Dement Neurocogn Disord.
2015 Mar;14(1):31-38. 10.12779/dnd.2015.14.1.31.
Factors Influencing Skin Tolerability to the Rivastigmine Patch in Patients with Alzheimer's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Bobath Memorial Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, Korea University College of Medicine, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. neuroksy@snu.ac.kr
- 4Department of Neurology, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Neurology, Inha University College of Medicine, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- 6Department of Neurology, Wonkwang University College of Medicine, Wonkwang University Sanbon Medical Center, Gunpo, Korea.
- 7Department of Neurology, VHS Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Neurology, Seonam University College of Medicine, Myongji Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 9Department of Neurology, Jeju National University College of Medicine, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju, Korea.
- 10Department of Neurology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 11Department of Neurology, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Guri, Korea.
- 12Department of Neurology, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 13Department of Neurology, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Hanyang University Seoul Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 14Department of Neurology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Dong-A University Medical Center, Busan, Korea.
- 15Department of Neurology, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 16Department of Neurology, Konyang University School of Medicine, Konyang University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea.
- 17Department of Neurology, Kyung Hee University College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2443041
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12779/dnd.2015.14.1.31
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
The one-day rivastigmine patch is reportedly well tolerated and has minimal side effects. However, Asian patients show more side effects than those in Western countries. We evaluated tolerability of the rivastigmine patch in South Korean patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) and the specific factors affecting adverse events of the skin.
METHODS
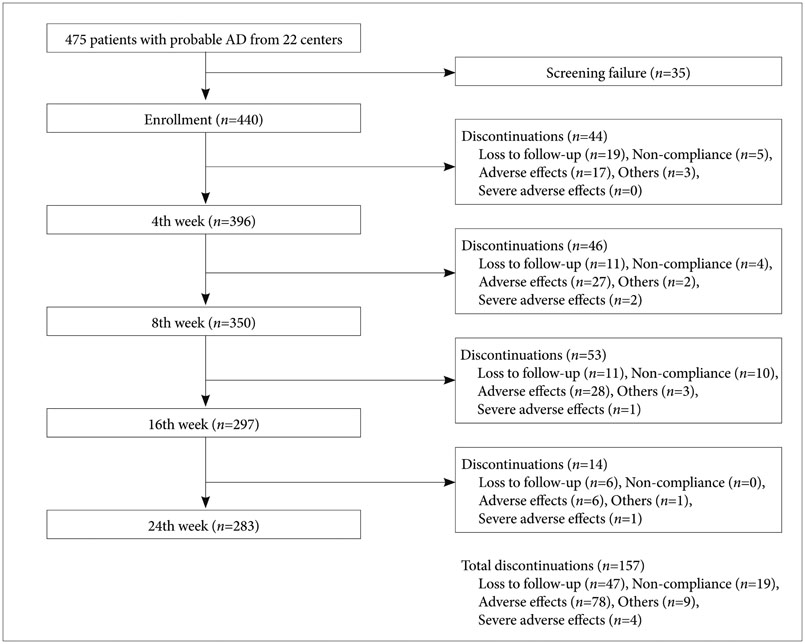
A 6-month, open labeled, multi-centered, observational study was carried out in 440 patients with probable AD from July 2009 to September 2010 (NCT01312363).
