Yonsei Med J.
2019 Mar;60(3):298-307. 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.3.298.
MiR-590 Inhibits Endothelial Cell Apoptosis by Inactivating the TLR4/NF-κB Pathway in Atherosclerosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Emergency, Zhengzhou University People's Hospital, Zhengzhou, China.
- 2Department of Coronary Heart Disease, Zhengzhou University People's Hospital, Fuwai Central China Cardiovascular Hospital, Zhengzhou, China. alonewoof@126.com
- KMID: 2441308
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2019.60.3.298
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Previous study has well documented the anti-apoptotic effects of miR-590 on oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-treated endothelial cells (ECs). However, the mechanism underlying the anti-apoptotic effects of miR-590 in ox-LDL-treated ECs remains to be further addressed.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
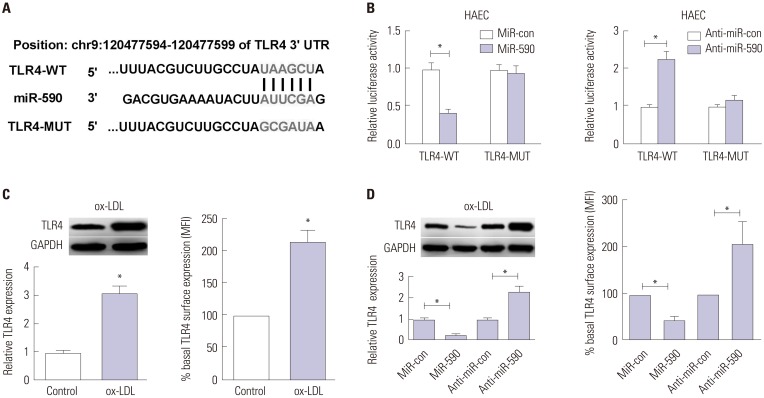
ApoE(−/−) mice fed with a high-fat diet (HFD) and human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs) treated with ox-LDL were used as in vivo and in vitro models of atherosclerosis. The expressions of miR-590 and toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) were detected by quantitative real-time PCR and Western blot, respectively. Atherosclerotic lesion analysis was performed using Evans blue and hematoxylin-eosin staining. Cell proliferation was assessed by MTT assay. Apoptosis was examined using flow cytometry analysis and Western blot analysis of Cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) and Cleaved Caspase-3 levels. The effect of miR-590 on TLR4/nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway was evaluated by Western blot. Binding between miR-590 and TLR4 was confirmed by luciferase reporter assay and Western blot.
