Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2019 Jan;11(1):68-78. 10.4168/aair.2019.11.1.68.
Comparison of Long-term Efficacy of Subcutaneous Immunotherapy in Pediatric and Adult Patients With Allergic Rhinitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Beijing TongRen Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China. louhongfei@yahoo.com, dr.luozhang@139.com
- 2Beijing Key Laboratory of Nasal Diseases, Beijing Institute of Otolaryngology, Beijing, China.
- 3Department of Allergy, Beijing TongRen Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China.
- KMID: 2426786
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2019.11.1.68
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Data comparing the long-term efficacy and safety of subcutaneous immunotherapy (SCIT) using house dust mite (HDM) in children and adults with allergic rhinitis (AR) are limited. This study aimed to compare the long-term effects of HDM-SCIT in a cohort of Chinese pediatric and adult patients with AR.
METHODS
A total of 124 pediatric and adult AR patients received HDM-SCIT for 3 years, with 118 patients being followed-up for 2 years. Prior to treatment (baseline), at the end of the 3-year treatment periods (third year) and 2 years after the discontinuation of treatment (fifth year), all patients were evaluated for total nasal symptom scores (TNSS), daily medication score (DMS), total combined score (TCS; symptoms [nasal + ocular] + DMS) and quality of life (QoL). Safety was assessed according to adverse events reported.
RESULTS
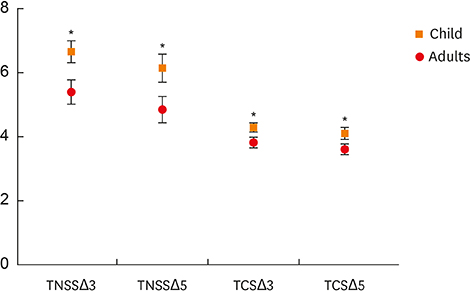
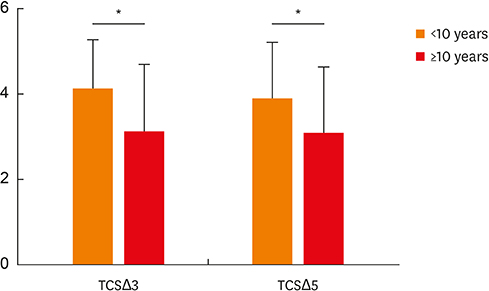
After 3-year treatment, HDM-SCIT significantly improved symptoms and QoL scores at the end of the third and fifth years in both groups. Better improvements were observed in the third and fifth years based on baseline, in children compared to adults (TNSSΔ3: 6.66 vs. 5.41, P = 0.011; TCSΔ3: 4.30 vs. 3.83, P = 0.027 and TNSSΔ5: 6.16 vs. 4.86, P = 0.037; TCSΔ5: 4.11 vs. 3.62, P = 0.044).Shorter duration of AR history before SCIT (<10 vs. ≥10 years) resulted in better improvements at the end of the third and fifth years (TCSΔ3: 4.12 vs. 3.13, P = 0.036; TCSΔ5: 3.90 vs. 3.09, P = 0.033). HDM-SCIT was safe and comparable in both children and adults with AR.
CONCLUSIONS
Children with AR may achieve better long-term efficacy of HDM-SCIT than adults with AR.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Safety of Ultra-rush Schedule of Subcutaneous Allergen Immunotherapy With House Dust Mite Extract Conducted in an Outpatient Clinic in Patients With Atopic Dermatitis and Allergic Rhinitis
So-Hee Lee, Myoung-Eun Kim, Yoo Seob Shin, Young-Min Ye, Hae-Sim Park, Dong-Ho Nahm
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2019;11(6):846-855. doi: 10.4168/aair.2019.11.6.846.
Reference
-
1. Brożek JL, Bousquet J, Agache I, Agarwal A, Bachert C, Bosnic-Anticevich S, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) guidelines-2016 revision. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017; 140:950–958.2. Werfel T, Breuer K, Ruéff F, Przybilla B, Worm M, Grewe M, et al. Usefulness of specific immunotherapy in patients with atopic dermatitis and allergic sensitization to house dust mites: a multi-centre, randomized, dose-response study. Allergy. 2006; 61:202–205.
