Tuberc Respir Dis.
2018 Oct;81(4):319-329. 10.4046/trd.2017.0122.
Effectiveness and Safety of High-Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Delivery during Bronchoalveolar Lavage in Acute Respiratory Failure Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Daegu Catholic University Medical Center, Daegu Catholic University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. solar903@chol.com
- KMID: 2420566
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2017.0122
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) is a necessary procedure for diagnosis of various lung diseases. High-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) oxygen delivery was recently introduced. This study aimed to investigate the safety and effectiveness of HFNC oxygen supply during BAL procedure in patients with acute respiratory failure (ARF).
METHODS
Patients who underwent BAL while using HFNC at a partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood/fraction of inspired oxygen (PaO2/FiO2; PF) ratio of 300 or below among patients who had been admitted from March 2013 to May 2017 were retrospectively investigated.
RESULTS
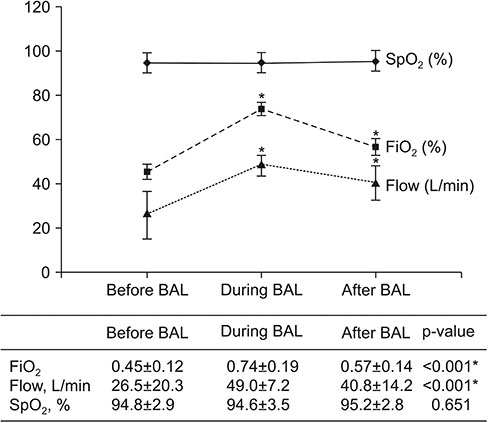
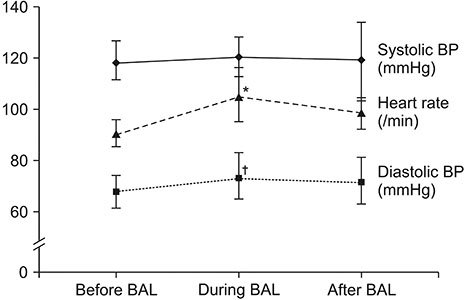
Thirty-three BAL procedures were confirmed. Their baseline PF ratio was 166.1±46.7. FiO2 values before, during, and after BAL were 0.45±0.12, 0.74±0.19, and 0.57±0.14, respectively. Flow (L/min) values before, during, and after BAL were 26.5±20.3, 49.0±7.2, and 40.8±14.2, respectively. Both FiO2 and flow during and after the procedure were significantly different from those before the procedure (both p < 0.001). Oxygen saturation levels before, during, and after BAL measured by pulse oximeter were 94.8±2.9, 94.6±3.5, and 95.2±2.8%, respectively. There were no significant differences in oxygen saturation among the three groups. Complications of BAL procedure included transient hypoxemia, hypotension, and fever. However, there was no endotracheal intubation within 24 hours. Baseline PF ratio in "without HFNC" group was significantly higher than that in "with HFNC" group. There were no differences in complications between the two groups.
CONCLUSION
The use of HFNC during BAL procedure in ARF patients was effective and safe. However, there were no significant differences in oxygen saturation level and complications comparing "without HFNC" group in mild ARF. More studies are needed for moderate to severe ARF patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
High-Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Delivery during Bronchoalveolar Lavage: A Question of Methodology Influence?
Subrata Kumar Singha, Antonio M Esquinas
Tuberc Respir Dis. 2019;82(1):86-87. doi: 10.4046/trd.2018.0058.
Reference
-
1. Artigas A, Castella X. Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) in adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). In : Vincent JL, editor. Update in intensive care and emergency medicine. Berline: Springer;1991. p. 192–197. Vol. 14, update 1991.2. Crystal RG, Reynolds HY, Kalica AR. Bronchoalveolar lavage: the report of an international conference. Chest. 1986; 90:122–131.3. Reynolds HY. Bronchoalveolar lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987; 135:250–263.4. Bronchoalveolar lavage constituents in healthy individuals, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, and selected comparison groups. The BAL Cooperative Group Steering Committee. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990; 141(5 Pt 2):S169–S202.5. Albertini RE, Harrell JH 2nd, Kurihara N, Moser KM. Arterial hypoxemia induced by fiberoptic bronchoscopy. JAMA. 1974; 230:1666–1667.
Article6. Antonelli M, Conti G, Riccioni L, Meduri GU. Noninvasive positive-pressure ventilation via face mask during bronchoscopy with BAL in high-risk hypoxemic patients. Chest. 1996; 110:724–728.
Article7. Song JU, Kim SA, Choi ER, SM Kim, Choi HJ, Lim SY, et al. Prediction of intubation after bronchoscopy with non-invasive positive pressure ventilation support in patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2009; 67:21–26.
Article8. Ricard JD. High flow nasal oxygen in acute respiratory failure. Minerva Anestesiol. 2012; 78:836–841.9. Sztrymf B, Messika J, Mayot T, Lenglet H, Dreyfuss D, Ricard JD. Impact of high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy on intensive care unit patients with acute respiratory failure: a prospective observational study. J Crit Care. 2012; 27:324.e9–324.e13.
Article10. Frat JP, Thille AW, Mercat A, Girault C, Ragot S, Perbet S, et al. High-flow oxygen through nasal cannula in acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. N Engl J Med. 2015; 372:2185–2196.
