J Bone Metab.
2018 Aug;25(3):181-186. 10.11005/jbm.2018.25.3.181.
Relationship between Bone Density, Eating Habit, and Nutritional Intake in College Students
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food and Nutrition, Yeonsung University, Anyang, Korea.
- 2Department of Preventive Medicine, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. parky@sch.ac.kr
- 3Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2419846
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2018.25.3.181
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The importance of bone health is emphasized throughout the life cycle. Young adults have problems with bone health due to irregular lifestyle and unbalanced diet, but studies related to them are insufficient. The purpose of this study was to measure the bone mineral density (BMD) of college students and to analyze the differences in BMD according to lifestyle.
METHODS
BMD was measured by bone ultrasound in 161 male and female college students. The questionnaire was surveyed about lifestyle, eating habits, and nutrient intake status.
RESULTS
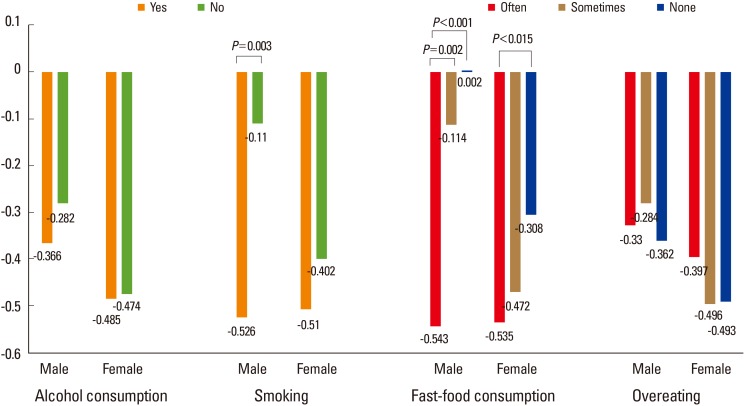
Osteopenia was 8.8% in male and 10.8% in female. The body fat percentage of female was significantly higher than male. Male college students, smoking, fast food consumption, and overeating rate were significantly higher than female. Nutrient intake was not significantly different between male and female students. But energy and vitamin A and C levels were inadequate, and protein and sodium intake was excessive compared with the recommended nutrient intake for Koreans. BMD was significantly lowest in male who often intake fast food than male who did not intake at all or intake sometimes. Female who often intake fast food had significantly lower BMD than female who did not eat at all.
CONCLUSIONS
College students have different BMDs according to lifestyle. There was a difference in BMD according to smoking and fast food consumption.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Associations between Dietary Fiber Intake and Bone Mineral Density in Adult Korean Population: Analysis of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey in 2011
Taehoon Lee, Heuy Sun Suh
J Bone Metab. 2019;26(3):151-160. doi: 10.11005/jbm.2019.26.3.151.
Reference
-
1. Ha YC, Park YG, Nam KW, et al. Trend in hip fracture incidence and mortality in Korea: a prospective cohort study from 2002 to 2011. J Korean Med Sci. 2015; 30:483–488. PMID: 25829818.
Article2. Armas LA, Recker RR. Pathophysiology of osteoporosis: new mechanistic insights. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2012; 41:475–486. PMID: 22877425.3. Spencer H, Kramer L. NIH consensus conference: osteoporosis. Factors contributing to osteoporosis. J Nutr. 1986; 116:316–319. PMID: 3944667.4. Gourlay ML, Hammett-Stabler CA, Renner JB, et al. Associations between body composition, hormonal and lifestyle factors, bone turnover, and BMD. J Bone Metab. 2014; 21:61–68. PMID: 24707468.
Article5. Cvijetic S, Baric IC, Satalic Z, et al. Influence of nutrition and lifestyle on bone mineral density in children from adoptive and biological families. J Epidemiol. 2014; 24:209–215. PMID: 24646813.
Article6. Rezaei A, Dragomir-Daescu D. Femoral strength changes faster with age than BMD in both women and men: a biomechanical study. J Bone Miner Res. 2015; 30:2200–2206. PMID: 26096829.
Article7. Shin HJ, Cho E, Lee HJ, et al. Instant noodle intake and dietary patterns are associated with distinct cardiometabolic risk factors in Korea. J Nutr. 2014; 144:1247–1255. PMID: 24966409.
Article8. Cha E, Burke LE, Kim KH, et al. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among overweight and obese college students in Korea. J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2010; 25:61–68. PMID: 20134283.
Article9. Plotnikoff RC, Costigan SA, Williams RL, et al. Effectiveness of interventions targeting physical activity, nutrition and healthy weight for university and college students: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2015; 12:45. PMID: 25890337.
Article10. Cho J, Lee HE, Kim SJ, et al. Effects of body image on college students' attitudes toward diet/fitness apps on smartphones. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2015; 18:41–45. PMID: 25584729.
Article11. The Korean Society for Bone and Mineral Research. Physician's guide for diagnosis & treatment of osteoporosis. 2015. cited by 2018 June 11. Available from: http://www.ksbmr.org/image/journal/골다공증%20지침서2015_final_1002.pdf.12. The Korean Nutrition Society. Dietary reference intakes for Koreans 2015. Sejong: Ministry of Health and Welfare, The Korean Nutrition Society;2015.13. Choi SN, Chung NY. Bone density, nutrient intake, blood composition and food habits in non-smoking and non-alcohol drinking male university students. Korean J Food Cult. 2010; 25:389–399.14. Kwon S, Lee BK, Kim HS. Relation between nutritional factors and bone status by broadband ultrasound attenuation among college students. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2009; 38:1551–1558.
Article15. Kim HY, Ha YC, Kim TY, et al. Healthcare costs of osteoporotic fracture in Korea: information from the national health insurance claims database, 2008-2011. J Bone Metab. 2017; 24:125–133. PMID: 28642857.
Article16. Kim KW, Shin EM, Moon EH. A study on fast food consumption, nutritional knowledge, food behavior and dietary intake of university students. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2004; 10:13–24.17. Kim SH. Coffee consumption behaviors, dietary habits, and dietary nutrient intakes according to coffee intake amount among university students. J Nutr Health. 2017; 50:270–283.
Article18. Ahn Y, Kim KW. Beliefs regarding vegetable consumption, self-efficacy and eating behaviors according to the stages of change in vegetable consumption among college students. Korean J Community Nutr. 2012; 17:1–13.
Article19. Lee YJ, You JS, Chang KJ. Dietary habits score, nutrients intake and dietary quality related to coffee consumption of college students in Incheon. J Nutr Health. 2013; 46:560–572.
Article20. Chung KH, Shin KO, Jung TH, et al. Study on the dietary habit, nutrient intake, and health status according to their majors among college women in Sahmyook university. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2010; 39:826–836.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Nutrition, Food Habit, and Bone Mineral Density in Young College Females
- Factors influencing on intention to intake fruit: moderating effect of fruit intake habit
- A Study on the Perception of Nutritional Education by Students in Elementary School and Their Parents in the Chungnam Area
- Do types of snacks, sleep hours, and eating places affect nutritional intakes and its adequacy in adolescents?
- Comparisons of Food Intake Patterns and Iron Nutritional Status by Dietary Iron Density Among College Students