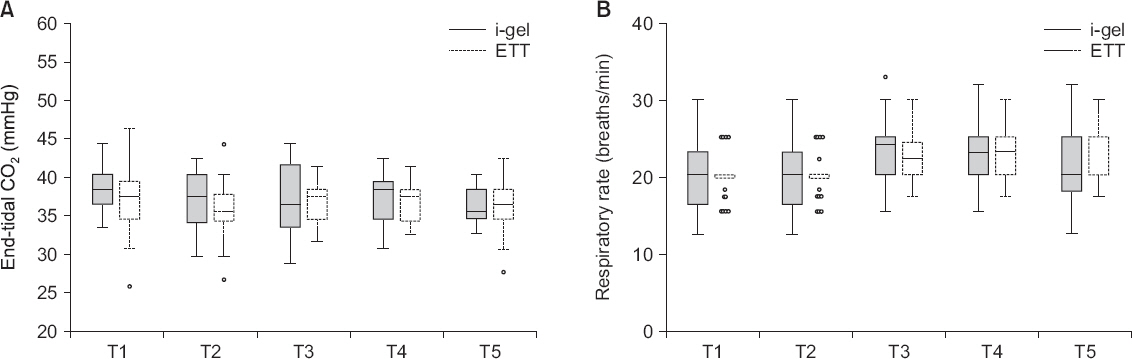
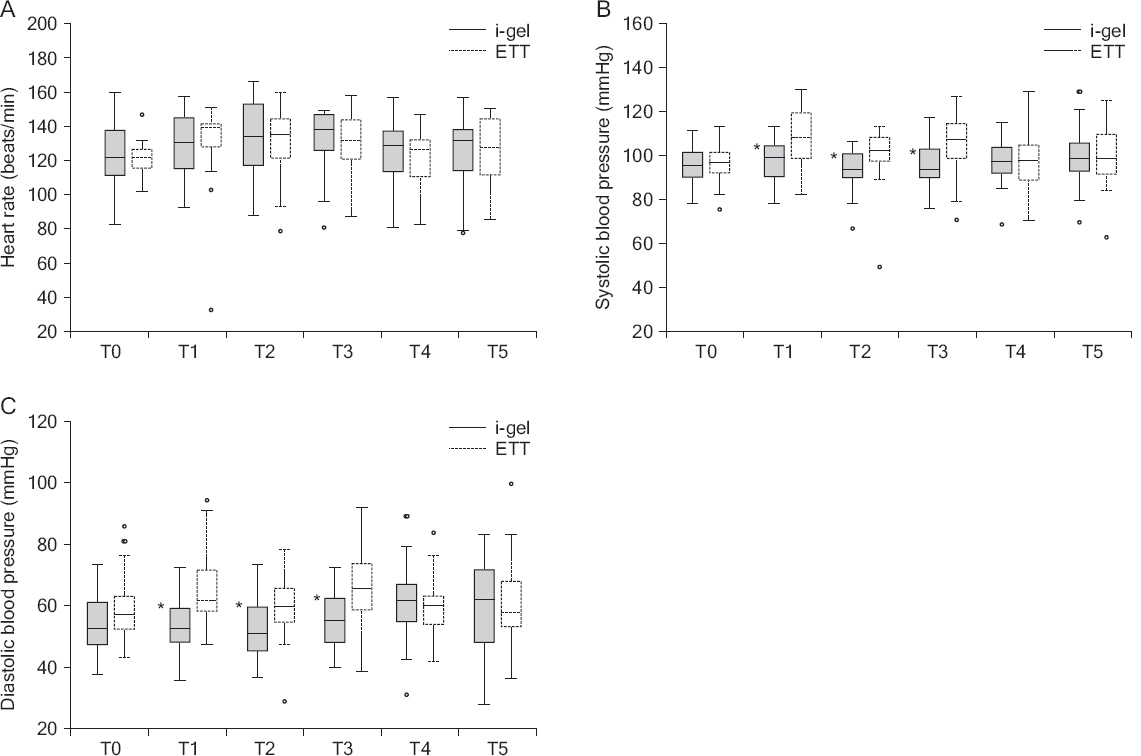
A total of 60 pediatric patients undergoing elective laparoscopic surgeries were randomly allocated to either the i-gel or ETT groups. Anesthetics used included ketamine, sevoflurane, and rocuronium. The primary outcome measured was the peak airway pressure (PAP) and the secondary outcomes measured were leak fraction, end-tidal COâ‚‚, respiratory rate, insertion time, heart rate, blood pressure and perioperative complications.
