Dement Neurocogn Disord.
2016 Sep;15(3):82-87. 10.12779/dnd.2016.15.3.82.
Ideographic Alexia without Involvement of the Fusiform Gyrus in a Korean Stroke Patient: A Serial Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Gil Medical Center, Gachon University, Incheon, Korea. khpark@gachon.ac.kr
- 2Neuroscience Research Institute, Gachon University, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2442850
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12779/dnd.2016.15.3.82
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Korean orthography is composed of Hanja (ideograms) and Hangul (phonograms). Based on previous studies, the fusiform gyrus has been associated with ideogram reading. We examine serial functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) images in a patient exhibiting dissociation of Hanja and Hangul reading to identify brain areas associated with Hanja reading.
CASE REPORT
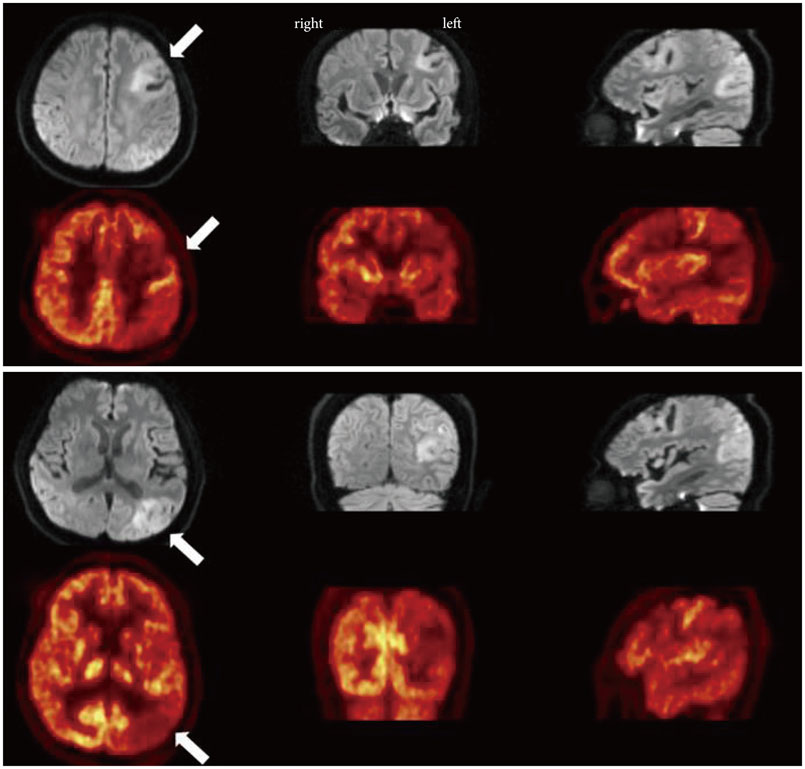
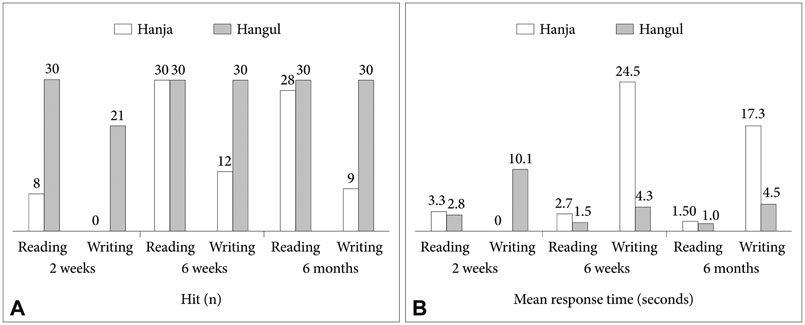
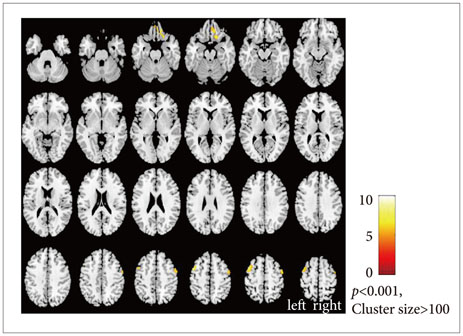
fMRI were taken of a 63-year-old man showing profound Hanja alexia with normal Hangul reading after an acute stroke involving the left frontal and parietal lobes, who later spontaneously recovered his Hanja reading ability. Scans were taken while performing Hanja and Hangul reading tasks on three occasions. As a result, in spite of having profound Hanja alexia, partial activation of the fusiform gyrus was observed on the first fMRI. Serial fMRI scans showed activation of the bilateral middle frontal gyri that increased in parallel with the patient's recovery of Hanja reading.