Article11. Lucangelo U, Vassallo FG, Marras E, Ferluga M, Beziza E, Comuzzi L, et al. High-flow nasal interface improves oxygenation in patients undergoing bronchoscopy. Crit Care Res Pract. 2012; 2012:506382.
Article12. Simon M, Braune S, Frings D, Wiontzek AK, Klose H, Kluge S. High-flow nasal cannula oxygen versus non-invasive ventilation in patients with acute hypoxaemic respiratory failure undergoing flexible bronchoscopy: a prospective randomised trial. Crit Care. 2014; 18:712.
Article13. La Combe B, Messika J, Labbe V, Razazi K, Maitre B, Sztrymf B, et al. High-flow nasal oxygen for bronchoalveolar lavage in acute respiratory failure patients. Eur Respir J. 2016; 47:1283–1286.
Article14. Ferguson ND, Fan E, Camporota L, Antonelli M, Anzueto A, Beale R, et al. The Berlin definition of ARDS: an expanded rationale, justification, and supplementary material. Intensive Care Med. 2012; 38:1573–1582.
Article15. Cairo JM. Administering medical gases: regulators, flowmeters, and controlling device. In : Cairo JM, Pilbeam SP, editors. Mosby's respiratory care equipment. 8th ed. St. Louis: Mosby;2010. p. 59–87.16. Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, et al. Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension. 2003; 42:1206–1252.
Article17. Sund-Levander M, Forsberg C, Wahren LK. Normal oral, rectal, tympanic and axillary body temperature in adult men and women: a systematic literature review. Scand J Caring Sci. 2002; 16:122–128.
Article18. Maitre B, Jaber S, Maggiore SM, Bergot E, Richard JC, Bakthiari H, et al. Continuous positive airway pressure during fiberoptic bronchoscopy in hypoxemic patients: a randomized double-blind study using a new device. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000; 162(3 Pt 1):1063–1067.19. Hilbert G, Gruson D, Vargas F, Valentino R, Favier JC, Portel L, et al. Bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage via the laryngeal mask airway in high-risk hypoxemic immunosuppressed patients. Crit Care Med. 2001; 29:249–255.
Article20. Baumann HJ, Klose H, Simon M, Ghadban T, Braune SA, Hennigs JK, et al. Fiber optic bronchoscopy in patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure requiring noninvasive ventilation: a feasibility study. Crit Care. 2011; 15:R179.21. Fishman JA. Approach to the patient with pulmonary infection. In : Grippi MA, Elias JA, Fishman JA, Kotloff RM, Pack AI, Senior RM, editors. Fishman's pulmonary diseases and disorders. 5th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Co, Inc.;2015. p. 1853–1879.22. Cordier JF. Cryptogenic organising pneumonia. Eur Respir J. 2006; 28:422–446.
Article23. Payne CB Jr, Goyal PC, Gupta SC. Effects of transoral and transnasal fiberoptic bronchoscopy on oxygenation and cardiac rhythm. Endoscopy. 1986; 18:1–3.
Article24. Katz AS, Michelson EL, Stawicki J, Holford FD. Cardiac arrhythmias: frequency during fiberoptic bronchoscopy and correlation with hypoxemia. Arch Intern Med. 1981; 141:603–606.
Article25. Goldstein RA, Rohatgi PK, Bergofsky EH, Block ER, Daniele RP, Dantzker DR, et al. Clinical role of bronchoalveolar lavage in adults with pulmonary disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990; 142:481–486.
Article26. Matsumoto T, Sato Y, Fukuda S, Katayama S, Miyazaki Y, Ozaki M, et al. Safety and efficacy of bronchoalveolar lavage using a laryngeal mask airway in cases of acute hypoxaemic respiratory failure with diffuse lung infiltrates. Intern Med. 2015; 54:731–735.
Article27. Lee JH, Rehder KJ, Williford L, Cheifetz IM, Turner DA. Use of high flow nasal cannula in critically ill infants, children, and adults: a critical review of the literature. Intensive Care Med. 2013; 39:247–257.
Article28. Parke R, McGuinness S, Eccleston M. Nasal high-flow therapy delivers low level positive airway pressure. Br J Anaesth. 2009; 103:886–890.
Article29. Gotera C, Diaz Lobato S, Pinto T, Winck JC. Clinical evidence on high flow oxygen therapy and active humidification in adults. Rev Port Pneumol. 2013; 19:217–227.
Article30. Miyagi K, Haranaga S, Higa F, Tateyama M, Fujita J. Implementation of bronchoalveolar lavage using a high-flow nasal cannula in five cases of acute respiratory failure. Respir Investig. 2014; 52:310–314.
Article31. Delclaux C, L'Her E, Alberti C, Mancebo J, Abroug F, Conti G, et al. Treatment of acute hypoxemic nonhypercapnic respiratory insufficiency with continuous positive airway pressure delivered by a face mask: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2000; 284:2352–2360.32. Demoule A, Girou E, Richard JC, Taille S, Brochard L. Increased use of noninvasive ventilation in French intensive care units. Intensive Care Med. 2006; 32:1747–1755.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- High-Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Delivery during Bronchoalveolar Lavage: A Question of Methodology Influence?
- High-flow nasal cannula for respiratory failure in adult patients
- Treatment of acute respiratory failure: high-flow nasal cannula
- Factors about Failure after High Flow Oxygen through Nasal Cannula Therapy in Hypoxic Respiratory Failure Patients at Emergency Department Presentation
- Study on the Changes of SaO2, According to the Different Type of Oxygen Suppliers