RESULTS
The PAP during surgeries was higher in the ETT group than in the i-gel group. There were no statistically significant differences in the leak fraction, end-tidal COâ‚‚, and respiratory rate. The i-gel group had a shorter insertion time compared with the ETT group. The changes in heart rate were comparable in both groups. However, systolic and diastolic pressures were higher in the ETT group following intubation, before and after the creation of pneumoperitoneum. The incidence of perioperative complications was similar in both groups.
CONCLUSIONS
The i-gel provided adequate ventilation with lower PAP compared with ETT. In addition, it provided minimal hemodynamic changes compared with ETT. Therefore, the i-gel may provide a suitable alternative to ETT in pediatric laparoscopic surgeries.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Valenza F, Chevallard G, Fossali T, Salice V, Pizzocri M, Gattinoni L. Management of mechanical ventilation during laparoscopic surgery. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2010; 24:227–41. DOI: 10.1016/j.bpa.2010.02.002. PMID: 20608559.2. Manner T, Aantaa R, Alanen M. Lung compliance during laparoscopic surgery in paediatric patients. Paediatr Anaesth. 1998; 8:25–9. DOI: 10.1046/j.1460-9592.1998.00699.x. PMID: 9483594.3. Bannister CF, Brosius KK, Wulkan M. The effect of insufflation pressure on pulmonary mechanics in infants during laparoscopic surgical procedures. Paediatr Anaesth. 2003; 13:785–9. DOI: 10.1046/j.1460-9592.2003.01149.x. PMID: 14617119.4. Ozdamar D, Güvenç BH, Toker K, Solak M, Ekingen G. Comparison of the effect of LMA and ETT on ventilation and intragastric pressure in pediatric laparoscopic procedures. Minerva Anestesiol. 2010; 76:592–9. PMID: 20661199.5. Sinha A, Sharma B, Sood J. ProSeal as an alternative to endotracheal intubation in pediatric laparoscopy. Paediatr Anaesth. 2007; 17:327–32. DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-9592.2006.02127.x. PMID: 17359400.6. Intersurgical, i-gel user guide [Internet]. Wokingham: Intersurgical Ltd;2017. [cited 2016 Dec 3]. Available from http://www.i-gel.com .7. Levitan RM, Kinkle WC. Initial anatomic investigations of the igel airway: a novel supraglottic airway without inflatable cuff. Anaesthesia. 2005; 60:1022–6. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.2005.04258.x. PMID: 16179048.8. Wharton NM, Gibbison B, Gabbott DA, Haslam GM, Muchatuta N, Cook TM. I-gel insertion by novices in manikins and patients. Anaesthesia. 2008; 63:991–5. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.2008.05542.x. PMID: 18557971.9. Theiler LG, Kleine-Brueggeney M, Luepold B, Stucki F, Seiler S, Urwyler N, et al. Performance of the pediatric-sized i-gel compared with the Ambu AuraOnce laryngeal mask in anesthetized and ventilated children. Anesthesiology. 2011; 115:102–10. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e318219d619. PMID: 21572318.10. Badheka JP, Jadliwala RM, Chhaya VA, Parmar VS, Vasani A, Rajyaguru AM. I-gel as an alternative to endotracheal tube in adult laparoscopic surgeries: a comparative study. J Minim Access Surg. 2015; 11:251–6. DOI: 10.4103/0972-9941.140210. PMID: 26622115. PMCID: PMC4640024.11. Park SY, Rim JC, Kim H, Lee JH, Chung CJ. Comparison of i-gel®and LMA Supreme®during laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2015; 68:455–61. DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2015.68.5.455. PMID: 26495055. PMCID: PMC4610924.12. Lai CJ, Liu CM, Wu CY, Tsai FF, Tseng PH, Fan SZ. I-Gel is a suitable alternative to endotracheal tubes in the laparoscopic pneumoperitoneum and trendelenburg position. BMC Anesthesiol. 2017; 17:3. DOI: 10.1186/s12871-016-0291-1. PMID: 28125979. PMCID: PMC5267400.13. Cole F. Pediatric formulas for the anesthesiologist. AMA J Dis Child. 