Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
2018 Sep;23(3):154-157. 10.6065/apem.2018.23.3.154.
Successful switching from insulin to sulfonylurea in a 3-month-old infant with diabetes due to p.G53D mutation in KCNJ11
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. seaon98@ajoumc.or.kr
- 2Department of Medical Genetics, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2422480
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2018.23.3.154
Abstract
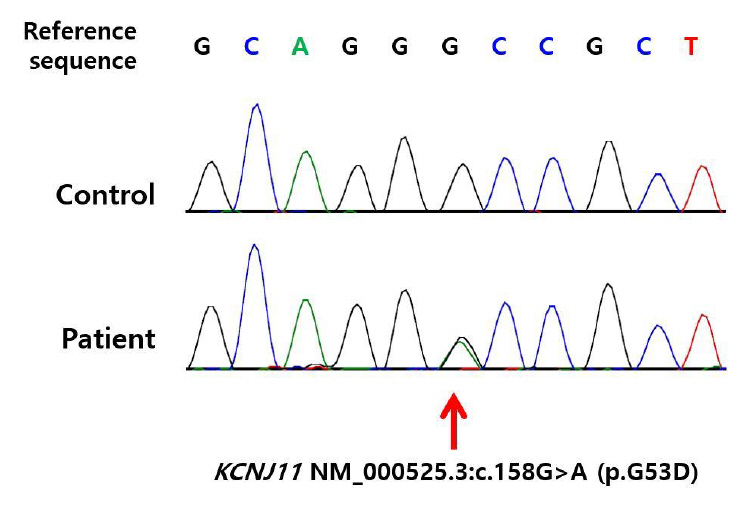
- Permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus is most commonly caused by mutations in the ATP-sensitive potassium channel (KATP) subunits. Prompt initiation of sulfonylurea treatment can improve glycemic control in children with KCNJ11 mutation. In this report, we present a case of permanent neonatal diabetes caused by a mutation in the KCNJ11 gene that was successfully treated via early switching of insulin to sulfonylurea treatment. A 53-day-old female infant presented with diabetic ketoacidosis. Insulin was administered for the ketoacidosis and blood glucose regulation. At 3 months of age, using genomic DNA extracted from peripheral lymphocytes, direct sequencing of KCNJ11 identified a heterozygous mutation of c.158G>A (p.G53D) and confirmed the diagnosis of permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus. Subsequently, treatment with sulfonylurea was initiated, and the insulin dose was gradually tapered. At 4 months of age, insulin therapy was discontinued, and sulfonylurea (glimepiride, 0.75 mg/kg) was administered alone. At 6 months after initiation of administration of sulfonylurea monotherapy, blood glucose control was stable, and no hypoglycemic events or developmental delays were reported. C-peptide levels increased during treatment with sulfonylurea. Early switching to sulfonylurea in infants with permanent diabetes mellitus owing to a KCNJ11 mutation could successfully help regulate glycemic control, which suggests the need for early genetic testing in patients presenting with diabetes before 6 months of age.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Naylor RN, Greeley SA, Bell GI, Philipson LH. Genetics and pathophysiology of neonatal diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Investig. 2011; 2:158–69.
Article2. Gloyn AL, Pearson ER, Antcliff JF, Proks P, Bruining GJ, Slingerland AS, et al. Activating mutations in the gene encoding the ATP-sensitive potassium-channel subunit Kir6.2 and permanent neonatal diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:1838–49.
Article3. Pearson ER, Flechtner I, Njølstad PR, Malecki MT, Flanagan SE, Larkin B, et al. Switching from insulin to oral sulfonylureas in patients with diabetes due to Kir6.2 mutations. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:467–77.
Article4. Ahn SY, Kim GH, Yoo HW. Successful sulfonylurea treatment in a patient with permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus with a novel KCNJ11 mutation. Korean J Pediatr. 2015; 58:309–12.
Article5. Cho JH, Kang E, Lee BH, Kim GH, Choi JH, Yoo HW. DEND syndrome with heterozygous KCNJ11 mutation successfully treated with sulfonylurea. J Korean Med Sci. 2017; 32:1042–5.
