Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2019 Apr;7(2):109-112. 10.4168/aard.2019.7.2.109.
A case of rapid desensitization for rituximab-induced delayed hypersensitivity reaction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Wonkwang University College of Pharmacy, Iksan, Korea.
- 2Drug Safety Monitoring Center Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. helenmed@snu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Preventive Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Seoul National University College of Pharmacy, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2444845
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2019.7.2.109
Abstract
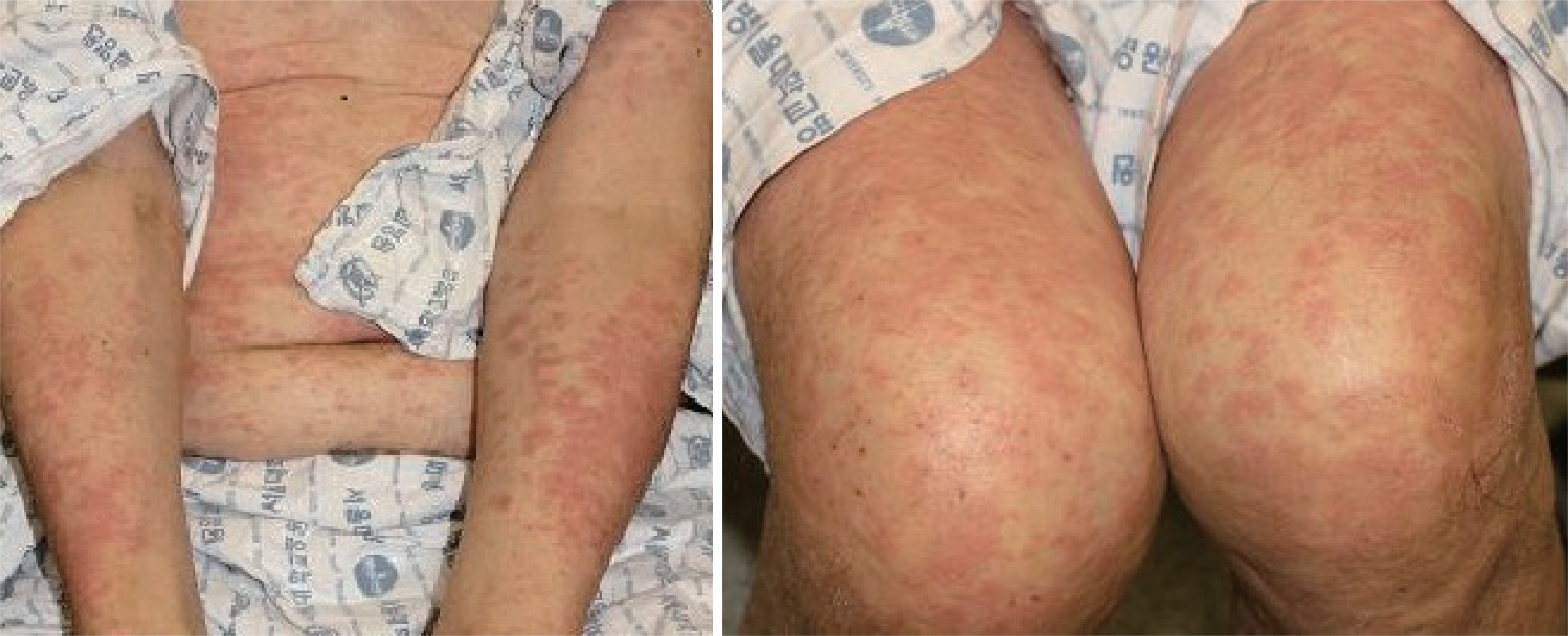
- Rituximab is a monoclonal antibody used for the treatment of B-cell malignancies, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Infusion-related hypersensitivity reactions to rituximab is well known, and delayed hypersensitivity reactions to rituximab are also reported. Desensitization is commonly used to prevent immediate hypersensitivity reactions, but recently there have been cases of successful desensitization therapy for delayed hypersensitivity reactions. A 66-year-old patient who underwent rituximab treatment for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma showed repeated rituximab-induced delayed hypersensitivity reactions with whole body rashes. Intravenous rapid desensitization was performed by using a 1-bottle, 11-step protocol for 6 cycles and thereafter hypersensitivity reaction did not recur. We herein reported a case of delayed hypersensitivity reaction caused by rituximab, which was successfully desensitized using our 11-step protocol.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Lee EJ, Kim YJ, Rhie SJ. Rituximab Infusion-related adverse events and risk factors. Korean J Clin Pharm. 2013; 23:223–31.2. Jung JW, Kang HR, Lee SH, Cho SH. The incidence and risk factors of infusion-related reactions to rituximab for treating B cell malignancies in a single tertiary hospital. Oncology. 2014; 86:127–34.
Article3. Wong JT, Long A. Rituximab hypersensitivity: evaluation, desensitization, and potential mechanisms. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2017; 5:1564–71.
Article4. Kim SN, Chae YS, Kim JG, Moon JH, Lee SJ, Kim YJ, et al. Prognostic value of the absolute lymphocyte count reduction in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Korean J Med. 2009; 76:52–9.5. Kimby E. Tolerability and safety of rituximab (MabThera). Cancer Treat Rev. 2005; 31:456–73.
Article6. Cho YJ. Update on the diagnosis of drug allergy. Korean J Med. 2009; 76:282–90.7. Roselló S, Blasco I, García Fabregat L, Cervantes A, Jordan K. ESMO Guidelines Committee. Management of infusion reactions to systemic anticancer therapy: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines. Ann Oncol. 2017; 28(suppl_4):iv100–18.
Article8. Yawalkar N. Maculopapular drug eruptions. Pichier WJ, editor. Drug hypersensitivity. Basel (Switzerland): Karger;2007. p. 242–50.
Article9. Yoon D, Ahn H, Kim SY, Hwang SJ, Park HK, Kang HR. Successful rapid desensitization to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole-induced delayed hypersensitivity. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015; 3:155–8.
Article10. Posadas SJ, Pichler WJ. Delayed drug hypersensitivity reactions – new concepts. Clin Exp Allergy. 2007; 37:989–99.
Article11. Heo YJ, Park SW, Lee KS, Kang HR, Kwon JW. Successful desensitization to fluconazole induced delayed hypersensitivity: a case report. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018; 6:68–71.
Article12. Lee AR, Kim SJ, Kim J, Park JH, Lee JK, Kim JY, et al. Successful desensitization for antitubercular drugs. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013; 1:395–9.
Article13. Teraki Y, Shiohara T. Successful desensitization to fixed drug eruption: the presence of CD25+CD4+ T cells in the epidermis of fixed drug eruption lesions may be involved in the induction of desensitization. Dermatology. 2004; 209:29–32.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Successful rapid desensitization to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole-induced delayed hypersensitivity
- Successful desensitization to fluconazole induced delayed hypersensitivity: A case report
- Effectiveness of premedication and rapid desensitization in hypersensitivity to L-asparaginase
- Delayed Allergic Reaction to Secondary Administrated Epidural Hyaluronidase
- Rapid desensitization to isoniazid and rifampin in an adolescent with active pulmonary tuberculosis