Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2018 Sep;11(3):181-185. 10.21053/ceo.2017.01473.
Microbiological Results From Middle Ear Effusion in Pediatric Patients Receiving Ventilation Tube Insertion: Multicenter Registry Study on the Effectiveness of Ventilation Tube Insertion in Pediatric Patients With Chronic Otitis Media With Effusion: Part I
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Kyungpook National University Hospital, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Ansan, Korea.
- 4Department of Otolaryngology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 5Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Hanyang University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jwchung@amc.seoul.kr
- 7Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Graduate School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 8Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Incheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Incheon, Korea.
- 9Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Uijeongbu, Korea.
- 10Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Daejeon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Daejeon, Korea.
- 11Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 12Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 13Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 14Department of OtorhinolaryngologyHead and Neck Surgery, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 15Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Bucheon St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea.
- 16Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2429007
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2017.01473
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The aim of this multicenter registry study was to investigate the effectiveness of ventilation tube insertion and the microbiology of otitis media with effusion (OME) in children. This part I study was conducted to evaluate the microbiological profile of children with OME who needed ventilation tube insertion.
METHODS
Patients < 15 years old who were diagnosed as having OME and received ventilation tube insertion were prospectively enrolled in 16 tertiary hospitals from June 2014 to December 2016. After excluding patients with missing data, the data of 397 patients were analyzed among a total of 433 enrolled patients. The clinical symptoms, findings of the tympanic membrane, hearing level, and microbiological findings were collected.
RESULTS
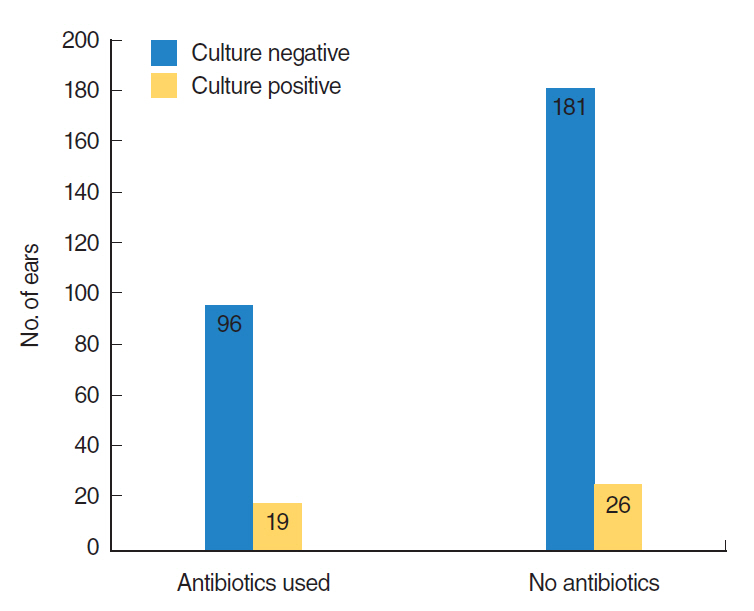
In 103 patients (25.9%), antibiotics were used within 3 weeks before surgery. Ventilation tube insertion was performed in a total of 710 ears (626 in both ears in 313 patients, 55 in the left ear only, and 29 in the right ear only). Culture of middle ear effusion was done in at least one ear in 221 patients (55.7%), and in a total of 346 ears. Only 46 ears (13.3%) showed positive results in middle ear effusion culture. Haemophilus influenzae (17.3%, followed by coagulase-negative Staphylococcus and Staphylococcus auricularis) was the most common bacteria detected.
CONCLUSION
H. influenzae was the most commonly found bacteria in middle ear effusion. Relatively low rates of culture positivity were noted in middle ear effusion of patients with OME in Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Factors Affecting the Extrusion Rate and Complications After Ventilation Tube Insertion: A Multicenter Registry Study on the Effectiveness of Ventilation Tube Insertion in Pediatric Patients With Chronic Otitis Media With Effusion—Part II
Myung Hoon Yoo, Yang-Sun Cho, June Choi, Yun Hoon Choung, Jae-Ho Chung, Jong Woo Chung, Gyu Cheol Han, Beom Cho Jun, Dong-Kee Kim, Kyu Sung Kim, Jun Ho Lee, Kyu-Yup Lee, Seung Hwan Lee, In Seok Moon, Hong Ju Park, Shi Nae Park, Jihye Rhee, Jae Hyun Seo, Seung Geun Yeo
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2022;15(4):326-334. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2022.00934.
Reference
-
1. Lous J, Burton MJ, Felding JU, Ovesen T, Rovers MM, Williamson I. Grommets (ventilation tubes) for hearing loss associated with otitis media with effusion in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005; Jan. (1):CD001801.
Article2. Hong HR, Kim TS, Chung JW. Long-term follow-up of otitis media with effusion in children: comparisons between a ventilation tube group and a non-ventilation tube group. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2014; Jun. 78(6):938–43.
Article3. Stenstrom R, Pless IB, Bernard P. Hearing thresholds and tympanic membrane sequelae in children managed medically or surgically for otitis media with effusion. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2005; Dec. 159(12):1151–6.
Article4. Venekamp RP, Burton MJ, van Dongen TM, van der Heijden GJ, van Zon A, Schilder AG. Antibiotics for otitis media with effusion in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016; Jun. (6):CD009163.
