Neonatal Med.
2021 May;28(2):94-98. 10.5385/nm.2021.28.2.94.
Neonatal Diabetes Mellitus Due to KCNJ11 (KIR6.2) Mutation Successfully Treated with Sulfonylurea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2516492
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5385/nm.2021.28.2.94
Abstract
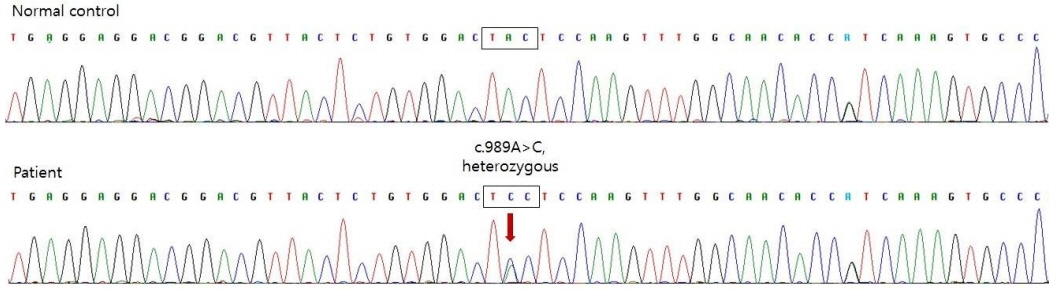
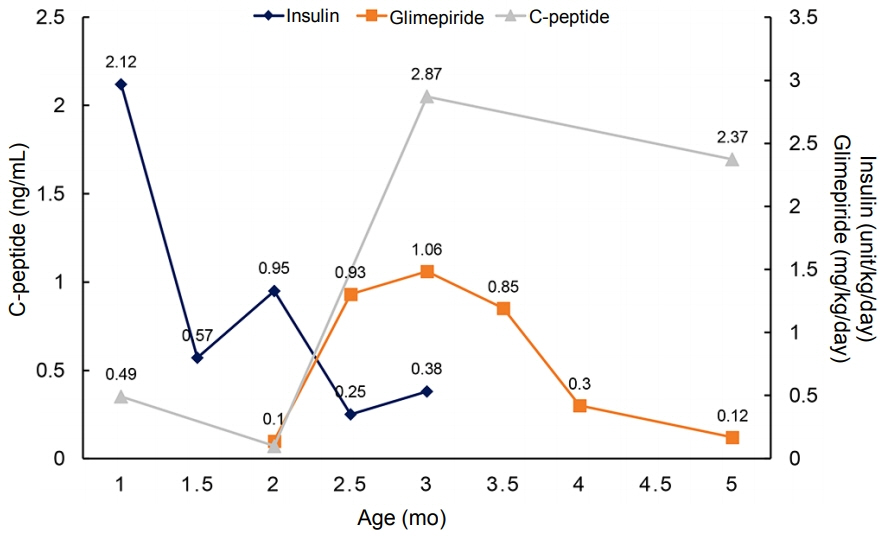
- Neonatal diabetes mellitus (NDM) is a rare disease that occurs at less than 6 months of age and is presumably caused by a mutation in the gene that affects pancreatic beta-cell function. Approximately 80% of NDM cases reveal a known genetic mutation, and mutations in potassium inwardly rectifying channel subfamily J member 11 (KCNJ11) and ABCC8 affecting the pancreatic beta-cell adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channel may be treated with oral sulfonylurea. Early recognition of mutations in KCNJ11 and ABCC8 is important because early administration of sulfonylurea can not only control blood glucose levels but also improve neurodevelopmental outcomes. In the present study, we report a case of NDM that initially presented as diabetic ketoacidosis at the age of 1 month, accompanied by seizures during hospitalization. After confirmation of the KCNJ11 gene mutation (c.989A>C), we started administering oral sulfonylurea (glimepiride) at the age of 2 months. After gradually increasing the dosage of glimepiride, insulin was discontinued at the age of 3 months. To date, the infant’s blood glucose levels have been well controlled without significant hypoglycemic events. No further episodes of seizures have occurred, and his developmental status is favorable.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Letourneau LR, Carmody D, Wroblewski K, Denson AM, Sanyoura M, Naylor RN, et al. Diabetes presentation in infancy: high risk of diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes Care. 2017; 40:e147–8.2. Nansseu JR, Ngo-Um SS, Balti EV. Incidence, prevalence and genetic determinants of neonatal diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis protocol. Syst Rev. 2016; 5:188.3. De Franco E, Flanagan SE, Houghton JA, Lango Allen H, Mackay DJ, Temple IK, et al. The effect of early, comprehensive genomic testing on clinical care in neonatal diabetes: an international cohort study. Lancet. 2015; 386:957–63.4. Shah RP, Spruyt K, Kragie BC, Greeley SA, Msall ME. Visuomotor performance in KCNJ11-related neonatal diabetes is impaired in children with DEND-associated mutations and may be improved by early treatment with sulfonylureas. Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:2086–8.5. Bowman P, Sulen A, Barbetti F, Beltrand J, Svalastoga P, Codner E, et al. Effectiveness and safety of long-term treatment with sulfonylureas in patients with neonatal diabetes due to KCNJ11 mutations: an international cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018; 6:637–46.6. Brereton MF, Rohm M, Shimomura K, Holland C, Tornovsky- Babeay S, Dadon D, et al. Hyperglycaemia induces metabolic dysfunction and glycogen accumulation in pancreatic β-cells. Nat Commun. 