J Korean Endocr Soc.
2009 Jun;24(2):138-143. 10.3803/jkes.2009.24.2.138.
A Case of Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism with Normal Stature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Korea.
- KMID: 1468510
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2009.24.2.138
Abstract
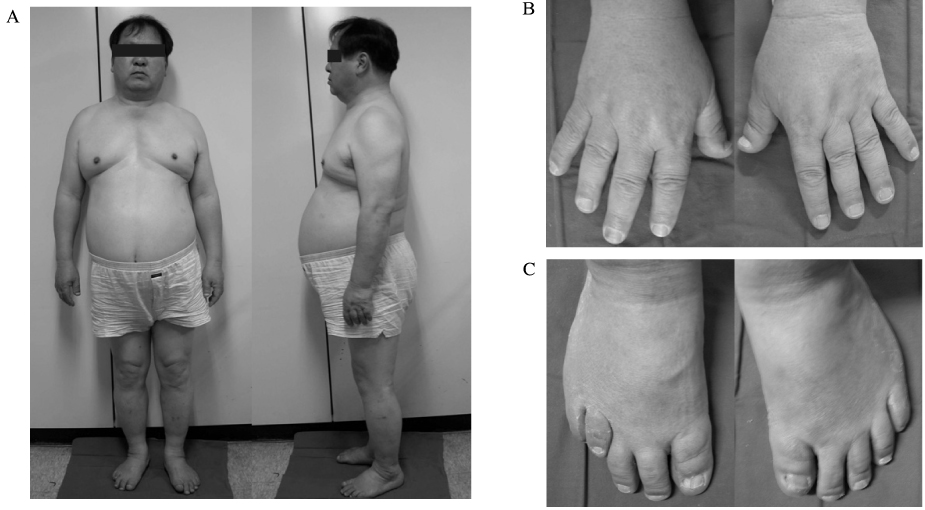
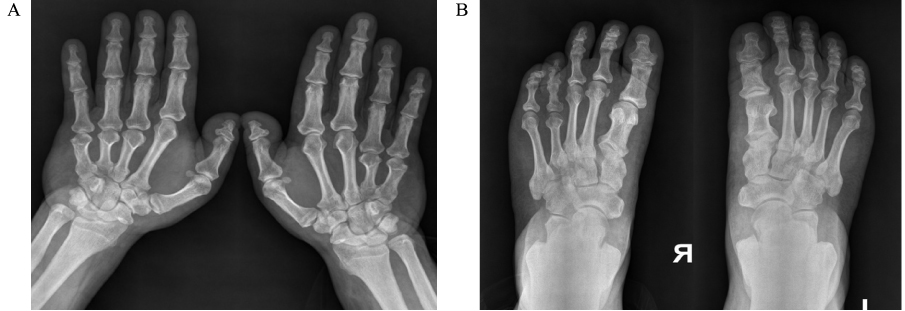
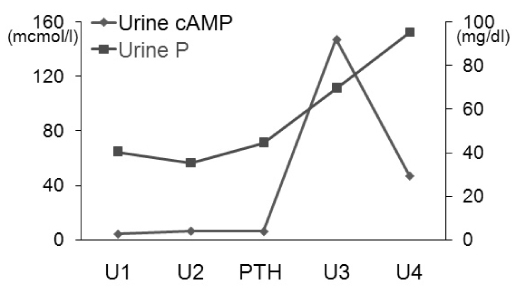
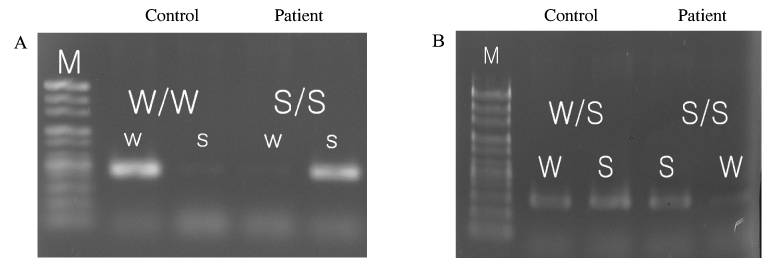
- Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism (PPHP) is characterized by the phenotype of Albright hereditary osteodystrophy (AHO) alone without biochemical evidence of multihormone resistance, which is unlike pseudohypoparathyroidism. AHO is associated with characteristic developmental abnormalities that include a short stocky stature, a short neck, brachydactyly, a round face, central obesity, mental retardation and subcutaneous ossifications. AHO is an autosomal dominant disease that's caused by heterozygous inactivating mutations in the Gsalpha gene (GNAS1). Melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) is a hypothalamic Gs-coupled receptor that is thought to mediate the central effect of leptin on satiety. MC4R mutations cause morbid obesity starting in infancy, as well as an elevated leptin level. A 62 year old man with a height of 171.5 cm, a round face, a short neck, central obesity and brachydactyly had normal ranges of serum calcium, phosphorus and PTH and a normal Ellsworth-Howard test. GNAS1 gene analysis revealed substitution of alanine to cysteine in the 165 codon of exon 6 and substitution of alanine to cysteine in the 231 codon of exon 9. Two known SNPs (Cyt-1042Thy, Gua-719Ade) in the MC4R were detected in the patient. We report here on a case of PPHP and the patient had normal stature. We propose that MC4R may have contributed to the obesity & normal stature of this patient.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Alanine
Alkenes
Brachydactyly
Calcium
Codon
Cysteine
Exons
Fibrous Dysplasia, Polyostotic
Humans
Intellectual Disability
Leptin
Neck
Obesity
Obesity, Abdominal
Obesity, Morbid
Phenotype
Phosphorus
Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide
Pseudohypoparathyroidism
Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism
Receptor, Melanocortin, Type 4
Reference Values
Alanine
Alkenes
Calcium
Codon
Cysteine
Fibrous Dysplasia, Polyostotic
Leptin
Phosphorus
Receptor, Melanocortin, Type 4
Figure
Reference
-
1. Levine MA, Germain-Lee E, Jan de Beur S. Genetic basis for resistance to parathyroid hormone. Horm Res. 2003. 60:87–95.2. Lemay M, McNeely WF, Raisz LG. Dyschondroplasia with soft tissue calcification and ossification, and normal parathyroid function (pseudo-pseudohypoparathyroidism). Am J Med. 1956. 21:649–656.3. Bastepe M, Jüppner H. GNAS locus and pseudohypoparathyroidism. Horm Res. 2005. 63:65–74.4. Hayward BE, Moran V, Strain L, Bonthron DT. Bidirectional imprinting of a single gene: GNAS1 encodes maternally, paternally, and biallelically derived proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998. 95:15475–15480.5. Weinstein LS, Yu S, Warner DR, Liu J. Endocrine manifestations of stimulatory G protein alpha-subunit mutations and the role of genomic imprinting. Endocr Rev. 2001. 22:675–705.6. Koh JH, Lee Y, Choi JW, Hong TW, Kim MJ, Shin YG, Chung CH. A case of pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism with partial empty sella. J Korean Endocr Soc. 2004. 19:433–438.7. Jung WY, Kang SJ, Bae HY. A case of benign intracranial hypertension in pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1999. 