Endocrinol Metab.
2018 Jun;33(2):252-259. 10.3803/EnM.2018.33.2.252.
Novel Mutation in PTHLH Related to Brachydactyly Type E2 Initially Confused with Unclassical Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine and Laboratory of Genomics and Translational Medicine, Gachon University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. shleemd@gachon.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Cheil General Hospital & Women's Healthcare Center, Dankook University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Private Practice, Lafayette, CA, USA.
- KMID: 2420494
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.2.252
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
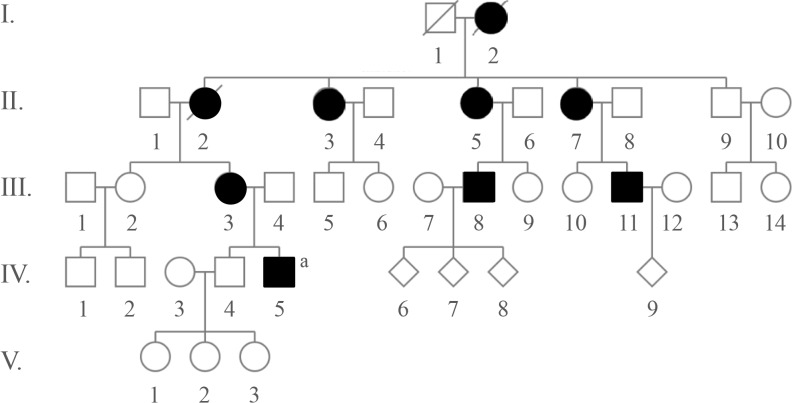
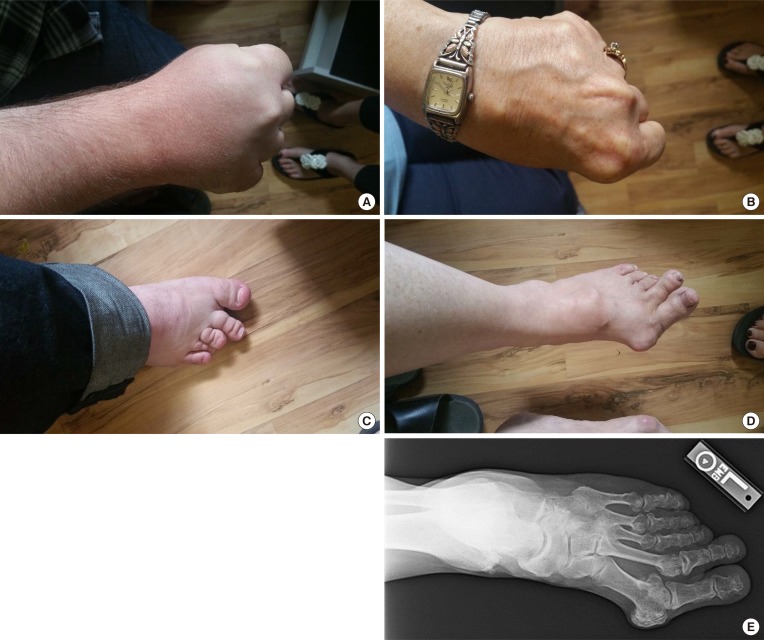
Autosomal-dominant brachydactyly type E is a congenital abnormality characterized by small hands and feet, which is a consequence of shortened metacarpals and metatarsals. We recently encountered a young gentleman exhibiting shortening of 4th and 5th fingers and toes. Initially, we suspected him having pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism (PPHP) because of normal biochemical parameters, including electrolyte, Ca, P, and parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels; however, his mother and maternal grandmother had the same conditions in their hands and feet. Furthermore, his mother showed normal biochemical parameters. To the best of our knowledge, PPHP is inherited via a mutated paternal allele, owing to the paternal imprinting of GNAS (guanine nucleotide binding protein, alpha stimulating) in the renal proximal tubule. Therefore, we decided to further analyze the genetic background in this family.
