J Korean Acad Nurs.
2016 Aug;46(4):534-541. 10.4040/jkan.2016.46.4.534.
Effect of Observation Window at Peripheral Intravenous Catheter Site on Early Recognition of Infiltration among Hospitalized Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Nursing, Pusan National University, Yangsan, Korea. jeongis@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Department of Nursing, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2424550
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.4.534
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to identify the effect of an observation window (OW) at peripheral intravenous (IV) catheter sites on early detection of IV infiltration among hospitalized children.
METHODS
This was a retrospective observational study with history control group design. Participants were children who had IV infiltration after peripheral catheterization when hospitalized from January to May, 2014 and January to May, 2015 at a children's hospital located in Yangsan city, Korea. The 193 patients, who were hospitalized from January to May, 2014 formed the control group and did not have OW, and the 167 patients, who were hospitalized from January to May, 2015 formed the window group and had OW. Data were analyzed using χ²-test, independent samples t-test and multiple logistic regression.
RESULTS
First stage IV infiltration was 39.5% for the window group and 25.9% for the control group, which was significantly different (p=.007). The likelihood of 2nd stage and above IV infiltration decreased by 44% in the window group, which was significantly different (p=.014).
CONCLUSION
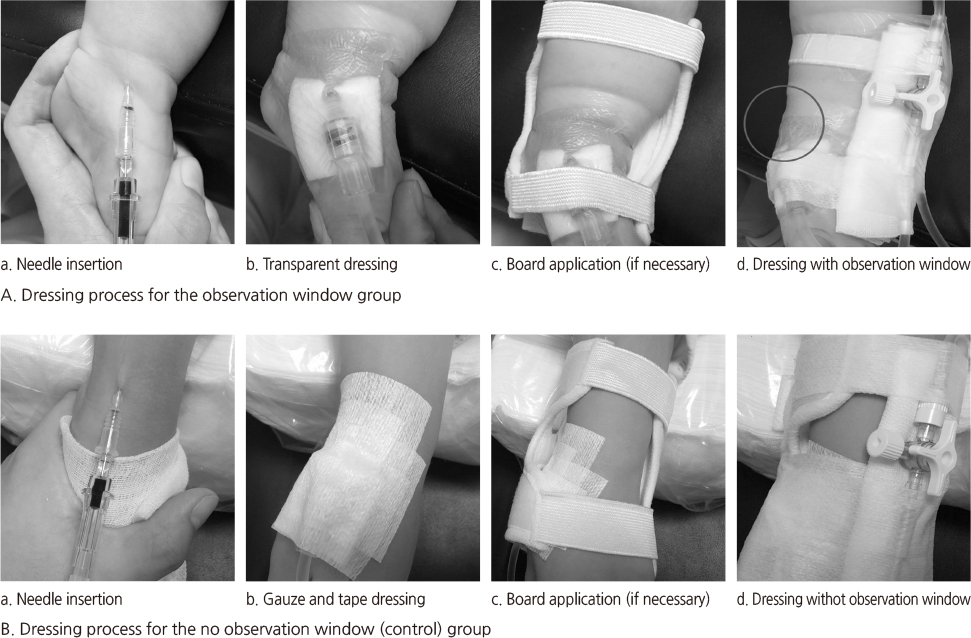
OW at the peripheral IV catheter site was found to be an effective measure in early recognition of IV infiltration. Considering the effect of OW, we recommend that nurses should make an OW with transparent dressing during stabilization of the IV catheter site in hospitalized children in clinical settings.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Bandages
Case-Control Studies
Catheterization, Peripheral/instrumentation/*methods
Child
Child, Hospitalized
Child, Preschool
Clinical Competence
Extravasation of Diagnostic and Therapeutic Materials/*prevention & control
Female
Humans
Infant
Infusions, Intravenous/adverse effects
Logistic Models
Male
Odds Ratio
Retrospective Studies
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hadaway L. Short peripheral intravenous catheters and infections. J Infus Nurs. 2012; 35(4):230–240. DOI: 10.1097/NAN.0b013e31825af099.2. Rickard CM, Webster J, Wallis MC, Marsh N, McGrail MR, French V, et al. Routine versus clinically indicated replacement of peripheral intravenous catheters: A randomised controlled equivalence trial. Lancet. 2012; 380(9847):1066–1074. DOI: 10.1016/s0140-6736(12)61082-4.3. Thomas J. Standard practice and evolving trends in pediatric intravenous access. Air Med J. 2007; 26(1):8–11. DOI: 10.1016/j.amj.2006.10.006.4. Webster J, Osborne S, Rickard CM, New K. Clinically-indicated replacement versus routine replacement of peripheral venous catheters. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015; (8):CD007798. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007798.pub4.5. Pettit J. Assessment of the infant with a peripheral intravenous device. Adv Neonatal Care. 2003; 3(5):230–240.6. Thigpen JL. Peripheral intravenous extravasation: Nursing procedure for initial treatment. Neonatal Netw. 2007; 26(6):379–384. DOI: 10.1891/0730-0832.26.6.379.7. Doellman D, Hadaway L, Bowe-Geddes LA, Franklin M, LeDonne J, Papke-O'Donnell L, et al. Infiltration and extravasation: Update on prevention and management. J Infus Nurs. 2009; 32(4):203–211. DOI: 10.1097/NAN.0b013e3181aac042.8. Hadaway L. Infiltration and extravasation. Am J Nurs. 2007; 107(8):64–72. DOI: 10.1097/01.NAJ.0000282299.03441.c7.9. Hetzler R, Wilson M, Hill EK, Hollenback C. Securing pediatric peripheral IV. catheters-application of an evidence-based practice model. J Pediatr Nurs. 2011; 26(2):143–148. DOI: 10.1016/j.pedn.2010.12.008.10. de Lima Jacinto AK, Avelar AF, Pedreira ML. Predisposing factors for infiltration in children submitted to peripheral venous catheterization. J Infus Nurs. 2011; 34(6):391–398. DOI: 10.1097/NAN.0b013e3182306491.11. Kim JS, Lee YR, Kim NS. Effects of the structured nursing intervention for caregivers on maintenance of intravenous infusions in infants. J Korean Acad Child Health Nurs. 2012; 18(3):135–142. DOI: 10.4094/jkachn.2012.18.3.135.12. Jung JH. A study of peripheral intravenous cannulation & intravenou injection pain in hospitalized children[master's thesis]. Daejeon: Eulji University;2009. 1–84.13. McCullen KL, Pieper B. A retrospective chart review of risk factors for extravasation among neonates receiving peripheral intravascular fluids. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 2006; 33(2):133–139.14. Fang L, Fang SH, Chung YH. Factors affecting the unplanned peripheral reinsertion in pediatric patients from a teaching hospital in Taiwan. J Infus Nurs. 2011; 34(6):366–372. DOI: 10.1097/NAN.0b013e31823061c1.15. Talbot SG, Rogers GF. Pediatric compartment syndrome caused by intravenous infiltration. Ann Plast Surg. 2011; 67(5):531–533. DOI: 10.1097/SAP.0b013e3182085915.16. Lamagne P, McPhee M. Troubleshooting pediatric peripheral IVs: Phlebitis and infiltration. Nurs Spectr. 2004; 8(13):18–20.17. Amjad I, Murphy T, Nylander-Housholder L, Ranft A. A new approach to management of intravenous infiltration in pediatric patients: Pathophysiology, classification, and treatment. J Infus Nurs. 2011; 34(4):242–249. DOI: 10.1097/NAN.0b013e31821da1b3.18. Woody G, Davis BA. Increasing nurse competence in peripheral intravenous therapy. J Infus Nurs. 2013; 36(6):413–419. DOI: 10.1097/nan.0000000000000013.19. Clifton-Koeppel R. Wound care after peripheral intravenous extravasation: What is the evidence? Newborn Infant Nurs Rev. 2006; 6(4):202–211. DOI: 10.1053/j.nainr.2006.10.001.20. Roth D. Pediatric infiltration and extravasation. J Assoc Vasc Access. 2006; 11(1):14. DOI: 10.2309/java.11-1-5.21. Park SM, Jeong IS, Kim KL, Park KJ, Jung MJ, Jun SS. The effect of intravenous infiltration management program for hospitalized children. J Pediatr Nurs. 2016; 31(2):172–178. DOI: 10.1016/j.pedn.2015.10.013.22. Flemmer L, Chan JS. A pediatric protocol for management of extravasation injuries. Pediatr Nurs. 1993; 19(4):355–358. 42423. Park SM. Identification of risk factors and development of a risk prediction model for infiltration among hospitalized children[dissertation]. Busan: Pusan National University;2014. 1–62.24. Infusion Nurses Society. Infusion nursing standards of practice. J Infus Nurs. 2006; 29:1 Suppl. S1–S92.25. Sauerland C, Engelking C, Wickham R, Corbi D. Vesicant extravasation part I: Mechanisms, pathogenesis, and nursing care to reduce risk. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2006; 33(6):1134–1141. DOI: 10.1188/06.onf.1134-1141.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of a Video Education Program for Caregivers on the Maintenance of Peripheral Intravenous Catheter among Hospitalized Children
- Investigation for Phlebitis Development by Peripheral Venous Catheter in Burn Patients
- Peripheral Intravenous Injection Pain in Hospitalized Children
- Effects of Distraction using Balloon Art on Pain during Intravenous Injections in Preschool Children
- Comparison of Intravenous Administration and Surgical Site Infiltration of Ketorolac Combined with Preincisional Infiltration of Bupivacaine