Article3. Asher MI, Montefort S, Björkstén B, Lai CK, Strachan DP, Weiland SK, et al. Worldwide time trends in the prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in childhood: ISAAC Phases One and Three repeat multicountry cross-sectional surveys. Lancet. 2006; 368:733–743.
Article4. Blaiss MS. Allergic rhinitis: direct and indirect costs. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2010; 31:375–380.
Article5. Roberts G, Pfaar O, Akdis CA, Ansotegui IJ, Durham SR, Gerth van Wijk R, et al. EAACI guidelines on allergen immunotherapy: allergic rhinoconjunctivitis. Allergy. 2018; 73:765–798.6. Durham SR, Penagos M. Sublingual or subcutaneous immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016; 137:339–349.e10.
Article7. Noon L. Prophylactic inoculations against hay fever. Lancet. 1911; 177:1572–1573.8. Cingi C, Bayar Muluk N, Ulusoy S, Acar M, Şirin S, Çobanoğlu B, et al. Efficacy of sublingual immunotherapy for house dust mite allergic rhinitis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2015; 272:3341–3346.
Article9. Lin Z, Liu Q, Li T, Chen D, Chen D, Xu R. The effects of house dust mite sublingual immunotherapy in patients with allergic rhinitis according to duration. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016; 6:82–87.
Article10. Okubo K, Masuyama K, Imai T, Okamiya K, Stage BS, Seitzberg D, et al. Efficacy and safety of the SQ house dust mite sublingual immunotherapy tablet in Japanese adults and adolescents with house dust mite-induced allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017; 139:1840–1848.e10.
Article11. Karakoc-Aydiner E, Eifan AO, Baris S, Gunay E, Akturk E, Akkoc T, et al. Long-term effect of sublingual and subcutaneous immunotherapy in dust mite-allergic children with asthma/rhinitis: a 3-year prospective randomized controlled trial. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2015; 25:334–342.12. Peng H, Li CW, Lin ZB, Li TY. Long-term efficacy of specific immunotherapy on house dust mite-induced allergic rhinitis in China. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013; 149:40–46.
Article13. Sahin E, Dizdar D, Dinc ME, Cirik AA. Long-term effects of allergen-specific subcutaneous immunotherapy for house dust mite induced allergic rhinitis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017; 131:997–1001.
Article14. Tahamiler R, Saritzali G, Canakcioglu S. Long-term efficacy of sublingual immunotherapy in patients with perennial rhinitis. Laryngoscope. 2007; 117:965–969.
Article15. Han DH, Choi YS, Lee JE, Kim DY, Kim JW, Lee CH, et al. Clinical efficacy of sublingual immunotherapy in pediatric patients with allergic rhinitis sensitized to house dust mites: comparison to adult patients. Acta Otolaryngol. 2012; 132:Suppl 1. S88–S93.
Article16. Qi S, Chen H, Huang N, Li W, Liu G, Wang Y, et al. Early intervention improves clinical responses to house dust mite immunotherapy in allergic rhinitis patients. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2016; 171:234–240.
Article17. Soh JY, Thalayasingam M, Ong S, Loo EX, Shek LP, Chao SS. Sublingual immunotherapy in patients with house dust mite allergic rhinitis: prospective study of clinical outcomes over a two-year period. J Laryngol Otol. 2016; 130:272–277.
Article18. Lou H, Ma S, Zhao Y, Cao F, He F, Liu Z, et al. Sensitization patterns and minimum screening panels for aeroallergens in self-reported allergic rhinitis in China. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:9286.