RESULTS
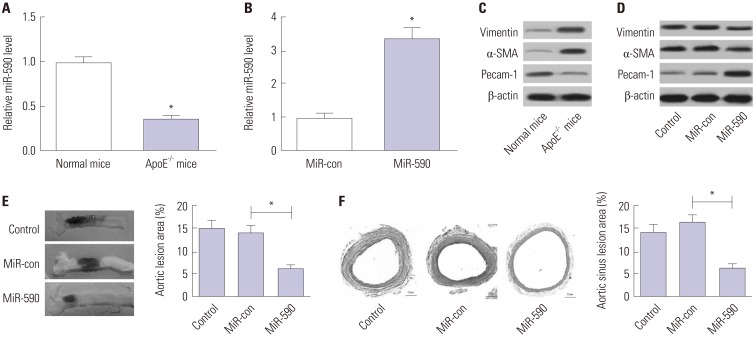
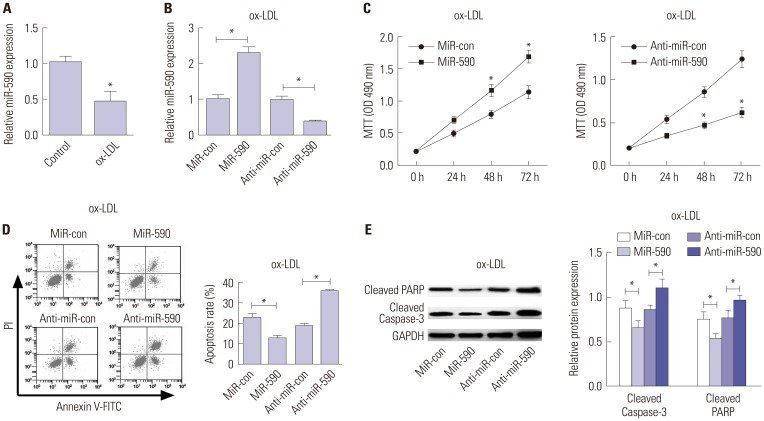
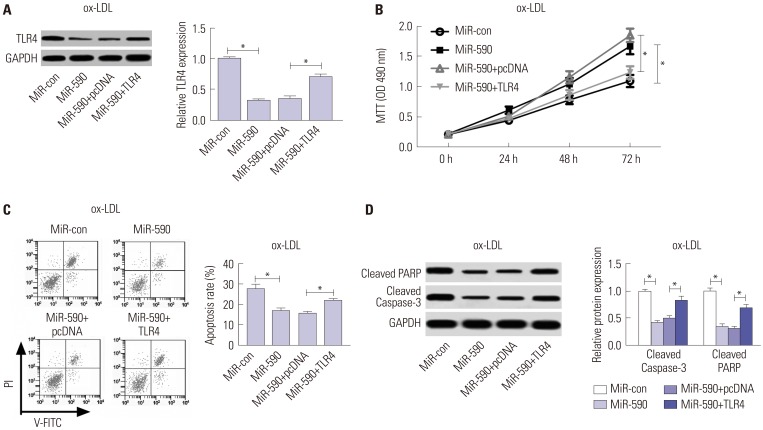
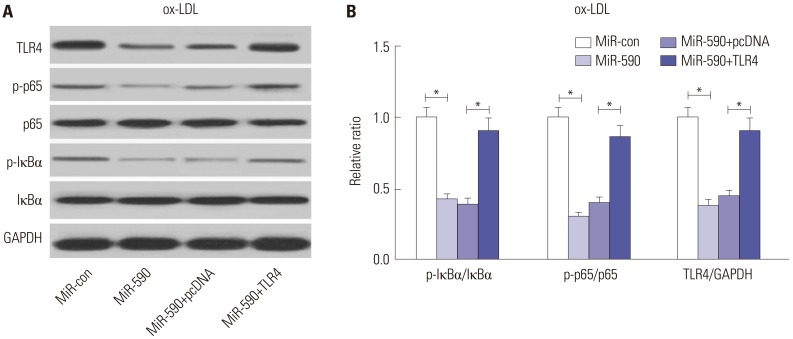
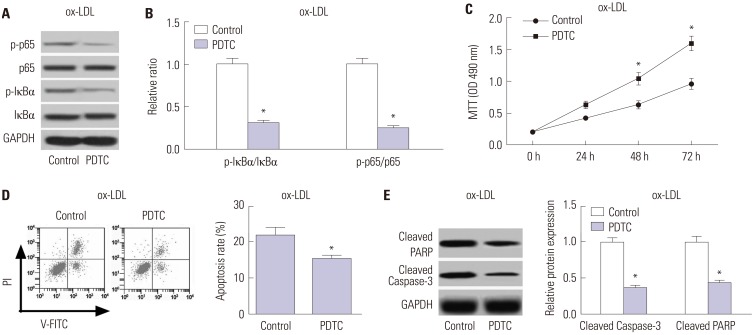
miR-590 was downregulated in the aorta tissues from HFD-fed apoE(−/−) mice and ox-LDL-treated HAECs. miR-590 overexpression inhibited atherosclerotic lesion in HFD-induced apoE(−/−) mice and promoted proliferation and inhibited apoptosis of ox-LDL-treated HAECs. Additionally, TLR4 was identified as a direct target of miR-590 in ox-LDL-treated HAECs. Moreover, anti-miR-590 reversed TLR4 knockdown-mediated promotion of cell proliferation and suppression of apoptosis in ox-LDL-treated HAECs. miR-590 overexpression suppressed the TLR4/NF-κB pathway, and inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κB pathway promoted cell proliferation and impeded apoptosis in ox-LDL-treated HAECs.
CONCLUSION
miR-590 promoted proliferation and blocked ox-LDL-induced apoptosis in HAECs through inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κB pathway.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Aorta
Apoptosis*
Atherosclerosis*
Blotting, Western
Caspase 3
Cell Proliferation
Diet, High-Fat
Endothelial Cells*
Evans Blue
Flow Cytometry
Humans
In Vitro Techniques
Lipoproteins
Luciferases
Mice
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
Toll-Like Receptor 4
Caspase 3
Evans Blue
Lipoproteins
Luciferases
Toll-Like Receptor 4
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rafieian-Kopaei M, Setorki M, Doudi M, Baradaran A, Nasri H. Atherosclerosis: process, indicators, risk factors and new hopes. Int J Prev Med. 2014; 5:927–946. PMID: 25489440.2. Tabas I, García-Cardeña G, Owens GK. Recent insights into the cellular biology of atherosclerosis. J Cell Biol. 2015; 209:13–22. PMID: 25869663.