CONCLUSIONS
The frontal lobe, not only fusiform gyrus, may play role in reading Hanja, although more evidence is needed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Iwata M. Neural mechanism of reading and writing in the Japanese language. Funct Neurol. 1986; 1:43–52.
Article2. Kawamura M, Hirayama K, Hasegawa K, Takahashi N, Yamaura A. Alexia with agraphia of kanji (Japanese morphograms). J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987; 50:1125–1129.
Article3. Sakurai Y, Asami M, Mannen T. Alexia and agraphia with lesions of the angular and supramarginal gyri: evidence for the disruption of sequential processing. J Neurol Sci. 2010; 288:25–33.
Article4. Soma Y, Sugishita M, Kitamura K, Maruyama S, Imanaga H. Lexical agraphia in the Japanese language. Pure agraphia for Kanji due to left posteroinferior temporal lesions. Brain. 1989; 112(Pt 6):1549–1561.
Article5. Kim H, Na DL. Dissociation of pure korean words and Chinese-derivative words in phonological dysgraphia. Brain Lang. 2000; 74:134–137.
Article6. Kwon JC, Lee HJ, Chin J, Lee YM, Kim H, Na DL. Hanja alexia with agraphia after left posterior inferior temporal lobe infarction: a case study. J Korean Med Sci. 2002; 17:91–95.
Article7. Kwon M, Kim JS, Lee JH, Sim H, Nam K, Park H. Double dissociation of Hangul and Hanja reading in Korean patients with stroke. Eur Neurol. 2005; 54:199–203.
Article8. Lee KM. Functional MRI comparison between reading ideographic and phonographic scripts of one language. Brain Lang. 2004; 91:245–251.
Article9. Yoon HW, Cho KD, Chung JY, Park H. Neural mechanisms of Korean word reading: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Neurosci Lett. 2005; 373:206–211.
Article10. Yoon HW, Chung JY, Kim KH, Song MS, Park HW. An fMRI study of Chinese character reading and picture naming by native Korean speakers. Neurosci Lett. 2006; 392:90–95.
Article11. Kawahata N, Nagata K, Shishido F. Alexia with agraphia due to the left posterior inferior temporal lobe lesion--neuropsychological analysis and its pathogenetic mechanisms. Brain Lang. 1988; 33:296–310.
Article12. Sakurai Y, Yagishita A, Goto Y, Ohtsu H, Mannen T. Fusiform type alexia: pure alexia for words in contrast to posterior occipital type pure alexia for letters. J Neurol Sci. 2006; 247:81–92.
Article13. Sakurai Y, Terao Y, Ichikawa Y, Ohtsu H, Momose T, Tsuji S, et al. Pure alexia for kana. Characterization of alexia with lesions of the inferior occipital cortex. J Neurol Sci. 2008; 268:48–59.
Article14. Wu CY, Ho MH, Chen SH. A meta-analysis of fMRI studies on Chinese orthographic, phonological, and semantic processing. Neuroimage. 2012; 63:381–391.
Article15. Tan LH, Spinks JA, Gao JH, Liu HL, Perfetti CA, Xiong J, et al. Brain activation in the processing of Chinese characters and words: a functional MRI study. Hum Brain Mapp. 2000; 10:16–27.
Article16. Chee MW, Weekes B, Lee KM, Soon CS, Schreiber A, Hoon JJ, et al. Overlap and dissociation of semantic processing of Chinese characters, English words, and pictures: evidence from fMRI. Neuroimage. 2000; 12:392–403.
Article17. Pillai JJ. Insights into adult postlesional language cortical plasticity provided by cerebral blood oxygen level-dependent functional MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010; 31:990–996.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Occupational Trauma Exposure on Brain Functional Connectivity in Firefighters With Subclinical Post-Traumatic Stress Symptoms: A Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study
- Working Memory Mapping Analysis using fMRI
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Idiopathic Herniation of the Lingual Gyrus: a Case Report
- Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Brain: Principle and Practical Application
- Changes of Motor Deactivation Regions in Patients with Intracranial Lesions