METHODS
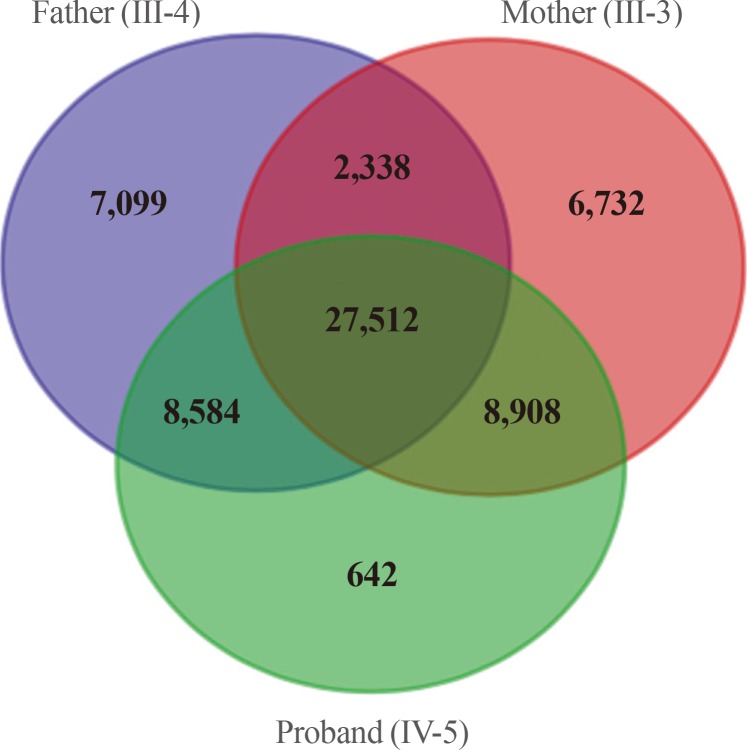
Whole exome sequencing was performed using genomic DNA from the affected mother, son, and the unaffected father as a negative control.
RESULTS
We selected the intersection between 45,490 variants from the mother and 45,646 variants from the son and excluded 27,512 overlapping variants identified from the father. By excluding homogenous and compound heterozygous variants and removing all previously reported variants, 147 variants were identified to be shared by the mother and son. Variants that had least proximities among species were excluded and finally 23 variants remained.
CONCLUSION
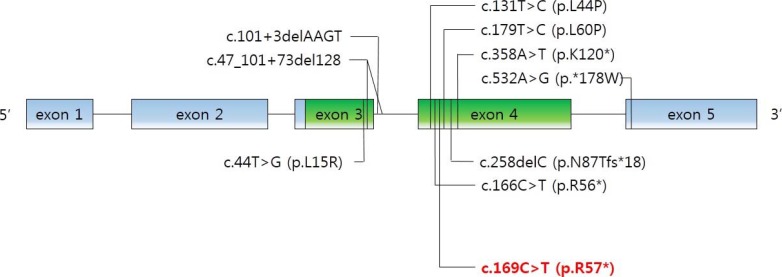
Among them, we identified a defect in parathyroid hormone like hormone (PTHLH), encoding the PTH-related protein, to be disease-causative. Herein, we report a family affected with brachydactyly type E2 caused by a novel PTHLH mutation, which was confused with PPHP with unclassical genetic penetrance.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Alleles
Brachydactyly*
Carrier Proteins
Congenital Abnormalities
DNA
Exome
Fathers
Fingers
Foot
Genetic Background
Grandparents
Hand
Humans
Metacarpal Bones
Metatarsal Bones
Mothers
Parathyroid Hormone
Parathyroid Hormone-Related Protein
Penetrance
Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism*
Toes
Carrier Proteins
DNA
Parathyroid Hormone
Parathyroid Hormone-Related Protein
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Parathyroid Hormone-Related Protein in the Hand or Out of Hand?
Sang Wan Kim
Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(2):202-203. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2018.33.2.202.Search for Novel Mutational Targets in Human Endocrine Diseases
So Young Park, Myeong Han Seo, Sihoon Lee
Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(1):23-28. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2019.34.1.23.