17:431–434.8. Ogata E, Yamamoto M, Matsumoto T, Fujita T, Fukase M, Kinoshita Y, Furukawa Y, Sohn HE, Nakajima H, Yasuda T. Standard procedure and the diagnostic criteria for the Ellsworth-Howard test using human PTH-(1-34). Nippon Naibunpi Gakkai Zasshi. 1984. 60:971–984.9. Kim YS. Interpretation and reading of endocrine function test. 2001. 1st ed. Seoul: Korea Medical Book Publisher;116–118.10. Shiohara M, Shiozawa R, Kurata K, Matsuura H, Arai F, Yasuda T, Koike K. Effect of parathyroid hormone administration in a patient with severe hypoparathyroidism caused by gain-of-function mutation of calcium-sensing receptor. Endocr J. 2006. 53:797–802.11. Weinstein LS, Shenker A. G protein mutations in human disease. Clin Biochem. 1993. 26:333–338.12. Gejman PV, Weinstein LS, Martinez M, Spiegel AM, Cao Q, Hsieh WT, Hoehe MR, Gershon ES. Genetic mapping of the Gs-alpha subunit gene (GNAS1) to the distal long arm of chromosome 20 using a polymorphism detected by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Genomics. 1991. 9:782–783.13. Yu S, Yu D, Lee E, Eckhaus M, Lee R, Corria Z, Accili D, Westphal H, Weinstein LS. Variable and tissue-specific hormone resistance in heterotrimeric Gs protein alpha-subunit (Gsalpha knockout mice is due to tissue-specific imprinting of the Gsalpha gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998. 95:8715–8720.14. Levine MA, Jap TS, Mauseth RS, Downs RW, Spiegel AM. Activity of the stimulatory guanine nucleotide-binding protein is reduced in erythrocytes from patients with pseudohypoparathyroidism and pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism: biochemical, endocrine, and genetic analysis of Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy in six kindreds. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986. 62:497–502.15. Auerbach GD, Marx SJ, Spiegel AM. Wilson JD, Foster DW, editors. Parathyroid hormone, calcitonin, and the calciferols. Williams textbook of endocrinology. 1985. 7th ed. Oxford: WB Saunders Co;1397–1476.16. Ahrens W, Hiort O, Staedt P, Kirschner T, Marschke C, Kruse K. Analysis of the GNAS1 gene in albright's hereditary osteodystrophy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001. 86:4630–4634.17. Miric A, Vechio JD, Levine MA. Heterogeneous mutations in the gene encoding the α subunit of the stimulatory G protein of adenylyl cyclase in Albright hereditary osteodystrophy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993. 76:1560–1568.18. Warner DR, Gejman PV, Collins RM, Wenstein LS. A novel mutation adjacent to the switch III domain of G(S alpha) in a patient with pseudohypoparathyroidism. Mol Endocrinol. 1997. 11:1718–1727.19. Ong KK, Amin R, Dunger DB. Pseudohypoparathyroidism-another monogenic obesity syndrome. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2000. 52:389–391.20. Long DN, McGuire S, Levine MA, Weinstein LS, Germain-Lee EL. Body mass index differences in pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1a versus pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism may implicate paternal imprinting of Galpha(s) in the development of human obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007. 92:1073–1079.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Benign Intracranial Hypertension in Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism
- A Case Report of Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism
- Two Cases of Albright's Hereditary Osteodystrophy Occurring in Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism
- Osteoma Cutis as the Presenting Feature of Albright Hereditary Osteodystrophy Associated with Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism
- A Case of Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism with Partial Empty Sella