J Clin Neurol.
2018 Oct;14(4):464-471. 10.3988/jcn.2018.14.4.464.
Abnormal Oculomotor Functions in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. kkkim@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Neurology, Dankook University College of Medicine, Dankook University Hospital, Cheonan, Korea.
- KMID: 2424173
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2018.14.4.464
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
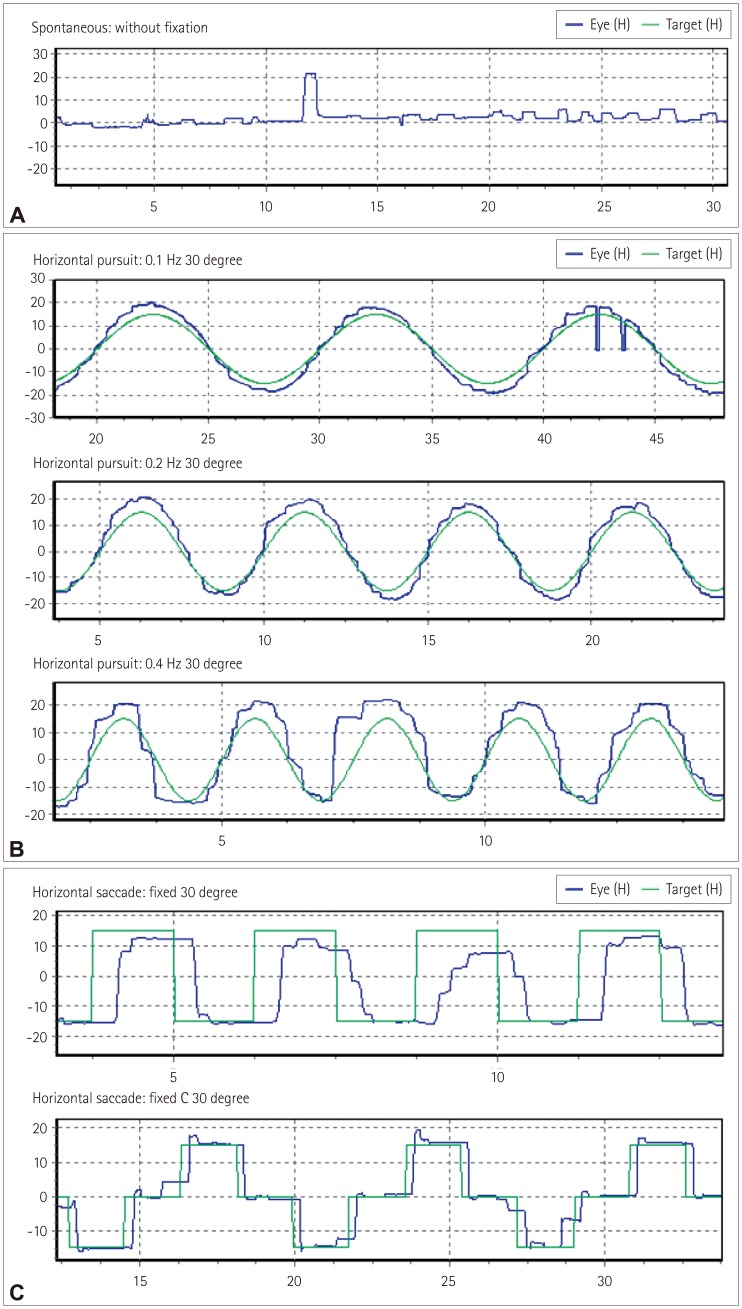
Although traditionally regarded as spared, a range of oculomotor dysfunction has been recognized in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) patients. ALS is nowadays considered as a neurodegenerative disorder of a third compartment comprising widespread areas of extra-motor brain including cerebellum. Our objective was to perform an observational study to examine for ocular motor dysfunction in patients with ALS and for any differences between bulbar-onset and spinal-onset patients.
METHODS
Thirty two ALS patients (bulbar onset: 10, spinal onset: 22) underwent the standardized systemic evaluations using video-oculography.
RESULTS
Oculomotor dysfunctions such as square wave jerks, saccadic dysmetria, abnormal cogwheeling smooth pursuits and head shaking and positional nystagmus of central origin have been observed in the ALS patients at a relatively early stage. Abnormal smooth pursuits and saccadic dysmetria were increased in the bulbar-onset compared to the spinal-onset (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
These oculomotor abnormalities may be a marker of neuro-degeneration beyond motor neurons in ALS, especially in bulbar-onset disease. Future longitudinal studies of eye movement abnormalities have provided insights into the distribution and nature of the disease process.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brooks BR. El Escorial World Federation of Neurology criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. subcommittee on motor neuron diseases/amyotrophic lateral sclerosis of the world federation of neurology research group on neuromuscular diseases and the El Escorial “clinical limits of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis” workshop contributors. J Neurol Sci. 1994; 124(Suppl):96–107. PMID: 7807156.2. Averbuch-Heller L, Helmchen C, Horn AK, Leigh RJ, Buttner-Ennerver JA. Slow vertical saccades in motor neuron disease: correlation of structure and function. Ann Neurol. 1998; 44:641–648. PMID: 9778263.