1957; 94:672–3. DOI: 10.1001/archpedi.1957.04030070084009. PMID: 13478300.14. Lopez-Gil M, Brimacombe J, Keller C. A comparison of four methods for assessing oropharyngeal leak pressure with the laryngeal mask airway (LMA) in paediatric patients. Paediatr Anaesth. 2001; 11:319–21. DOI: 10.1046/j.1460-9592.2001.00649.x. PMID: 11359590.15. Cook TM, Gatward JJ, Handel J, Hardy R, Thompson C, Srivastava R, et al. Evaluation of the LMA Supreme in 100 non-paralysed patients. Anaesthesia. 2009; 64:555–62. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.2008.05824.x. PMID: 19413827.16. Berry A, Brimacombe J, Keller C, Verghese C. Pulmonary airway resistance with the endotracheal tube versus laryngeal mask airway in paralyzed anesthetized adult patients. Anesthesiology. 1999; 90:395–7. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-199902000-00011. PMID: 9952143.17. Jagannathan N, Sommers K, Sohn LE, Sawardekar A, Shah RD, Mukherji II, et al. A randomized equivalence trial comparing the i-gel and laryngeal mask airway Supreme in children. Paediatr Anaesth. 2013; 23:127–33. DOI: 10.1111/pan.12078. PMID: 23189931.18. Beringer RM, Kelly F, Cook TM, Nolan J, Hardy R, Simpson T, et al. A cohort evaluation of the paediatric i-gel(™) airway during anaesthesia in 120 children. Anaesthesia. 2011; 66:1121–6. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.2011.06884.x. PMID: 21883132.19. Richez B, Saltel L, Banchereau F, Torrielli R, Cros AM. A new single use supraglottic airway device with a noninflatable cuff and an esophageal vent: an observational study of the i-gel. Anesth Analg. 2008; 106:1137–9. DOI: 10.1213/ane.0b013e318164f062. PMID: 18349185.20. Hardman JG, Wills JS. The development of hypoxaemia during apnoea in children: a computational modelling investigation. Br J Anaesth. 2006; 97:564–70. DOI: 10.1093/bja/ael178. PMID: 16873387.21. Derbyshire DR, Chmielewski A, Fell D, Vater M, Achola K, Smith G. Plasma catecholamine responses to tracheal intubation. Br J Anaesth. 1983; 55:855–60. DOI: 10.1093/bja/55.9.855. PMID: 6615672.22. Eschertzhuber S, Brimacombe J, Kaufmann M, Keller C, Tiefenthaler W. Directly measured mucosal pressures produced by the i-gel™ and Laryngeal Mask Airway Supreme™ in paralysed anaesthetised patients. Anaesthesia. 2012; 67:407–10. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.2011.07024.x. PMID: 22324968.23. Park SK, Choi GJ, Choi YS, Ahn EJ, Kang H. Comparison of the i-gel and the laryngeal mask airway proseal during general anesthesia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0119469. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119469. PMID: 25812135. PMCID: PMC4374933.24. Beylacq L, Bordes M, Semjen F, Cros AM. The i-gel, a singleuse supraglottic airway device with a non-inflatable cuff and an esophageal vent: an observational study in children. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2009; 53:376–9. DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2008.01869.x. PMID: 19243322.25. Kim H, Lee S, Shin HJ, Lee JH, Choi SR, Chung CJ. A clinical evaluation of i-gel™ during general anesthesia in children. Anesth Pain Med. 2015; 10:46–51. DOI: 10.17085/apm.2015.10.1.46.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of differences in ventilation volume according to fixation method of I-gel during cardiopulmonary resuscitation in hospital: a study using a simulation manikin
- Evaluation of the Vacutainer Gel Plasma Tube for Common Clinical Chemistry Assays
- A Case of Endotracheal Tube Injury during Maxillofacial Surgery: Case report
- Comparison of the Diameter-Dependent Lubricant Effects on Stylet Removal from an Endotracheal Tube
- A comparison of ProSeal laryngeal mask airway, I-gel and endotracheal tube insertion by novices in a simulated difficult airway scenario