Article5. Rosenfeld RM, Shin JJ, Schwartz SR, Coggins R, Gagnon L, Hackell JM, et al. Clinical practice guideline: otitis media with effusion (update). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016; Feb. 154(1 Suppl):S1–41.
Article6. Maw R, Wilks J, Harvey I, Peters TJ, Golding J. Early surgery compared with watchful waiting for glue ear and effect on language development in preschool children: a randomised trial. Lancet. 1999; Mar. 353(9157):960–3.
Article7. Paradise JL, Feldman HM, Campbell TF, Dollaghan CA, Colborn DK, Bernard BS, et al. Effect of early or delayed insertion of tympanostomy tubes for persistent otitis media on developmental outcomes at the age of three years. N Engl J Med. 2001; Apr. 344(16):1179–87.
Article8. Chan CL, Wabnitz D, Bardy JJ, Bassiouni A, Wormald PJ, Vreugde S, et al. The microbiome of otitis media with effusion. Laryngoscope. 2016; Dec. 126(12):2844–51.
Article9. Kim H, Choo OS, Jang JH, Park HY, Choung YH. Chronological changes in microbial profiles in external and middle ear diseases: a 20-year study in Korea. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017; Mar. 274(3):1375–81.
Article10. Lee JS, Kim MG, Hong SM, Na SY, Byun JY, Park MS, et al. Changing patterns of bacterial strains in adults and children with otitis media in Korean tertiary care centers. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2014; Jun. 7(2):79–86.
Article11. Almac A, Elicora SS, Yumuk Z, Dundar V, Willke A. The relationship between chronic otitis media with effusion and surface and deep flora of hypertrophic adenoids. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2009; Oct. 73(10):1438–40.
Article12. Eser OK, Ipci K, Alp S, Akyol U, Unal OF, Hascelik G, et al. Efficacy of nasopharyngeal culture in identification of pathogen in middle ear fluid in chronic otitis media with effusion. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2009; Jul-Sep. 27(3):237–41.
Article13. Park CW, Han JH, Jeong JH, Cho SH, Kang MJ, Tae K, et al. Detection rates of bacteria in chronic otitis media with effusion in children. J Korean Med Sci. 2004; Oct. 19(5):735–8.
Article14. Poetker DM, Lindstrom DR, Edmiston CE, Krepel CJ, Link TR, Kerschner JE. Microbiology of middle ear effusions from 292 patients undergoing tympanostomy tube placement for middle ear disease. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2005; Jun. 69(6):799–804.
Article15. Jung H, Lee SK, Cha SH, Byun JY, Park MS, Yeo SG. Current bacteriology of chronic otitis media with effusion: high rate of nosocomial infection and decreased antibiotic sensitivity. J Infect. 2009; Nov. 59(5):308–16.
Article16. Ngo CC, Massa HM, Thornton RB, Cripps AW. Predominant bacteria detected from the middle ear fluid of children experiencing otitis media: a systematic review. PLoS One. 2016; Mar. 11(3):e0150949.
Article17. Brook I, Yocum P, Shah K, Feldman B, Epstein S. Microbiology of serous otitis media in children: correlation with age and length of effusion. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2001; Jan. 110(1):87–90.
Article18. Shishegar M, Faramarzi A, Kazemi T, Bayat A, Motamedifar M. Polymerase chain reaction, bacteriologic detection and antibiogram of bacteria isolated from otitis media with effusion in children, Shiraz, Iran. Iran J Med Sci. 2011; Dec. 36(4):273–80.19. Jero J, Virolainen A, Salo P, Leinonen M, Eskola J, Karma P. PCR assay for detecting Streptococcus pneumoniae in the middle ear of children with otitis media with effusion. Acta Otolaryngol. 1996; Mar. 116(2):288–92.
Article20. Matar GM, Sidani N, Fayad M, Hadi U. Two-step PCR-based assay for identification of bacterial etiology of otitis media with effusion in infected Lebanese children. J Clin Microbiol. 1998; May. 36(5):1185–8.
Article21. Run Sigurdardottir N, Nielsen AB, Munck A, Bjerrum L. Appropriateness of antibiotic prescribing for upper respiratory tract infections in general practice: comparison between Denmark and Iceland. Scand J Prim Health Care. 2015; Dec. 33(4):269–74.22. Uijen JH, Bindels PJ, Schellevis FG, van der Wouden JC. ENT problems in Dutch children: trends in incidence rates, antibiotic prescribing and referrals 2002-2008. Scand J Prim Health Care. 2011; Jun. 29(2):75–9.
Article23. Buzatto GP, Tamashiro E, Proenca-Modena JL, Saturno TH, Prates MC, Gagliardi TB, et al. The pathogens profile in children with otitis media with effusion and adenoid hypertrophy. PLoS One. 2017; Feb. 12(2):e0171049.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Study of Laser Myringotomy with Ventilation Tube Insertion on Pediatric Chronic Otitis Media with Effusion
- Efficiency of Tympanostomy Tube Insertion in Children with Chronic Otitis Media with Effusion
- Changes in External Ear Resonance after Ventilation Tube Insertion in Pediatric Patients with Middle Ear Effusion
- Treatment Outcome of Laser Tympanostomy with Ventilation Tube Insertion under Topical Anesthesia
- Clinical Approaches for Understanding the Expression Levels of Pattern Recognition Receptors in Otitis Media with Effusion