Article3. Prell T, Grosskreutz J. The involvement of the cerebellum in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener. 2013; 14:507–515. PMID: 23889583.
Article4. Talbot PR, Goulding PJ, Lloyd JJ, Snowden JS, Neary D, Testa HJ. Inter-relation between “classic” motor neuron disease and frontotemporal dementia: neuropsychological and single photon emission computed tomography study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1995; 58:541–547. PMID: 7745399.
Article5. McCluskey LF, Elman LB, Martinez-Lage M, Van Deerlin V, Yuan W, Clay D, et al. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-plus syndrome with TAR DNA-binding protein-43 pathology. Arch Neurol. 2009; 66:121–124. PMID: 19139310.
Article6. Donaghy C, Thurtell MJ, Pioro EP, Gibson JM, Leigh RJ. Eye movements in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and its mimics: a review with illustrative cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2011; 82:110–116. PMID: 21097546.
Article7. Donaghy C, Pinnock R, Abrahams S, Cardwell C, Hardiman O, Patterson V, et al. Ocular fixation instabilities in motor neurone disease. a marker of frontal lobe dysfunction? J Neurol. 2009; 256:420–426. PMID: 19306041.8. Palmowski A, Jost WH, Prudlo J, Osterhage J, Kasmann B, Schimrigk K, et al. Eye movement in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a longitudinal study. Ger J Ophthalmol. 1995; 4:355–362. PMID: 8751101.9. Moon SY, Lee BH, Seo SW, Kang SJ, Na DL. Slow vertical saccades in the frontotemporal dementia with motor neuron disease. J Neurol. 2008; 255:1337–1343. PMID: 18825435.
Article10. Donaghy C, Pinnock R, Abrahams S, Cardwell C, Hardiman O, Patterson V, et al. Slow saccades in bulbar-onset motor neurone disease. J Neurol. 2010; 257:1134–1140. PMID: 20146069.
Article11. Leveille A, Kiernan J, Goodwin JA, Antel J. Eye movements in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Arch Neurol. 1982; 39:684–686. PMID: 7125995.
Article12. Ohki M, Kanayama R, Nakamura T, Okuyama T, Kimura Y, Koike Y. Ocular abnormalities in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1994; 511:138–142. PMID: 8203216.
Article13. Abel LA, Williams IM, Gibson KL, Levi L. Effects of stimulus velocity and acceleration on smooth pursuit in motor neuron disease. J Neurol. 1995; 242:419–424. PMID: 7595671.
Article14. Jacobs L, Bozian D, Heffner RR Jr, Barron SA. An eye movement disorder in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology. 1981; 31:1282–1287. PMID: 7202138.
Article15. Moss HE, McCluskey L, Elman L, Hoskins K, Talman L, Grossman M, et al. Cross-sectional evaluation of clinical neuro-ophthalmic abnormalities in an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis population. J Neurol Sci. 2012; 314:97–101. PMID: 22192877.
Article16. Mizutani T, Aki M, Shiozawa R, Unakami M, Nozawa T, Yajima K, et al. Development of ophthalmoplegia in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis during long-term use of respirators. J Neurol Sci. 1990; 99:311–319. PMID: 2086731.
Article17. Kushner MJ, Parrish M, Burke A, Behrens M, Hays AP, Frame B, et al. Nystagmus in motor neuron disease: clinicopathological study of two cases. Ann Neurol. 1984; 16:71–77. PMID: 6465863.
Article18. Carvalho MD, Swash M. Awaji diagnostic algorithm increases sensitivity of El Escorial criteria for ALS diagnosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler. 2009; 10:53–57. PMID: 18985466.
Article19. Choi KD, Oh SY, Park SH, Kim JH, Koo JW, Kim JS. Head-shaking nystagmus in lateral medullary infarction: patterns and possible mechanisms. Neurology. 2007; 68:1337–1344. PMID: 17452577.
Article20. Huh YE, Kim JS. Patterns of spontaneous and head-shaking nystagmus in cerebellar infarction: imaging correlations. Brain. 2011; 134:3662–3671. PMID: 22036958.
Article21. Choi JY, Kim JH, Kim HJ, Glasauer S, Kim JS. Central paroxysmal positional nystagmus: characteristics and possible mechanisms. Neurology. 2015; 84:2238–2246. PMID: 25957336.
Article22. Lee TK. [Central positional vertigo]. Res Vestib Sci. 2011; 10:19–23.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Associated With CADASIL
- Syndrome of Progressive Bulbar Palsy in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Case Report
- Apraxia of Eyelid Closure and Motor Impersistence of Eyelid in a Patient with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- Psychosocial Responses and Quality of Life among Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients and Their Caregivers
- Diagnosis and management of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis