J Dent Anesth Pain Med.
2018 Oct;18(5):305-308. 10.17245/jdapm.2018.18.5.305.
Medical adhesive related skin injury after dental surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, Pusan National University, Yangsan, Korea.
- 2Department of Dental Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, Pusan National University Dental Hospital, Dental Research Institute, Yangsan, Korea. kejdream84@naver.com
- 3Department of Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2424372
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2018.18.5.305
Abstract
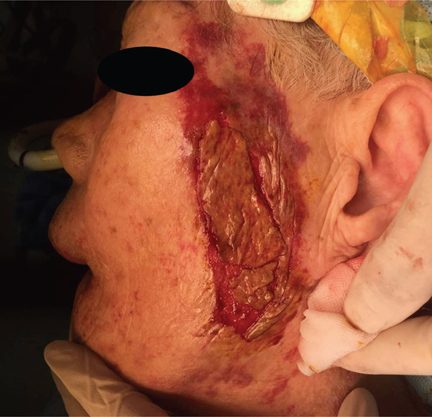
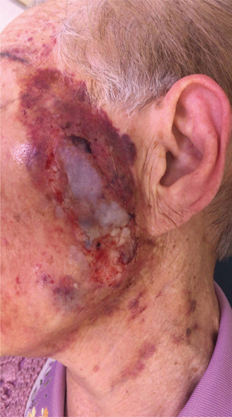
- An 87-year-old woman was referred for the extraction of residual teeth and removal of tori prior to prosthetic treatment. After surgery under general anesthesia, the surgical tape was removed to detach the bispectral index sensor and the hair cover. After the surgical tape was removed, skin injury occurred on the left side of her face. After epidermis repositioning and ointment application, a dressing was placed over the injury. Her wound was found to have healed completely on follow-up examination. Medical adhesive related skin injury (MARSI) is a complication that can occur after surgery and subjects at the extremes of age with fragile skin are at a higher risk for such injuries. Careful assessment of the risk factors associated with MARSI is an absolute necessity.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. McNichol L, Lund C, Rosen T, Gray M. Medical adhesives and patient safety: state of the science: consensus statements for the assessment, prevention, and treatment of adhesive-related skin injuries. Orthop Nurs. 2013; 32:267–281.2. Lober CW, Fenske NA. Cutaneous aging: effect of intrinsic changes on surgical considerations. South Med J. 1991; 84:1444–1446.3. Cutting KF. Impact of adhesive surgical tape and wound dressings on the skin, with reference to skin stripping. J Wound Care. 2008; 17:157–162.
Article4. Groom M, Shannon RJ, Chakravarthy D, Fleck CA. An evaluation of costs and effects of a nutrient-based skin care program as a component of prevention of skin tears in an extended convalescent center. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 2010; 37:46–51.
Article5. LeBlanc K, Baranoski S. Skin Tear Consensus Panel Members. Skin tears: state of the science: consensus statements for the prevention, prediction, assessment, and treatment of skin tears(c). Adv Skin Wound Care. 2011; 24:2–15.6. Conway J, Whettam J. Adverse reactions to wound dressings. Nurs Stand. 2002; 16:52–54. 5658passim.
Article7. Norris P, Storrs FJ. Allergic contact dermatitis to adhesive bandages. Dermatol Clin. 1990; 8:147–152.
Article8. Bryant RA. Types of skin damage and differential diagnosis. In : Bryant R, Nix D, editors. Acute & Chronic wounds: Current Management Concepts. 4th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier Mosby;2012. p. 83–107.9. Zeng LA, Lie SA, Chong SY. Comparison of Medical Adhesive Tapes in Patients at Risk of Facial Skin Trauma under Anesthesia. Anesthesiol Res Pract. 2016; 2016:4878246.
Article10. Grove GL, Zerweck CR, Houser TP, Smith GE, Koski NI. A randomized and controlled comparison of gentleness of 2 medical adhesive tapes in healthy human subjects. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 2013; 40:51–59.
Article11. LaVelle BE. Reducing the risk of skin trauma related to medical adhesives. Manag Infect Control. 2004; 182:1289–1294.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Management of the Accidental STSG Donor Site Injury: Case Reports
- Management of a High-Pressure Hot-Melt Adhesive Injection Injury
- Shear bond strength of metal brackets bonded with light-cured adhesive: an in vitro comparative study
- Intraoperative Neuromonitoring with Adhesive Skin Electrodes for a Patient with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma with Lateral Neck Metastasis: a Case Report
- Surgical skin adhesive bond is safe and feasible wound closure method to reduce surgical site infection following minimally invasive colorectal cancer surgery