Lab Anim Res.
2018 Mar;34(1):20-29. 10.5625/lar.2018.34.1.20.
Higher incidence of sperm granuloma in the epididymis of C57BL/6N mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Advanced Toxicology Research, Korea Institute of Toxicology (KIT), Daejeon, Korea. ybkim@kitox.re.kr
- 2Department of Inhalation Research, Korea Institute of Toxicology (KIT), Jeongeup, Korea.
- 3Department of Veterinary Pathology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea. hyson@cnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2430882
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2018.34.1.20
Abstract
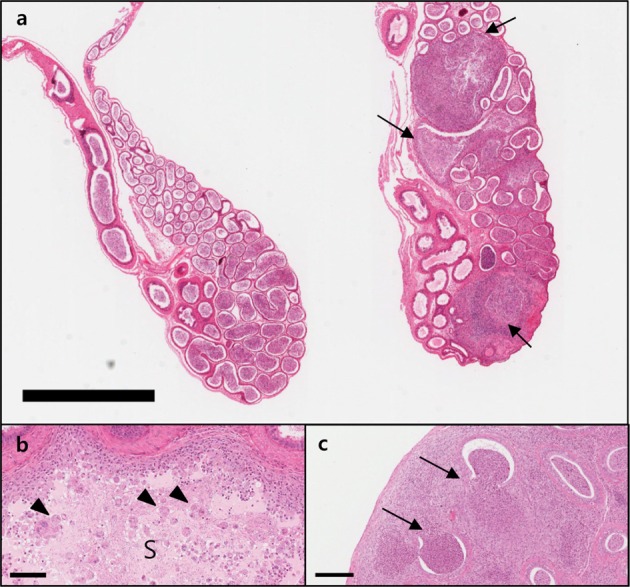
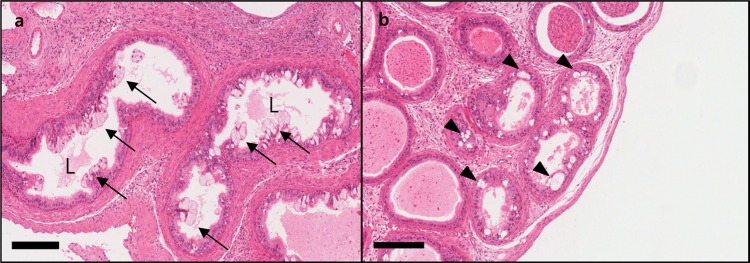
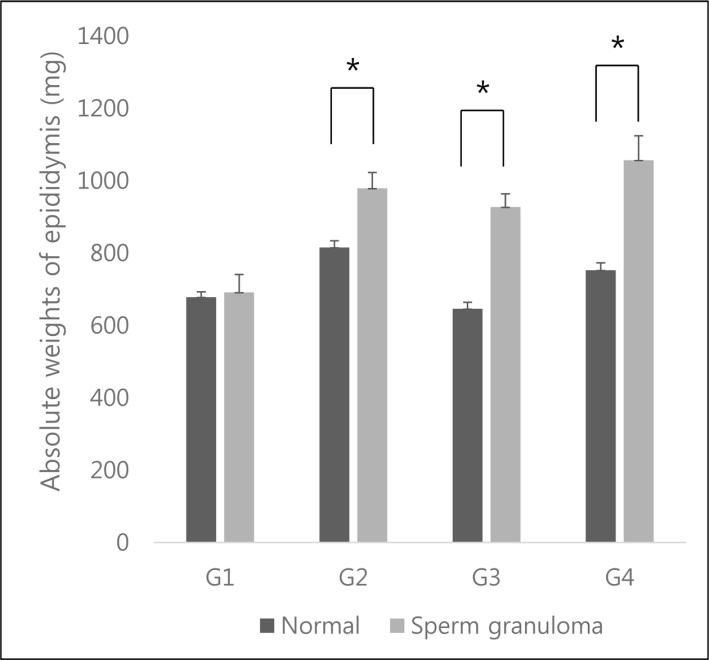
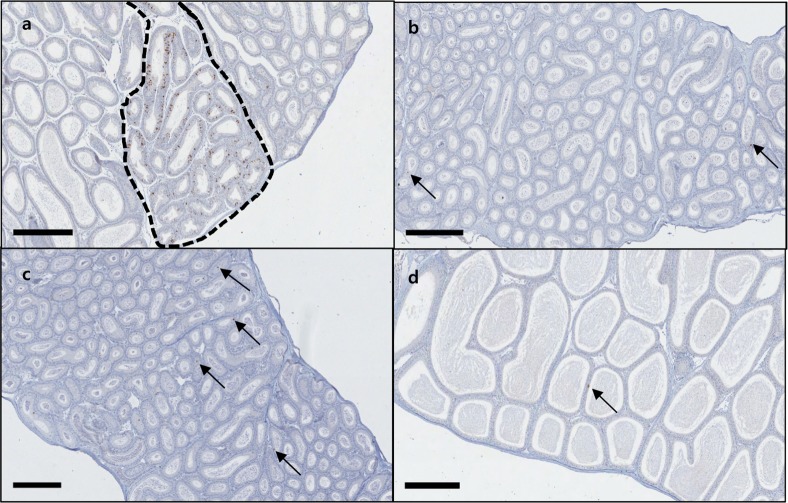
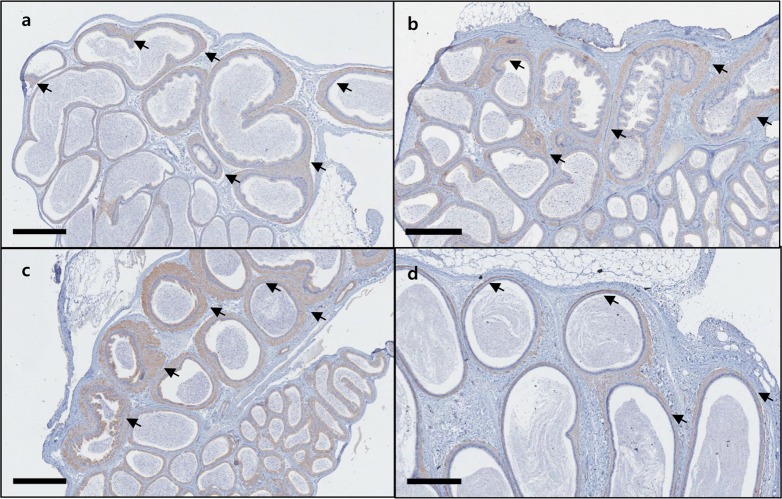
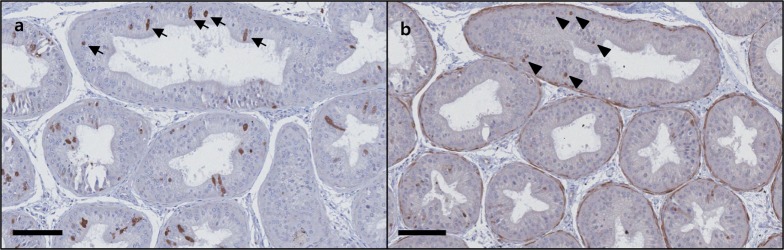
- C57BL/6N mice are inbred strains widely used in biomedical research. Hence, a large amount of basic data has been accumulated. However, in the field of histopathology, spontaneous data for relatively younger mice that are used more frequently are not yet abundant, in contrast to data for older mice and their neoplastic lesions. To acquire the essential background data required by various research and toxicological assessments, 120 mice of the C57BL/6N strain (10 and 13 weeks of age) were collected from two institutions (From Korea and Japan) and subjected to histopathological analyses of the major organs (liver, spleen, kidney, thymus, heart, testis, epididymis). The results showed significantly higher incidence of sperm granulomas in the epididymides (10-56%) of these mice, compared with that in other strains or species of lab animals. Upon closer inspection, oligospermia/clear cell hyperplasia, cellular debris, and tubular vacuolation were also observed in the epididymides with sperm granulomas. Moreover, diseased organs were significantly heavier than healthy ones. Immunohistochemical staining showed a significant increase in the chromatic figures of cysteine-dependent aspartate-directed proteases-3 (caspase-3) and cleaved-poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (c-PARP), and damages to the tubule due to spontaneous apoptosis, which may have led to the sperms leaking out of the tubule, causing the granuloma. To conclude, spontaneous sperm granuloma can occur in 10- and 13-week-old C57BL/6N mice and may thus affect the results of various studies using these mice. Therefore, sperm granuloma in epididymis needs to be carefully considered as an important factor when design the study using C57BL/6N.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Treuting PM, Dintzis SM. Comparative Atlas Anatomy and Histology: A Mouse and Human Atlas. Cambridge: Academic Press;2012. p. 5.2. Flurkey K, Currer JM, Leiter EH, Witham B. The Jackson Laboratory Handbook on Genetically Standardized Mice. 6th ed. Maine: The Jackson laboratory, Bar Harbor;1997. p. 138.3. Maronpot RR, Boorman GA, Gaul BW. Pathology of the Mouse Reference and Atlas. Saint Louis: Cache River Press;1999. p. 1–2.4. McInnes EF. Background Lesions in Laboratory Animals A Color Atlas. Philadelphia: Sounders Elsevier;2012. p. 7.5. Szymanska H, Lechowska-Piskorowska J, Krysiak E, Strzalkowska A, Unrug-Bielawska K, Grygalewicz B, Skurzak HM, Pienkowska-Grela B, Gajewska M. Neoplastic and nonneoplastic lesions in aging mice of unique and common inbred strains contribution to modeling of human neoplastic diseases. Vet Pathol. 2014; 51(3):663–679. PMID: 24019352.
Article6. Haines DC, Chattopadhyay S, Ward JM. Pathology of aging B6;129 mice. Toxicol Pathol. 2001; 29(6):653–661. PMID: 11794381.
Article7. Paranjpe MG, Shah SA, Denton MD, Elbekai RH. Incidence of spontaneous non-neoplastic lesions in transgenic CBYB6F1-Tg(HRAS)2Jic mice. Toxicol Pathol. 2013; 41(8):1137–1145. PMID: 23427275.
Article8. Blankenship B, Skaggs H. Findings in historical control harlan RCCHantm: WIST rats from 4-, 13-, 26-week studies. Toxicol Pathol. 2013; 41(3):537–547. PMID: 23033222.9. Dixon D, Heider K, Elwell MR. Incidence of nonneoplastic lesions in historical control male and female Fischer-344 rats from 90-day toxicity studies. Toxicol Pathol. 1995; 23(3):338–348. PMID: 7659956.
Article10. Lanning LL, Creasy DM, Chapin RE, Mann PC, Barlow NJ, Regan KS, Goodman DG. Recommended approaches for the evaluation of testicular and epididymal toxicity. Toxicol Pathol. 2002; 30(4):507–520. PMID: 12187942.
Article11. De Grava Kempinas W, Klinefelter GR. Interpreting histopathology in the epididymis. Spermatogenesis. 2015; 4(2):e979114. PMID: 26413396.
Article12. Haschek WM, Rousseaux CG, Wallig MA. Haschek and Rousseaux's Handbook of Toxicologic Pathology. Cambridge: Academic Press;2013. p. 2557–2558.13. Flickinger CJ, Howard SS. Consequences of Obstruction on the Epididymis. In : Robaire B, Hinton BT, editors. The Epididymis: from Molecules to Clinical Practice. New York: Kluwer Academic Plenum Publishers;2002. p. 503–522.14. Pritam S, Sahota JAP, Hardisty JF, Gopinath C. Toxicologic Pathology: Nonclinical Safety Assessment. Abingdon: Taylor & Francis Group;2013. p. 750.15. Wang H, Bloom O, Zhang M, Vishnubhakat JM, Ombrellino M, Che J, Frazier A, Yang H, Ivanova S, Borovikova L, Manogue KR, Faist E, Abraham E, Andersson J, Andersson U, Molina PE, Abumrad NN, Sama A, Tracey KJ. HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice. Science. 1999; 285(5425):248–251. PMID: 10398600.
Article16. Elmore S. Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 2007; 35(4):495–516. PMID: 17562483.
Article17. Tanida I, Ueno T, Kominami E. LC3 and Autophagy. Methods Mol Biol. 2008; 445:77–88. PMID: 18425443.
Article18. Pias EK, Ekshyyan OY, Rhoads CA, Fuseler J, Harrison L, Aw TY. Differential effects of superoxide dismutase isoform expression on hydroperoxide-induced apoptosis in PC-12 cells. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278(15):13294–13301. PMID: 12551919.
Article19. Boulares AH, Yakovlev AG, Ivanova V, Stoica BA, Wang G, Iyer S, Smulson M. Role of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage in apoptosis. Caspase 3-resistant PARP mutant increases rates of apoptosis in transfected cells. J Biol Chem. 1999; 274(33):22932–22940. PMID: 10438458.20. Fuchs Y, Steller H. Programmed cell death in animal development and disease. Cell. 2011; 147(4):742–758. PMID: 22078876.
Article21. Friedlander RM. Apoptosis and caspases in neurodegenerative diseases. N Engl J Med. 2003; 348:1365–1375. PMID: 12672865.
Article22. Thompson CB. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science. 1995; 267(5203):1456–1462. PMID: 7878464.
Article23. Byun HS, Song JK, Kim YR, Piao L, Won M, Park KA, Choi BL, Lee H, Hong JH, Park J, Seok JH, Lee YJ, Kang SW, Hur GM. Caspase-8 has an essential role in resveratrol-induced apoptosis of rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008; 47(3):301–308. PMID: 18276737.
Article24. Dharmapatni AA, Smith MD, Findlay DM, Holding CA, Evdokiou A, Ahern MJ, Weedon H, Chen P, Screaton G, Xu XN, Haynes DR. Elevated expression of caspase-3 inhibitors, survivin and xIAP correlates with low levels of apoptosis in active rheumatoid synovium. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009; 11(1):R13. PMID: 19171073.
Article25. Lee IC, Kim KH, Kim SH, Baek HS, Moon C, Kim SH, Yun WK, Nam KH, Kim HC, Kim JC. Apoptotic cell death in rat epididymis following epichlorohydrin treatment. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2013; 32(6):640–646. PMID: 23386780.
Article26. Marx JO, Brice AK, Boston RC, Smith AL. Incidence Rates of Spontaneous Disease in Laboratory Mice Used at a Large Biomedical Research Institution. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2013; 52(6):782–791. PMID: 24351767.27. Fox JG, Davisson MT, Quimby FW, Barthold SW, Newcomer QE, Smith AL. Spontaneous Diseases in Commonly used Mouse Strains, the Mouse in Biomedical Research. Cambridge: Academic press;2012. p. 623–717.28. Smith RS, Roderick TH, Sundberg JP. Microphthalmia and associated abnormalities in inbred black mice. Lab Anim Sci. 1994; 44(6):551–560. PMID: 7898027.29. Van Winkle TJ, Balk MW. Spontaneous corneal opacities in laboratory mice. Lab Anim Sci. 1986; 36(3):248–255. PMID: 3724049.30. Li HS, Hultcrantz M. Age-related degeneration of the organ of Corti in two genotypes of mice. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 1994; 56(2):61–67. PMID: 8177586.
Article31. McFadden SL, Ding D, Salvi R. Anatomical, metabolic and genetic aspects of age-related hearing loss in mice. Audiology. 2001; 40(6):313–321. PMID: 11781044.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Compensatory role of C3 convertase on the strain difference for C3 protein expression in FVB/N, C3H/HeN and C57BL/6N mice
- Effect of the Vasectomy and Seminal Vesiculectomy on the Fine Structure of the Sperm-Acrosome
- Comparative study of fertilization rates of C57BL/6NKorl and C57BL/6N mice obtained from two other sources
- Epididymis and Sperm Maturation
- Use of C57BL/6N mice on the variety of immunological researches