Article6. Kim MS, Kim SY, Kim GH, Yoo HW, Lee DW, Lee DY. Sulfonylurea therapy in two Korean patients with insulin-treated neonatal diabetes due to heterozygous mutations of the KCNJ11 gene encoding Kir6.2. J Korean Med Sci. 2007; 22:616–20.
Article7. Heo JW, Kim SW, Cho EH. Unsuccessful switch from insulin to sulfonylurea therapy in permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus due to an R201H mutation in the KCNJ11 gene: a case report. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2013; 100:e1–2.
Article8. Koster JC, Cadario F, Peruzzi C, Colombo C, Nichols CG, Barbetti F. The G53D mutation in Kir6.2 (KCNJ11) is associated with neonatal diabetes and motor dysfunction in adulthood that is improved with sulfonylurea therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008; 93:1054–61.
Article9. Arce KM, Pantalone KM. Not all diabetes in infants is type 1: a case report. Diabetes Ther. 2016; 7:369–75.
Article10. Ioacara S, Flanagan S, Fröhlich-Reiterer E, Goland R, Fica S. First case of neonatal diabetes with KCNJ11 Q52R mutation successfully switched from insulin to sulphonylurea treatment. J Diabetes Investig. 2017; 8:716–9.11. Marshall BA, Green RP, Wambach J, White NH, Remedi MS, Nichols CG. Remission of severe neonatal diabetes with very early sulfonylurea treatment. Diabetes Care. 2015; 38:e38–9.
Article12. Remedi MS, Agapova SE, Vyas AK, Hruz PW, Nichols CG. Acute sulfonylurea therapy at disease onset can cause permanent remission of KATP-induced diabetes. Diabetes. 2011; 60:2515–22.
Article13. Slingerland AS, Hurkx W, Noordam K, Flanagan SE, Jukema JW, Meiners LC, et al. Sulphonylurea therapy improves cognition in a patient with the V59M KCNJ11 mutation. Diabet Med. 2008; 25:277–81.14. Shah RP, Spruyt K, Kragie BC, Greeley SA, Msall ME. Visuomotor performance in KCNJ11-related neonatal diabetes is impaired in children with DEND-associated mutations and may be improved by early treatment with sulfonylureas. Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:2086–8.15. Sola D, Rossi L, Schianca GP, Maffioli P, Bigliocca M, Mella R, et al. Sulfonylureas and their use in clinical practice. Arch Med Sci. 2015; 11:840–8.16. Pantalone KM, Kattan MW, Yu C, Wells BJ, Arrigain S, Jain A, et al. Increase in overall mortality risk in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving glipizide, glyburide or glimepiride monotherapy versus metformin: a retrospective analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012; 14:803–9.
Article17. Codner E, Flanagan S, Ellard S, García H, Hattersley AT. High-dose glibenclamide can replace insulin therapy despite transitory diarrhea in early-onset diabetes caused by a novel R201L Kir6.2 mutation. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28:758–9.
Article18. Kumaraguru J, Flanagan SE, Greeley SA, Nuboer R, Støy J, Philipson LH, et al. Tooth discoloration in patients with neonatal diabetes after transfer onto glibenclamide: a previously unreported side effect. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:1428–30.19. Flanagan SE, Edghill EL, Gloyn AL, Ellard S, Hattersley AT. Mutations in KCNJ11, which encodes Kir6.2, are a common cause of diabetes diagnosed in the first 6 months of life, with the phenotype determined by genotype. Diabetologia. 2006; 49:1190–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Successful sulfonylurea treatment in a patient with permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus with a novel KCNJ11 mutation
- Neonatal Diabetes Mellitus Due to KCNJ11 (KIR6.2) Mutation Successfully Treated with Sulfonylurea
- Sulfonylurea Therapy in Two Korean Patients with Insulin-treated Neonatal Diabetes due to Heterozygous Mutations of the KCNJ11 Gene Encoding Kir6.2
- DEND Syndrome with Heterozygous KCNJ11 Mutation Successfully Treated with Sulfonylurea
- A Case of Transient Neonatal Diabetes Mellitus Attributable to a Nonspecific Mutation in the ABCC8 Gene