Ann Lab Med.
2012 Nov;32(6):420-425.
Elecsys Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Quantitative Assay: Performance Evaluation and Correlation with Hepatitis B Virus DNA during 96 Weeks of Follow-up in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. hhkim@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Medical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Treatment for chronic hepatitis B aims to suppress virus replication and virus sequestration in hepatocytes. Covalently closed circular (ccc) DNA is the template for transcription of viral genes and is responsible for viral persistence. However, limited data are available for quantification of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in Korea.
METHODS
We evaluated the Elecsys HBsAg II quant assay (Roche Diagnostics, USA) for within-run, between-run, and between-day precisions, linearity, carryover, and clinical specificity. In total, 156 serum samples were evaluated for correlation between HBsAg and hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA. Serial samples were obtained from 10 patients at 0, 12, 24, 48, 72, and 96 weeks during follow-up.
RESULTS
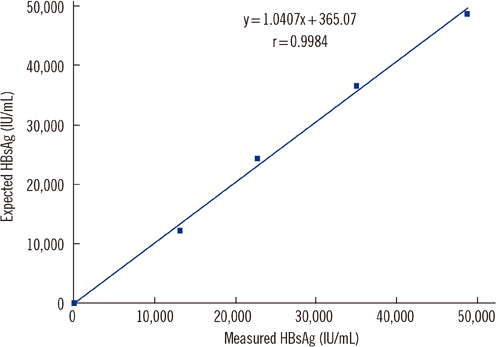
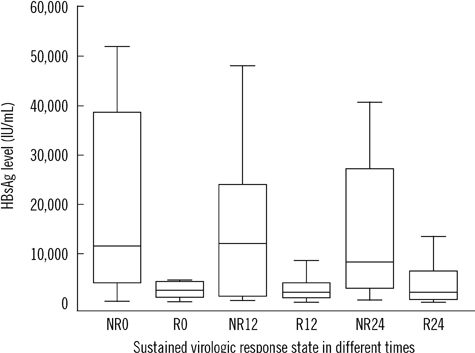
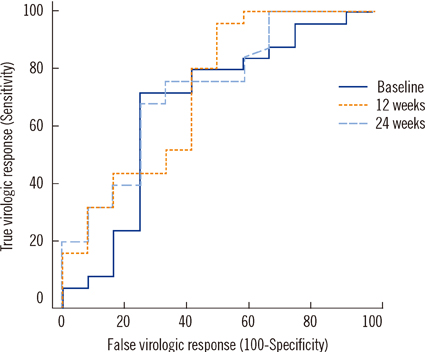
The assay detected HBsAg in a linear range of 0.5-48,696 IU/mL. Within-run, between-run, and between-day CVs were 2.9-4.1%, 0-1.5%, and 1.5-4.9%, respectively. Cross-reactivity between potentially interfering substances was absent, and the carryover rate was 0.00002%. The correlation of measurements between the Elecsys assay and HBV DNA PCR was weak (r=0.438, P=0.002). For predicting virologic response, cutoff values of 10,275 IU/mL and 3,846 IU/mL at 12 and 24 weeks after treatment initiation showed positive predictive values of 77.1% and 85% and negative predictive values of 84.6% and 50%, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
The Elecsys HBsAg II quant assay showed good performance for precision, linearity, carryover rate, and specificity. HBsAg level at baseline, 12 weeks, and 24 weeks after treatment initiation can predict virologic response, and the assay can be used for HBsAg quantification in clinical practice.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Analysis of Variance
Antiviral Agents/therapeutic use
DNA, Viral/analysis
Follow-Up Studies
Hepatitis B Surface Antigens/*blood
Hepatitis B virus/genetics/*metabolism
Hepatitis B, Chronic/drug therapy/*virology
Humans
Polymerase Chain Reaction
ROC Curve
Reagent Kits, Diagnostic
Time Factors
Antiviral Agents
DNA, Viral
Hepatitis B Surface Antigens
Reagent Kits, Diagnostic
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lin LY, Wong VW, Zhou HJ, Chan HY, Gui HL, Guo SM, et al. Relationship between serum hepatitis B virus DNA and surface antigen with covalently closed circular DNA in HBeAg-negative patients. J Med Virol. 2010. 82:1494–1500.
Article2. Lee WM. Hepatitis B virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1997. 337:1733–1745.
Article3. Nguyen T, Thompson AJ, Bowden S, Croagh C, Bell S, Desmond PV, et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen levels during the natural history of chronic hepatitis B: a perspective on Asia. J Hepatol. 2010. 52:508–513.
Article4. Jaroszewicz J, Calle Serrano B, Wursthorn K, Deterding K, Schlue J, Raupach R, et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) levels in the natural history of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-infection: a European perspective. J Hepatol. 2010. 52:514–522.
Article5. Thompson AJ, Nguyen T, Iser D, Ayres A, Jackson K, Littlejohn M, et al. Serum hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B e antigen titers: disease phase influences correlation with viral load and intrahepatic hepatitis B virus markers. Hepatology. 2010. 51:1933–1944.
Article6. Sonneveld MJ, Rijckborst V, Boucher CA, Zwang L, Beersma MF, Hansen BE, et al. A comparison of two assays for quantification of Hepatitis B surface Antigen in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Clin Virol. 2011. 51:175–178.
Article7. Wursthorn K, Jaroszewicz J, Zacher BJ, Darnedde M, Raupach R, Mederacke I, et al. Correlation between the Elecsys HBsAg II assay and the Architect assay for the quantification of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in the serum. J Clin Virol. 2011. 50:292–296.
Article8. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Evaluation of precision performance of puantitative measurement methods: Approved guideline, EP5-A2. 2004. Wayne, PA: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards.9. Tholen DW. Evaluation of linearity using the newly approved NCCLS EP6-A protocol. Clin Lab News. 2004. 30:10–12.10. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Preliminary evaluation of quantitative clinical laboratory methods: Approved guideline, EP10-A2. 2002. Second edition. Wayne, PA: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards.11. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Protocols for determination of limits of detection and limits of quantitation: Approved guideline EP17-A. 2004. Wayne, PA: National Committee for Clinical and Laboratory Standards.12. Glass DC, Gray CN. Estimating mean exposures from censored data: exposure to benzene in the Australian petroleum industry. Ann Occup Hyg. 2001. 45:275–282.
Article13. Chan HL, Thompson A, Martinot-Peignoux M, Piratvisuth T, Cornberg M, Brunetto MR, et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen quantification: why and how to use it in 2011-a core group report. J Hepatol. 2011. 55:1121–1131.14. Moucari R, Marcellin P. Quantification of hepatitis B surface antigen: a new concept for the management of chronic hepatitis B. Liver Int. 2011. 31:Suppl 1. 122–128.
Article15. Deguchi M, Yamashita N, Kagita M, Asari S, Iwatani Y, Tsuchida T, et al. Quantitation of hepatitis B surface antigen by an automated chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay. J Virol Methods. 2004. 115:217–222.
Article16. Ozaras R, Tabak F, Tahan V, Ozturk R, Akin H, Mert A, et al. Correlation of quantitative assay of HBsAg and HBV DNA levels during chronic HBV treatment. Dig Dis Sci. 2008. 53:2995–2998.
Article17. Wiegand J, Wedemeyer H, Finger A, Heidrich B, Rosenau J, Michel G, et al. A decline in hepatitis B virus surface antigen (hbsag) predicts clearance, but does not correlate with quantitative hbeag or HBV DNA levels. Antivir Ther. 2008. 13:547–554.18. Chen J, Wang Z, Guo Y, Peng J, Sun J, Ahmed CS, et al. Serum HBsAg changes in HBeAg positive chronic hepatitis B patients with continuous viral load reductions during treatment with adefovir or peg-interferon-alpha-2a. Antiviral Res. 2009. 81:88–91.19. Moucari R, Mackiewicz V, Lada O, Ripault MP, Castelnau C, Martinot-Peignoux M, et al. Early serum HBsAg drop: a strong predictor of sustained virological response to pegylated interferon alfa-2a in HBeAg-negative patients. Hepatology. 2009. 49:1151–1157.
Article20. Cho YK, Song BC. New insight for HBV DNA and HBsAg quantitation during antiviral therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2011. 57:144–149.
Article21. Chan HL, Wong VW, Tse AM, Tse CH, Chim AM, Chan HY, et al. Serum hepatitis B surface antigen quantitation can reflect hepatitis B virus in the liver and predict treatment response. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. 5:1462–1468.
Article22. Piratvisuth T, Marcellin P, Popescu M, Kapprell HP, Rothe V, Lu ZM. Hepatitis B surface antigen: association with sustained response to peginterferon alfa-2a in hepatitis B e antigen-positive patients. Hepatol Int. 2011. [Epub ahead of print].
Article23. Lee MH, Lee DM, Kim SS, Cheong JY, Cho SW. Correlation of serum hepatitis B surface antigen level with response to entecavir in naïve patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Med Virol. 2011. 83:1178–1186.
Article24. Cai W, Xie Q, An B, Wang H, Zhou X, Zhao G, et al. On-treatment serum HBsAg level is predictive of sustained off-treatment virologic response to telbivudine in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients. J Clin Virol. 2010. 48:22–26.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Increasing the Efficiency of Laboratory Performance by Using the Onboard Dilution Algorithm of the Elecsys Hepatitis B Surface Antigen II Quantitative Assay
- Prevention of Viral Hepatitis and Vaccination
- Occult Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C: Innocent Bystander or Not?
- Quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen predicts the antiviral response and hepatocellular carcinoma development in patients with chronic hepatitis B
- Comparison of Hepatitis B Virus Detection by Direct Hybridization Assay and Polymerase Chain Reaction