Reference
-
2. Temtamy SA, McKusick VA. The genetics of hand malformations. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1978; 14:1–619.3. Pereda A, Garin I, Garcia-Barcina M, Gener B, Beristain E, Ibanez AM, et al. Brachydactyly E: isolated or as a feature of a syndrome. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013; 8:141. PMID: 24028571.
Article4. Hertzog KP. Brachydactyly and pseudo-pseudohypoparathyroidism. Acta Genet Med Gemellol (Roma). 1968; 17:428–438. PMID: 5703222.
Article5. Drezner MK, Neelon FA, Haussler M, McPherson HT, Lebovitz HE. 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol deficiency: the probable cause of hypocalcemia and metabolic bone disease in pseudohypoparathyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976; 42:621–628. PMID: 1083395.
Article6. de Sanctis L, Vai S, Andreo MR, Romagnolo D, Silvestro L, de Sanctis C. Brachydactyly in 14 genetically characterized pseudohypoparathyroidism type Ia patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004; 89:1650–1655. PMID: 15070926.
Article7. Stone MD, Hosking DJ, Garcia-Himmelstine C, White DA, Rosenblum D, Worth HG. The renal response to exogenous parathyroid hormone in treated pseudohypoparathyroidism. Bone. 1993; 14:727–735. PMID: 8268047.
Article8. Tafaj O, Juppner H. Pseudohypoparathyroidism: one gene, several syndromes. J Endocrinol Invest. 2017; 40:347–356. PMID: 27995443.
Article9. Mantovani G, Bondioni S, Locatelli M, Pedroni C, Lania AG, Ferrante E, et al. Biallelic expression of the Gsalpha gene in human bone and adipose tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004; 89:6316–6319. PMID: 15579796.10. Bastepe M, Weinstein LS, Ogata N, Kawaguchi H, Juppner H, Kronenberg HM, et al. Stimulatory G protein directly regulates hypertrophic differentiation of growth plate cartilage in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004; 101:14794–14799. PMID: 15459318.
Article11. Weinstein LS, Yu S, Warner DR, Liu J. Endocrine manifestations of stimulatory G protein alpha-subunit mutations and the role of genomic imprinting. Endocr Rev. 2001; 22:675–705. PMID: 11588148.12. Levine MA, Germain-Lee E, Jan de Beur S. Genetic basis for resistance to parathyroid hormone. Horm Res. 2003; 60(Suppl 3):87–95. PMID: 14671404.
Article13. Mantovani G, Spada A. Resistance to growth hormone releasing hormone and gonadotropins in Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2006; 19(Suppl 2):663–670. PMID: 16789632.14. Mantovani G, Ballare E, Giammona E, Beck-Peccoz P, Spada A. The Gsalpha gene: predominant maternal origin of transcription in human thyroid gland and gonads. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002; 87:4736–4740. PMID: 12364467.15. Nakamoto JM, Sandstrom AT, Brickman AS, Christenson RA, Van Dop C. Pseudohypoparathyroidism type Ia from maternal but not paternal transmission of a Gsalpha gene mutation. Am J Med Genet. 1998; 77:261–267. PMID: 9600732.16. Simpson C, Grove E, Houston BA. Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism. Lancet. 2015; 385:1123. PMID: 25484027.
Article17. Liu X, Jian X, Boerwinkle E. dbNSFP v2.0: a database of human non-synonymous SNVs and their functional predictions and annotations. Hum Mutat. 2013; 34:E2393–E2402. PMID: 23843252.
Article18. Mundlos S. The brachydactylies: a molecular disease family. Clin Genet. 2009; 76:123–136. PMID: 19790289.
Article19. Strewler GJ. The physiology of parathyroid hormone-related protein. N Engl J Med. 2000; 342:177–185. PMID: 10639544.
Article20. Karaplis AC, Luz A, Glowacki J, Bronson RT, Tybulewicz VL, Kronenberg HM, et al. Lethal skeletal dysplasia from targeted disruption of the parathyroid hormone-related peptide gene. Genes Dev. 1994; 8:277–289. PMID: 8314082.
Article21. Amling M, Neff L, Tanaka S, Inoue D, Kuida K, Weir E, et al. Bcl-2 lies downstream of parathyroid hormone-related peptide in a signaling pathway that regulates chondrocyte maturation during skeletal development. J Cell Biol. 1997; 136:205–213. PMID: 9008714.
Article22. Vortkamp A, Lee K, Lanske B, Segre GV, Kronenberg HM, Tabin CJ. Regulation of rate of cartilage differentiation by Indian hedgehog and PTH-related protein. Science. 1996; 273:613–622. PMID: 8662546.
Article23. Wysolmerski JJ, Philbrick WM, Dunbar ME, Lanske B, Kronenberg H, Broadus AE. Rescue of the parathyroid hormone-related protein knockout mouse demonstrates that parathyroid hormone-related protein is essential for mammary gland development. Development. 1998; 125:1285–1294. PMID: 9477327.
Article24. Kovacs CS, Kronenberg HM. Maternal-fetal calcium and bone metabolism during pregnancy, puerperium, and lactation. Endocr Rev. 1997; 18:832–872. PMID: 9408745.
Article25. Philbrick WM, Dreyer BE, Nakchbandi IA, Karaplis AC. Parathyroid hormone-related protein is required for tooth eruption. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998; 95:11846–11851. PMID: 9751753.
Article26. Brines ML, Ling Z, Broadus AE. Parathyroid hormone-related protein protects against kainic acid excitotoxicity in rat cerebellar granule cells by regulating L-type channel calcium flux. Neurosci Lett. 1999; 274:13–16. PMID: 10530508.
Article27. Yamamoto M, Harm SC, Grasser WA, Thiede MA. Parathyroid hormone-related protein in the rat urinary bladder: a smooth muscle relaxant produced locally in response to mechanical stretch. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992; 89:5326–5330. PMID: 1376916.
Article28. Klopocki E, Hennig BP, Dathe K, Koll R, de Ravel T, Baten E, et al. Deletion and point mutations of PTHLH cause brachydactyly type E. Am J Hum Genet. 2010; 86:434–439. PMID: 20170896.
Article29. Thomas-Teinturier C, Pereda A, Garin I, Diez-Lopez I, Linglart A, Silve C, et al. Report of two novel mutations in PTHLH associated with brachydactyly type E and literature review. Am J Med Genet A. 2016; 170:734–742. PMID: 26640227.30. Wang J, Wang Z, An Y, Wu C, Xu Y, Fu Q, et al. Exome sequencing reveals a novel PTHLH mutation in a Chinese pedigree with brachydactyly type E and short stature. Clin Chim Acta. 2015; 446:9–14. PMID: 25801215.
Article31. Jamsheer A, Sowinska-Seidler A, Olech EM, Socha M, Kozlowski K, Pyrkosz A, et al. Variable expressivity of the phenotype in two families with brachydactyly type E, craniofacial dysmorphism, short stature and delayed bone age caused by novel heterozygous mutations in the PTHLH gene. J Hum Genet. 2016; 61:457–461. PMID: 26763883.
Article32. Pereda A, Garzon-Lorenzo L, Garin I, Cruz-Rojo J, Sanchez Del Pozo J, Perez de Nanclares G. The p.R56* mutation in PTHLH causes variable brachydactyly type E. Am J Med Genet A. 2017; 173:816–819. PMID: 28211986.
Article33. Bell J. On brachydactyly and symphalangism. London: Cambridge University Press;1951.34. Spranger J. Pattern recognition in bone dysplasias. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985; 200:315–342. PMID: 4080742.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A familial case with brachydactyly type C with a GDF5 mutation
- Osteoma Cutis as the Presenting Feature of Albright Hereditary Osteodystrophy Associated with Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism
- A Case of Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism with Partial Empty Sella
- A Case of Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism with Normal Stature
- Identification of a GDF5 Mutation in a Korean Patient with Brachydactyly Type C without Foot Involvement