Article19. Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, Denburg J, Fokkens WJ, Togias A, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) 2008 update (in collaboration with the World Health Organization, GA(2)LEN and AllerGen). Allergy. 2008; 63:Suppl 86. 8–160.20. Baris S, Kiykim A, Ozen A, Tulunay A, Karakoc-Aydiner E, Barlan IB. Vitamin D as an adjunct to subcutaneous allergen immunotherapy in asthmatic children sensitized to house dust mite. Allergy. 2014; 69:246–253.
Article21. Juniper EF, Guyatt GH. Development and testing of a new measure of health status for clinical trials in rhinoconjunctivitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 1991; 21:77–83.
Article22. Li J, Sun B, Huang Y, Lin X, Zhao D, Tan G, et al. A multicentre study assessing the prevalence of sensitizations in patients with asthma and/or rhinitis in China. Allergy. 2009; 64:1083–1092.
Article23. Zimmer A, Bouley J, Le Mignon M, Pliquet E, Horiot S, Turfkruyer M, et al. A regulatory dendritic cell signature correlates with the clinical efficacy of allergen-specific sublingual immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 129:1020–1030.
Article24. Cox L, Larenas-Linnemann D, Lockey RF, Passalacqua G. Speaking the same language: The World Allergy Organization Subcutaneous Immunotherapy Systemic Reaction Grading System. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:569–574. 574.e1–574.e7.
Article25. Canonica GW, Bachert C, Hellings P, Ryan D, Valovirta E, Wickman M, et al. Allergen immunotherapy (AIT): a prototype of precision medicine. World Allergy Organ J. 2015; 8:31.
Article26. Eng PA, Borer-Reinhold M, Heijnen IA, Gnehm HP. Twelve-year follow-up after discontinuation of preseasonal grass pollen immunotherapy in childhood. Allergy. 2006; 61:198–201.
Article27. Jacobsen L, Niggemann B, Dreborg S, Ferdousi HA, Halken S, Høst A, et al. Specific immunotherapy has long-term preventive effect of seasonal and perennial asthma: 10-year follow-up on the PAT study. Allergy. 2007; 62:943–948.
Article28. Lee JH, Kim SC, Choi H, Jung CG, Ban GY, Shin YS, et al. A retrospective study of clinical response predictors in subcutaneous allergen immunotherapy with house dust mites for allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018; 10:18–24.
Article29. Tahamiler R, Saritzali G, Canakcioglu S, Ozcora E, Dirican A. Comparison of the long-term efficacy of subcutaneous and sublingual immunotherapies in perennial rhinitis. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2008; 70:144–150.
Article30. Okamoto Y, Fujieda S, Okano M, Yoshida Y, Kakudo S, Masuyama K. House dust mite sublingual tablet is effective and safe in patients with allergic rhinitis. Allergy. 2017; 72:435–443.
Article31. Petalas K, Durham SR. Allergen immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis. Rhinology. 2013; 51:99–110.
Article32. Sohn MH. Efficacy and safety of subcutaneous allergen immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018; 10:1–3.
Article33. Calderon MA, Alves B, Jacobson M, Hurwitz B, Sheikh A, Durham S. Allergen injection immunotherapy for seasonal allergic rhinitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007; 24:CD001936.
Article34. Kouser L, Kappen J, Walton RP, Shamji MH. Update on biomarkers to monitor clinical efficacy response during and post treatment in allergen immunotherapy. Curr Treat Options Allergy. 2017; 4:43–53.
Article35. Shamji MH, Kappen JH, Akdis M, Jensen-Jarolim E, Knol EF, Kleine-Tebbe J, et al. Biomarkers for monitoring clinical efficacy of allergen immunotherapy for allergic rhinoconjunctivitis and allergic asthma: an EAACI Position Paper. Allergy. 2017; 72:1156–1173.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Update of Sublingual Immunotherapy for Allergic Rhinitis
- Present and future of allergen immunotherapy for allergic diseases
- Sublingual immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis
- Effects of Serum Vitamin D and Efficacy of Subcutaneous Immunotherapy in Adult Patients With Allergic Rhinitis
- Long-Term Follow-Up of Immunotherapy in Allergic Rhinitis to House Dust Mite