RESULTS
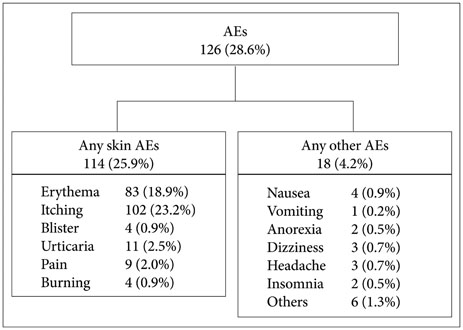
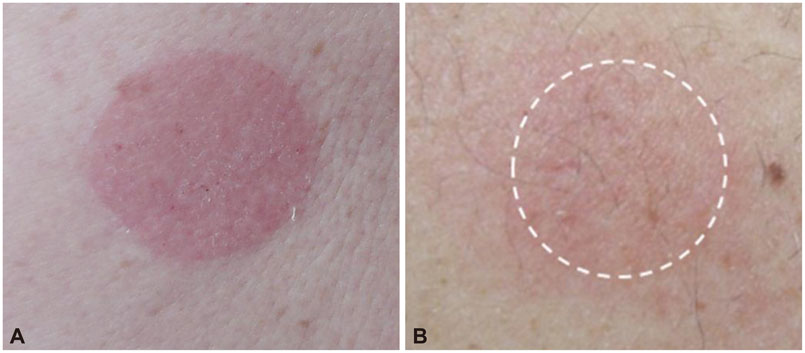
A total of 25.9% of the patients experienced adverse skin events at the rivastigmine patch application site and 17.0% discontinued treatment due to adverse events at the skin application site. The most common adverse events were itching and erythema. Patients with an allergic history and users of electric heating appliances reported skin discomfort. Older age was associated with discontinuing treatment.
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that the rivastigmine patch induced some adverse skin events and may contribute to understanding and improving skin tolerability to the rivastigmine patch.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Oertel W, Ross JS, Eggert K, Adler G. Rationale for transdermal drug administration in Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 2007; 69:4 Suppl 1. S4–S9.
Article2. Choi SH, Park KW, Na DL, Han HJ, Kim EJ, Shim YS, et al. Tolerability and efficacy of memantine add-on therapy to rivastigmine transdermal patches in mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease: a multicenter, randomized, open-label, parallel-group study. Curr Med Res Opin. 2011; 27:1375–1383.
Article3. Winblad B, Kawata AK, Beusterien KM, Thomas SK, Wimo A, Lane R, et al. Caregiver preference for rivastigmine patch relative to capsules for treatment of probable Alzheimer's disease. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2007; 22:485–491.
Article4. Lee JH, Sevigny J. Effects of body weight on tolerability of rivastigmine transdermal patch: a post-hoc analysis of a double-blind trial in patients with Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2011; 25:58–62.
Article5. Winblad B, Cummings J, Andreasen N, Grossberg G, Onofrj M, Sadowsky C, et al. A six-month double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of a transdermal patch in Alzheimer's disease--rivastigmine patch versus capsule. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2007; 22:456–467.
Article6. Cummings JL, Farlow MR, Meng X, Tekin S, Olin JT. Rivastigmine transdermal patch skin tolerability: results of a 1-year clinical trial in patients with mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease. Clin Drug Investig. 2010; 30:41–49.7. Widman TJ, Oostman H, Storrs FJ. Allergic contact dermatitis from medical adhesive bandages in patients who report having a reaction to medical bandages. Dermatitis. 2008; 19:32–37.
Article8. McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDSADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984; 34:939–944.
Article9. Kang Y, Na DL, Hahn S. A validity study on the Korean Mini-Mental State Examination (K-MMSE) in dementia patients. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1997; 15:300–308.10. Morris JC. The Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR): current version and scoring rules. Neurology. 1993; 43:2412–2414.11. Choi SH, Na DL, Lee BH, Hahm DS, Jeong JH, Yoon SJ, et al. Estimating the Validity of the Korean Version of Expanded Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR) Scale. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2001; 19:585–591.12. Bae JN, Cho MJ. Development of the Korean version of the Geriatric Depression Scale and its short form among elderly psychiatric patients. J Psychosom Res. 2004; 57:297–305.
Article13. Ku HM, Kim JH, Kwon EJ, Kim SH, Lee HS, Ko HJ, et al. A study on the reliability and validity of Seoul-instrumental activities of daily livings (S-IADL). J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2004; 43:189–199.14. Winblad B, Grossberg G, Frölich L, Farlow M, Zechner S, Nagel J, et al. IDEAL: a 6-month, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the first skin patch for Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 2007; 69:4 Suppl 1. S14–S22.
Article15. Choi SH, Kim SY, Na HR, Kim BK, Yang DW, Kwon JC, et al. Effect of ApoE genotype on response to donepezil in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2008; 25:445–450.