Article3. Trpkovic A, Resanovic I, Stanimirovic J, Radak D, Mousa SA, Cenic-Milosevic D, et al. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein as a biomarker of cardiovascular diseases. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2015; 52:70–85. PMID: 25537066.
Article4. Najafpour Boushehri S, Yusof RM, Nasir Mohammad Taib M, Mirzaei K, Yazdekhasti N, Akbarzadeh S. Effect of vitamin supplementation on serum oxidized low-density lipoprotein levels in male subjects with cardiovascular disease risk factors. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2012; 15:958–964. PMID: 23493764.5. Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009; 136:215–233. PMID: 19167326.
Article6. Natarelli L, Schober A. MicroRNAs and the response to injury in atherosclerosis. Hamostaseologie. 2015; 35:142–150. PMID: 25612846.
Article7. Shan Z, Yao C, Li ZL, Teng Y, Li W, Wang JS, et al. Differentially expressed microRNAs at different stages of atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013; 126:515–520. PMID: 23422117.8. Menghini R, Stöhr R, Federici M. MicroRNAs in vascular aging and atherosclerosis. Ageing Res Rev. 2014; 17:68–78. PMID: 24681293.
Article9. Eulalio A, Mano M, Dal Ferro M, Zentilin L, Sinagra G, Zacchigna S, et al. Functional screening identifies miRNAs inducing cardiac regeneration. Nature. 2012; 492:376–381. PMID: 23222520.
Article10. Bao MH, Li JM, Zhou QL, Li GY, Zeng J, Zhao J, et al. Effects of miR-590 on oxLDL-induced endothelial cell apoptosis: roles of p53 and NF-κB. Mol Med Rep. 2016; 13:867–873. PMID: 26648441.
Article11. den Dekker WK, Cheng C, Pasterkamp G, Duckers HJ. Toll like receptor 4 in atherosclerosis and plaque destabilization. Atherosclerosis. 2010; 209:314–320. PMID: 19900676.
Article12. Xing S, Zheng F, Zhang W, Wang D, Xing Q. Relationship between toll-like receptor 4 levels in aorta and severity of atherosclerosis. J Int Med Res. 2014; 42:958–965. PMID: 24925583.
Article13. Corbi G, Bianco A, Turchiarelli V, Cellurale M, Fatica F, Daniele A, et al. Potential mechanisms linking atherosclerosis and increased cardiovascular risk in COPD: focus on Sirtuins. Int J Mol Sci. 2013; 14:12696–12713. PMID: 23774840.
Article14. Gimbrone MA Jr, Topper JN, Nagel T, Anderson KR, Garcia-Cardeña G. Endothelial dysfunction, hemodynamic forces, and atherogenesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000; 902:230–239. PMID: 10865843.15. Sun X, Belkin N, Feinberg MW. Endothelial microRNAs and atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2013; 15:372. PMID: 24158362.
Article16. Chen Z, Wang M, He Q, Li Z, Zhao Y, Wang W, et al. MicroRNA-98 rescues proliferation and alleviates ox-LDL-induced apoptosis in HUVECs by targeting LOX-1. Exp Ther Med. 2017; 13:1702–1710. PMID: 28565756.
Article17. Tang F, Yang TL. MicroRNA-126 alleviates endothelial cells injury in atherosclerosis by restoring autophagic flux via inhibiting of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018; 495:1482–1489. PMID: 29203244.
Article18. Cui J, Ren Z, Zou W, Jiang Y. miR-497 accelerates oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced lipid accumulation in macrophages by repressing the expression of apelin. Cell Biol Int. 2017; 41:1012–1019. PMID: 28653788.
Article19. Luo P, Zhang WF, Qian ZX, Xiao LF, Wang H, Zhu TT, et al. MiR-590-5p-meidated LOX-1 upregulation promotes Angiotensin II-induced endothelial cell apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016; 471:402–408. PMID: 26906623.
Article20. He PP, OuYang XP, Li Y, Lv YC, Wang ZB, Yao F, et al. MicroRNA-590 inhibits lipoprotein lipase expression and prevents atherosclerosis in apoE knockout mice. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0138788. PMID: 26397958.
Article21. He PP, Ouyang XP, Tang YY, Liao L, Wang ZB, Lv YC, et al. MicroRNA-590 attenuates lipid accumulation and pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion by targeting lipoprotein lipase gene in human THP-1 macrophages. Biochimie. 2014; 106:81–90. PMID: 25149060.