2016; 7:13496.7. Ashcroft FM, Puljung MC, Vedovato N. Neonatal diabetes and the KATP channel: from mutation to therapy. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2017; 28:377–87.8. Garcin L, Mericq V, Fauret-Amsellem AL, Cave H, Polak M, Beltrand J. Neonatal diabetes due to potassium channel mutation: response to sulfonylurea according to the genotype. Pediatr Diabetes. 2020; 21:932–41.9. Lanning MS, Carmody D, Szczerbinski L, Letourneau LR, Naylor RN, Greeley SAW. Hypoglycemia in sulfonylurea-treated KCNJ11-neonatal diabetes: mild-moderate symptomatic episodes occur infrequently but none involving unconsciousness or seizures. Pediatr Diabetes. 2018; 19:393–7.10. Kim MS, Kim SY, Kim GH, Yoo HW, Lee DW, Lee DY. Sulfonylurea therapy in two Korean patients with insulin-treated neonatal diabetes due to heterozygous mutations of the KCNJ11 gene encoding Kir6.2. J Korean Med Sci. 2007; 22:616–20.11. Heo JW, Kim SW, Cho EH. Unsuccessful switch from insulin to sulfonylurea therapy in permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus due to an R201H mutation in the KCNJ11 gene: a case report. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2013; 100:e1–2.12. Ahn SY, Kim GH, Yoo HW. Successful sulfonylurea treatment in a patient with permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus with a novel KCNJ11 mutation. Korean J Pediatr. 2015; 58:309–12.13. Cho JH, Kang E, Lee BH, Kim GH, Choi JH, Yoo HW. DEND syndrome with heterozygous KCNJ11 mutation successfully treated with sulfonylurea. J Korean Med Sci. 2017; 32:1042–5.14. Yoon JS, Park KJ, Sohn YB, Lee HS, Hwang JS. Successful switching from insulin to sulfonylurea in a 3-month-old infant with diabetes due to p.G53D mutation in KCNJ11. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2018; 23:154–7.15. Carmody D, Bell CD, Hwang JL, Dickens JT, Sima DI, Felipe DL, et al. Sulfonylurea treatment before genetic testing in neonatal diabetes: pros and cons. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014; 99:E2709–14.16. Yildiz M, Akcay T, Aydin B, Akgun A, Dogan BB, De Franco E, et al. Emergence of insulin resistance following empirical glibenclamide therapy: a case report of neonatal diabetes with a recessive INS gene mutation. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2018; 31:345–8.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Successful sulfonylurea treatment in a patient with permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus with a novel KCNJ11 mutation
- Successful switching from insulin to sulfonylurea in a 3-month-old infant with diabetes due to p.G53D mutation in KCNJ11
- Sulfonylurea Therapy in Two Korean Patients with Insulin-treated Neonatal Diabetes due to Heterozygous Mutations of the KCNJ11 Gene Encoding Kir6.2
- A Case of Transient Neonatal Diabetes Mellitus Attributable to a Nonspecific Mutation in the ABCC8 Gene
- DEND Syndrome with Heterozygous KCNJ11 Mutation Successfully Treated with Sulfonylurea