Infect Chemother.
2016 Dec;48(4):330-333. 10.3947/ic.2016.48.4.330.
Epstein-Barr Virus Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome after Scrub Typhus Infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- 2Division of Infectious Diseases, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. zenmd@naver.com
- KMID: 2441328
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2016.48.4.330
Abstract
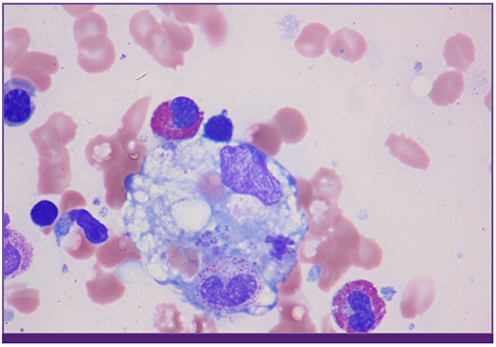
- There have been a small number of cases of scrub typhus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome (HPS), most of which were treated successfully using adequate antibiotics. Here, we report a case of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated HPS after scrub typhus infection that was not improved using antirickettsial treatment. A 73-year-old male who had been diagnosed with scrub typhus according to an eschar and a positive serology was transferred to our institution because of a persistent fever despite 7-day doxycycline therapy. Physical and laboratory data showed hepatosplenomegaly, bicytopenia, hyperferritinemia, and hypofibrinogenemia. A bone marrow examination (BM) revealed hypercellular marrow with hemophagocytosis and histiocyte infiltration. EBV was detected in BM aspirates using polymerase chain reaction. After a diagnosis of HPS was made, the patient was treated successfully using high-dose steroids.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fisman DN. Hemophagocytic syndromes and infection. Emerg Infect Dis. 2000; 6:601–608.
Article2. Scott R, Robb-Smith A. Histiocytic medullary reticulosis. Lancet. 1939; 2:194–198.3. Lee HG, Min SK, Kong SJ, Lee SJ, Song HH, Yoon JW, Lee MG, Shin DH, Kang SH, Lee JY, Park YI, Choi MG. Clinical features of tsutsugamushi disease in Chuncheon. Korean J Med. 2005; 69:190–196.4. Varghese GM, Abraham OC, Mathai D, Thomas K, Aaron R, Kavitha ML, Mathai E. Scrub typhus among hospitalised patients with febrile illness in South India: magnitude and clinical predictors. J Infect. 2006; 52:56–60.
Article5. Fujiwara F, Hibi S, Imashuku S. Hypercytokinemia in hemophagocytic syndrome. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1993; 15:92–98.
Article6. Henter JI, Horne A, Aricó M, Egeler RM, Filipovich AH, Imashuku S, Ladisch S, McClain K, Webb D, Winiarski J, Janka G. HLH-2004: Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2007; 48:124–131.
Article7. Rouphael NG, Talati NJ, Vaughan C, Cunningham K, Moreira R, Gould C. Infections associated with haemophagocytic syndrome. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007; 7:814–822.
Article8. Weitzman S. Approach to hemophagocytic syndromes. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2011; 2011:178–183.
Article9. Lay JD, Chuang SE, Rowe M, Su IJ. Epstein-barr virus latent membrane protein-1 mediates upregulation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in EBV-infected T cells: implications for the pathogenesis of hemophagocytic syndrome. J Biomed Sci. 2003; 10:146–155.
Article10. Lay JD, Tsao CJ, Chen JY, Kadin ME, Su IJ. Upregulation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene by Epstein-Barr virus and activation of macrophages in Epstein-Barr virus-infected T cells in the pathogenesis of hemophagocytic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1997; 100:1969–1979.
Article11. Filipovich AH. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) and related disorders. Hematology (Am Soc Hematol Educ Program). 2009; •••:127–131.
Article12. Yamashita N, Kimura H, Morishima T. Virological aspects of Epstein-Barr virus infections. Acta Med Okayama. 2005; 59:239–246.13. Walton AH, Muenzer JT, Rasche D, Boomer JS, Sato B, Brownstein BH, Pachot A, Brooks TL, Deych E, Shannon WD, Green JM, Storch GA, Hotchkiss RS. Reactivation of multiple viruses in patients with sepsis. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e98819.
Article14. Takami A, Yamauchi H, Asakura H, Ishiyama K, Nakao S. Tsutsugamushi disease (scrub typhus)-associated hemophagocytic syndrome. Int J Hematol. 2002; 75:337–338.
Article15. Miyakawa K, Ohsugi K, Sugahara S, Kuriyama C, Kikuchi A, Ohta M. Tsutsugamushi disease with hemophagocytosis complicated by Parvovirus B19 infection. Nippon Naika Gakkai Zasshi. 2006; 95:2544–2546.
Article16. Premaratna R, Williams HS, Chandrasena TG, Rajapakse RP, Kularatna SA, de Silva HJ. Unusual pancytopenia secondary to haemophagocytosis syndrome in rickettsioses. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2009; 103:961–963.
Article17. Kim HW, Choi BS, Kim JH, Shin YM, Lee SJ, Kim SR, Jun JB. A case of death due to hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis accompanied by scrub typhus. Infect Chemother. 2010; 42:266–270.
Article18. Hong JH, Cho HJ, Kim HM, Namgoong MK, Kwon O, Chun JK. A case of Epstein-Barr virus associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis after scrub typhus infection. Clin Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2012; 19:49–52.19. Lin YH, Lin YH, Shi ZY. A case report of scrub typhus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome and a review of literature. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2014; 67:115–117.
Article20. Kang CI, Choi CM, Park JT, Park TS. Seroprevalence of Epstein-Barr virus infection in young men of South Korea. Infect Chemother. 2007; 39:93–94.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Epstein-Barr Virus Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis after Scrub Typhus Infection
- A Case of Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome Demonstrated by In Situ Hybridization
- A Case of Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome with Ascites
- A case of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis caused by an Epstein-Barr virus infection, presenting with unremitting fever and rash
- A Case of Death Due to Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Accompanied by Scrub Typhus