Article22. Thompson MR, Kaminski JJ, Kurt-Jones EA, Fitzgerald KA. Pattern recognition receptors and the innate immune response to viral infection. Viruses. 2011; 3:920–940. PMID: 21994762.
Article23. Yang K, Zhang XJ, Cao LJ, Liu XH, Liu ZH, Wang XQ, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 mediates inflammatory cytokine secretion in smooth muscle cells induced by oxidized low-density lipoprotein. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e95935. PMID: 24755612.
Article24. Stoll LL, Denning GM, Li WG, Rice JB, Harrelson AL, Romig SA, et al. Regulation of endotoxin-induced proinflammatory activation in human coronary artery cells: expression of functional membrane-bound CD14 by human coronary artery smooth muscle cells. J Immunol. 2004; 173:1336–1343. PMID: 15240728.
Article25. Michelsen KS, Wong MH, Shah PK, Zhang W, Yano J, Doherty TM, et al. Lack of Toll-like receptor 4 or myeloid differentiation factor 88 reduces atherosclerosis and alters plaque phenotype in mice deficient in apolipoprotein E. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004; 101:10679–10684. PMID: 15249654.
Article26. Pasterkamp G, Van Keulen JK, De Kleijn DP. Role of Toll-like receptor 4 in the initiation and progression of atherosclerotic disease. Eur J Clin Invest. 2004; 34:328–334. PMID: 15147329.
Article27. Baker RG, Hayden MS, Ghosh S. NF-κB, inflammation, and metabolic disease. Cell Metab. 2011; 13:11–22. PMID: 21195345.
Article28. Tang YL, Jiang JH, Wang S, Liu Z, Tang XQ, Peng J, et al. TLR4/NF-κB signaling contributes to chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0123685. PMID: 25860573.
Article29. Hu ZP, Fang XL, Fang N, Wang XB, Qian HY, Cao Z, et al. Melatonin ameliorates vascular endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, and atherosclerosis by suppressing the TLR4/NF-κB system in high-fat-fed rabbits. J Pineal Res. 2013; 55:388–398. PMID: 24006943.
Article30. Lu Z, Zhang X, Li Y, Jin J, Huang Y. TLR4 antagonist reduces early-stage atherosclerosis in diabetic apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. J Endocrinol. 2013; 216:61–71. PMID: 23060524.
Article31. Lu Z, Zhang X, Li Y, Lopes-Virella MF, Huang Y. TLR4 antagonist attenuates atherogenesis in LDL receptor-deficient mice with diet-induced type 2 diabetes. Immunobiology. 2015; 220:1246–1254. PMID: 26162692.
Article32. Zhou Q, Zhu Z, Hu X, Shu C. HMGB1: a critical mediator for oxidized-low density lipoproteins induced atherosclerosis. Int J Cardiol. 2016; 202:956–957. PMID: 26549559.
Article33. Chen M, Li W, Zhang Y, Yang J. MicroRNA-20a protects human aortic endothelial cells from Ox-LDL-induced inflammation through targeting TLR4 and TXNIP signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018; 103:191–197. PMID: 29653364.
Article34. Du F, Yu F, Wang Y, Hui Y, Carnevale K, Fu M, et al. MicroRNA-155 deficiency results in decreased macrophage inflammation and attenuated atherogenesis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014; 34:759–767. PMID: 24504735.
Article35. Wang J, Bai X, Song Q, Fan F, Hu Z, Cheng G, et al. miR-223 inhibits lipid deposition and inflammation by suppressing toll-like receptor 4 signaling in macrophages. Int J Mol Sci. 2015; 16:24965–24982. PMID: 26492242.
Article36. Du XJ, Lu JM, Sha Y. MiR-181a inhibits vascular inflammation induced by ox-LDL via targeting TLR4 in human macrophages. J Cell Physiol. 2018; 233:6996–7003.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- miR-215 Enhances HCV Replication by Targeting TRIM22 and Inactivating NF-κB Signaling
- Upregulation of miR-27b Facilitates Apoptosis of TNF-α-Stimulated Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes
- Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Transplantation Inhibits Vascular Inflammatory Responses and Endothelial Dysfunction in Rats with Atherosclerosis
- MiR-182-5p Mediated by Exosomes Derived From Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Attenuates Inflammatory Responses by Targeting TLR4 in a Mouse Model of Myocardial Infraction
- Exosome-mediated lnc-ABCA12-3 promotes proliferation and glycolysis but inhibits apoptosis by regulating the tolllike receptor 4/nuclear factor kappa-B signaling pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma