Korean J Urol.
2013 Mar;54(3):183-188.
Effects and Mechanism of Action of a Tribulus terrestris Extract on Penile Erection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea. hyunjs@gnu.ac.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Tribulus terrestris has been used as an aphrodisiac. However, little is known about the effects and mechanism of action of T. terrestris on penile erection. Therefore, the effect of a T. terrestris extract and the mechanism of action of the extract on relaxation of the corpus cavernosum (CC) were investigated. The erectogenic effects of an oral preparation of the extract were also assessed.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The relaxation effects and mechanism of action of the T. terrestris extract on rabbit CC were investigated in an organ bath. The intracavernous pressure (ICP) was calculated after oral administration of the extract for 1 month to evaluate whether the relaxation response of the CC shown in the organ bath occurred in vivo. Additionally, cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) were measured in the CC by immunoassay. Smooth muscle relaxation was expressed as the percentage decrease in precontraction induced by phenylephrine. The ICP was also assessed in rats after oral administration of the extract for 1 month, and changes in concentrations of cGMP and cAMP were monitored.
RESULTS
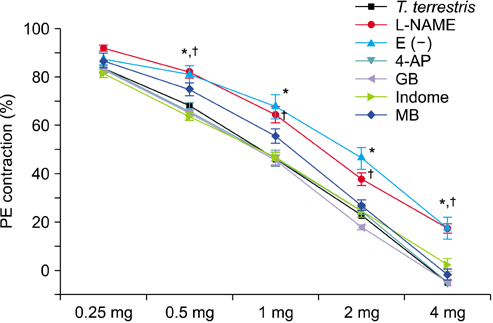
Concentration-dependent relaxation effects of the extract on the CC were detected in the organ bath study. Relaxation of the CC by the T. terrestris extract was inhibited in both an endothelium-removed group and an L-arginen methyl ester pretreatment group. The ICP measured after oral administration of the T. terrestris extract for 1 month was higher than that measured in the control group, and a significant increase in cAMP was observed in the T. terrestris extract group.
CONCLUSIONS
The T. terrestris extract induced concentration-dependent relaxation of the CC in an organ bath. The mechanism included a reaction involving the nitric oxide/nitric oxide synthase pathway and endothelium of the CC. Moreover, in an in vivo study, the T. terrestris extract showed a significant concentration-dependent increase in ICP. Accordingly, the T. terrestris extract may improve erectile function.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gholamine B, Shafiei M, Motevallian M, Mahmoudian M. Effects of pioglitazone on erectile dysfunction in sildenafil poor-responders: a randomized, controlled study. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2008. 11:22–31.2. Gauthaman K, Ganesan AP. The hormonal effects of Tribulus terrestris and its role in the management of male erectile dysfunction: an evaluation using primates, rabbit and rat. Phytomedicine. 2008. 15:44–54.3. Gauthaman K, Adaikan PG, Prasad RN. Aphrodisiac properties of Tribulus terrestris extract (Protodioscin) in normal and castrated rats. Life Sci. 2002. 71:1385–1396.4. Martino-Andrade AJ, Morais RN, Spercoski KM, Rossi SC, Vechi MF, Golin M, et al. Effects of Tribulus terrestris on endocrine sensitive organs in male and female Wistar rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010. 127:165–170.5. Bagcivan I, Gokce G, Yildirim S, Sarioglu Y. Investigation of the mechanism of nicotine induced relaxation in rabbit corpus cavernosum in vitro. Urol Res. 2004. 32:209–212.6. Utkan NZ, Utkan T, Sarioglu Y, Canturk NZ, Okay E. Investigation of the mechanism of nicotine-induced relaxation in guinea pig gallbladder. J Surg Res. 2003. 110:272–275.7. Skiker M, Mekhfi H, Aziz M, Haloui B, Lahlou S, Legssyer A, et al. Artemisia herba-alba Asso relaxes the rat aorta through activation of NO/cGMP pathway and K(ATP) channels. J Smooth Muscle Res. 2010. 46:165–174.8. Diederichs W, Stief CG, Lue TF, Tanagho EA. Norepinephrine involvement in penile detumescence. J Urol. 1990. 143:1264–1266.9. Gauthaman K, Ganesan AP, Prasad RN. Sexual effects of puncturevine (Tribulus terrestris) extract (protodioscin): an evaluation using a rat model. J Altern Complement Med. 2003. 9:257–265.10. Arsyad KM. Effect of protodioscin on the quantity and quality of sperms from males with moderate idiopathic oligozoospermia. Medika. 1996. 22:614–618.11. El-Tantawy WH, Temraz A, El-Gindi OD. Free serum testosterone level in male rats treated with Tribulus alatus extracts. Int Braz J Urol. 2007. 33:554–558.12. Burnett AL. Nitric oxide in the penis: physiology and pathology. J Urol. 1997. 157:320–324.13. Hedlund P, Aszodi A, Pfeifer A, Alm P, Hofmann F, Ahmad M, et al. Erectile dysfunction in cyclic GMP-dependent kinase I-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. 97:2349–2354.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anti-coccidial activity of the ethanol extract of Tribulus terrestris fruits on Eimeria tenella
- Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammation in human gastric epithelial AGS cells by the fruits of Tribulus terrestris L. extracts
- The Comparison of Nocturnal Erection Using Rigiscan with Erotic Erection Using Audiovisual Stimulating Penogram
- Age-related Erectile Response to Short Erotic Stimulation in Normal Adults
- Comparison of Audiovisually Stimulated and Nocturnal Penile Erection