Article16. Darreh-Shori T, Jelic V. Safety and tolerability of transdermal and oral rivastigmine in Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease dementia. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2010; 9:167–176.
Article17. Nakamura Y, Imai Y, Shigeta M, Graf A, Shirahase T, Kim H, et al. A 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy, safety and tolerability of the rivastigmine patch in Japanese patients with Alzheimer's disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra. 2011; 1:163–179.
Article18. Articus K, Baier M, Tracik F, Kühn F, Preuss UW, Kurz A. A 24-week, multicentre, open evaluation of the clinical effectiveness of the rivastigmine patch in patients with probable Alzheimer's disease. Int J Clin Pract. 2011; 65:790–796.
Article19. Pregelj P. Safety and tolerability of rivastigmine transdermal patch formulation in newly diagnosed patients with Alzheimer's dementia in naturalistic conditions. Psychogeriatrics. 2012; 12:165–171.
Article20. Kulkantrakorn K, Tanyakitpisal P, Towanabut S, Dejthevaporn C, Rangseekajee P, Pongpakdee S, et al. Rivastigmine patch for treatment of Alzheimer's disease in clinical practice in Thailand. Psychogeriatrics. 2013; 13:1–8.
Article21. Gauthier S, Robillard A, Cohen S, Black S, Sampalis J, Colizza D, et al. Real-life effectiveness and tolerability of the rivastigmine transdermal patch in patients with mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease: the EMBRACE study. Curr Med Res Opin. 2013; 29:989–1000.
Article22. Segers K, Cytryn E, Surquin M. Do local meteorological conditions influence skin irritation caused by transdermal rivastigmine? A retroprospective, pilot study. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2012; 32:412–415.
Article23. Upadhye MR, Maibach HI. Influence of area of application of allergen on sensitization in contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 1992; 27:281–286.
Article24. Hurkmans JF, Boddé HE, Van Driel LM, Van Doorne H, Junginger HE. Skin irritation caused by transdermal drug delivery systems during long-term (5 days) application. Br J Dermatol. 1985; 112:461–467.
Article25. Ale I, Lachapelle JM, Maibach HI. Skin tolerability associated with transdermal drug delivery systems: an overview. Adv Ther. 2009; 26:920–935.
Article26. Waller JM, Maibach HI. Age and skin structure and function, a quantitative approach (I): blood flow, pH, thickness, and ultrasound echogenicity. Skin Res Technol. 2005; 11:221–235.
Article27. Waller JM, Maibach HI. Age and skin structure and function, a quantitative approach (II): protein, glycosaminoglycan, water, and lipid content and structure. Skin Res Technol. 2006; 12:145–154.
Article28. Fisher AA. Dermatitis due to transdermal therapeutic systems. Cutis. 1984; 34:526–527.29. Beltrani VS, Beltrani VP. Contact dermatitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1997; 78:160–173. quiz 174-176.
Article30. Di Giampaolo L, Di Donato A, Antonucci A, Paiardini G, Travaglini P, Spagnoli G, et al. Follow up study on the immune response to low frequency electromagnetic fields in men and women working in a museum. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2006; 19:4 Suppl. 37–42.31. Gangi S, Johansson O. A theoretical model based upon mast cells and histamine to explain the recently proclaimed sensitivity to electric and/or magnetic fields in humans. Med Hypotheses. 2000; 54:663–671.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Rivastigmine Transdermal Patch on Sleep Apnea in Patients with Probable Alzheimer's Disease
- An Analysis on Prescribing Patterns of Alzheimer's Dementia Treatment and Choline Alfoscerate using HIRA Claims Data
- Real-world Evaluation of Tolerability, Safety and Efficacy of Rivastigmine Oral Solution in Patients with Mild to Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease Dementia
- Efficacy and Safety of Switching from Oral Cholinesterase Inhibitors to the Rivastigmine Transdermal Patch in Patients with Probable Alzheimer's Disease
- Recent Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease