Ann Lab Med.
2019 May;39(3):278-283. 10.3343/alm.2019.39.3.278.
Comparison of Clinical Performance Between BacT/Alert Virtuo and BacT/Alert 3D Blood Culture Systems
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Emergency Medicine, Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine and Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, Changwon, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine and Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, Changwon, Korea. sjkim8239@hanmail.net
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine and Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, Changwon, Korea.
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Division of Nursing, Gwangju Health University, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2431605
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2019.39.3.278
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
BacT/Alert Virtuo (BioMérieux, Durham, NC, USA) is a recently developed blood culture system that includes functions of automatic registration, loading, and unloading of the blood culture bottles, as well as measurement of blood volume. We compared the performances between the BacT/Alert Virtuo and 3D (BioMérieux) blood culture systems.
METHODS
A total of 952 patients (1,904 sets) visiting an university-affiliated hospital in Korea for blood cultures were enrolled. Five milliliters of blood was added into each of the two aerobic (FA Plus) and two anaerobic (FN Plus) bottles of the Virtuo and 3D systems for a single set. Positive rate and time to detection (TTD) were compared between the two systems.
RESULTS
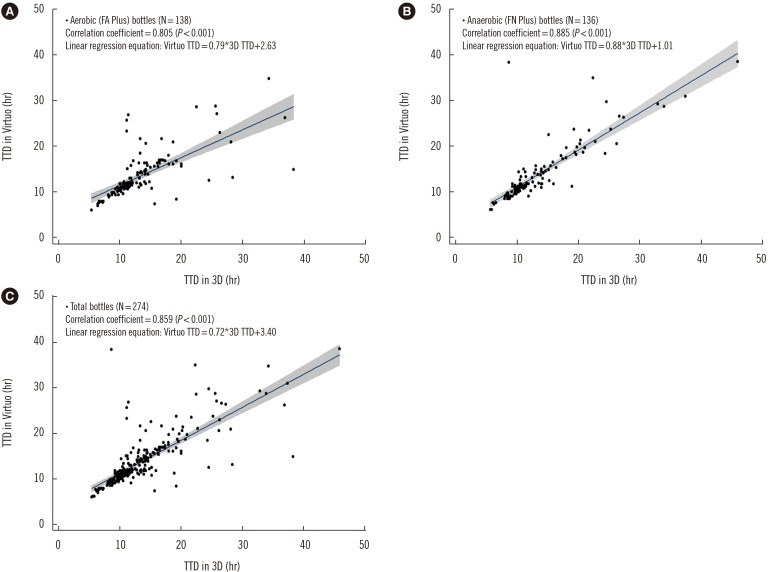
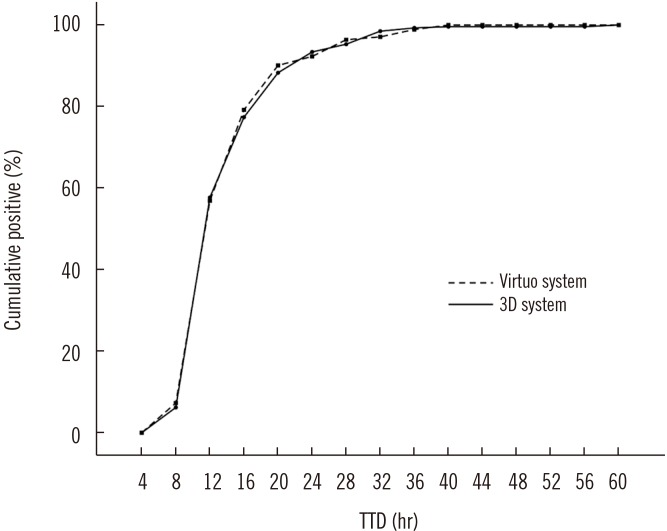
The positive rates were 8.3% and 8.4% in FA Plus bottles and 7.8% and 8.3% in FN Plus bottles, in the Virtuo and 3D systems, respectively (P>0.05). Median TTDs were shorter in the Virtuo than in the 3D system for all isolates (11.5 hours [N=305] vs 11.8 hours [N=318], P < 0.001), Staphylococcus aureus (N=38; 14.3 hours vs 16.0 hours, P=0.021), and Escherichia coli (N=117; 10.4 hours vs 11.0 hours, P < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
The Virtuo has the potential to detect pathogens early in all bottle types. This might improve the prognosis of sepsis by allowing for implementation of expeditious management.
Figure
Reference
-
1. CLSI. Principles and procedures for blood cultures; approved guideline M47-A. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2007.2. Pien BC, Sundaram P, Raoof N, Costa SF, Mirrett S, Woods CW, et al. The clinical and prognostic importance of positive blood cultures in adults. Am J Med. 2010; 123:819–828. PMID: 20800151.3. Goto M, Al-Hasan MN. Overall burden of bloodstream infection and nosocomial bloodstream infection in North America and Europe. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2013; 19:501–509. PMID: 23473333.4. Barenfanger J, Graham DR, Kolluri L, Sangwan G, Lawhorn J, Drake CA, et al. Decreased mortality associated with prompt Gram staining of blood cultures. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008; 130:870–876. PMID: 19019762.5. Opota O, Croxatto A, Prod'hom G, Greub G. Blood culture-based diagnosis of bacteraemia: state of the art. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015; 21:313–322. PMID: 25753137.6. Kirn TJ, Weinstein MP. Update on blood cultures: how to obtain, process, report, and interpret. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2013; 19:513–520. PMID: 23490046.7. Bouza E, Sousa D, Rodriguez-Creixems M, Lechuz JG, Munoz P. Is the volume of blood cultured still a significant factor in the diagnosis of bloodstream infections? J Clin Microbiol. 2007; 45:2765–2769. PMID: 17567782.8. Jacobs MR, Mazzulli T, Hazen KC, Good CE, Abdelhamed AM, Lo P, et al. Multicenter clinical evaluation of BacT/Alert Virtuo blood culture system. J Clin Microbiol. 2017; 55:2413–2421. PMID: 28539343.9. Akan OA, Yildiz E. Comparison of the effect of delayed entry into 2 different blood culture systems (BACTEC 9240 and BacT/ALERT 3D) on culture positivity. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2006; 54:193–196. PMID: 16427242.10. van der Velden LB, Vos FJ, Mouton JW, Sturm PD. Clinical impact of preincubation of blood cultures at 37℃. J Clin Microbiol. 2011; 49:275–280. PMID: 21068285.11. Brown DF, Warren RE. Effect of sample volume on yield of positive blood cultures from adult patients with haematological malignancy. J Clin Pathol. 1990; 43:777–779. PMID: 2212073.12. Kim SC, Kim S, Lee DH, Choi SR, Kim JS. Effect of blood volume in standard anaerobic blood culture bottles of the BacT/ALERT 3D system used for the detection of pathogens and time to detection. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0116728. PMID: 25646758.13. She RC, Romney MG, Jang W, Walker T, Karichu JK, Richter SS. Performance of the BacT/Alert Virtuo Microbial Detection System for the culture of sterile body fluids: prospective multicentre study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2018; 24:992–996. PMID: 29274462.14. Congestri F, Pedna MF, Fantini M, Samuelli M, Schiavone P, Torri A, et al. Comparison of ‘time to detection’ values between BacT/ALERT VIRTUO and BacT/ALERT 3D instruments for clinical blood culture samples. Int J Infect Dis. 2017; 62:1–5. PMID: 28625838.15. Altun O, Almuhayawi M, Luthje P, Taha R, Ullberg M, Ozenci V. Controlled evaluation of the new BacT/Alert Virtuo blood culture system for detection and time to detection of bacteria and yeasts. J Clin Microbiol. 2016; 54:1148–1151. PMID: 26842707.16. Miller N, Brassinne L, Allemeersch D. Implementation of the new VIRTUO blood culture system: evaluation and comparison to the 3D system using simulated blood cultures. Acta Clin Belg. 2018; 73:16–20. PMID: 28583022.17. Park J, Han S, Shin S. Comparison of growth performance of the BacT/ALERT VIRTUO and BACTEC FX blood culture systems under simulated bloodstream infection conditions. Clin Lab. 2017; 63:39–46. PMID: 28164485.18. Park SH, Shim H, Yoon NS, Kim MN. Clinical relevance of time-to-positivity in BACTEC9240 blood culture system. Korean J Lab Med. 2010; 30:276–283. PMID: 20603588.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of the BACTEC Peds Plus Pediatric Blood Culture Bottle to the BacT/Alert PF Pediatric Blood Culture Bottle for Culturing Blood from Pediatric Patients
- Comparison of BACTEC Plus Aerobic/F Media and BacT/Alert FA Media to Detect Bacteria in Blood Culture Bottles Containing Peak Therapeutic Levels of Antimicrobials
- Effect of Preincubation of Blood Culture Bottles in a BacT/Alert Unit Outside Laboratory Operating Hours on Detection Time
- Comparison of Methods for Detecting Bacterial Contamination in Platelet Concentrates
- Accuracy of BacT/Alert Virtuo for Measuring Blood Volume for Blood Culture