J Nutr Health.
2014 Apr;47(2):134-144. 10.4163/jnh.2014.47.2.134.
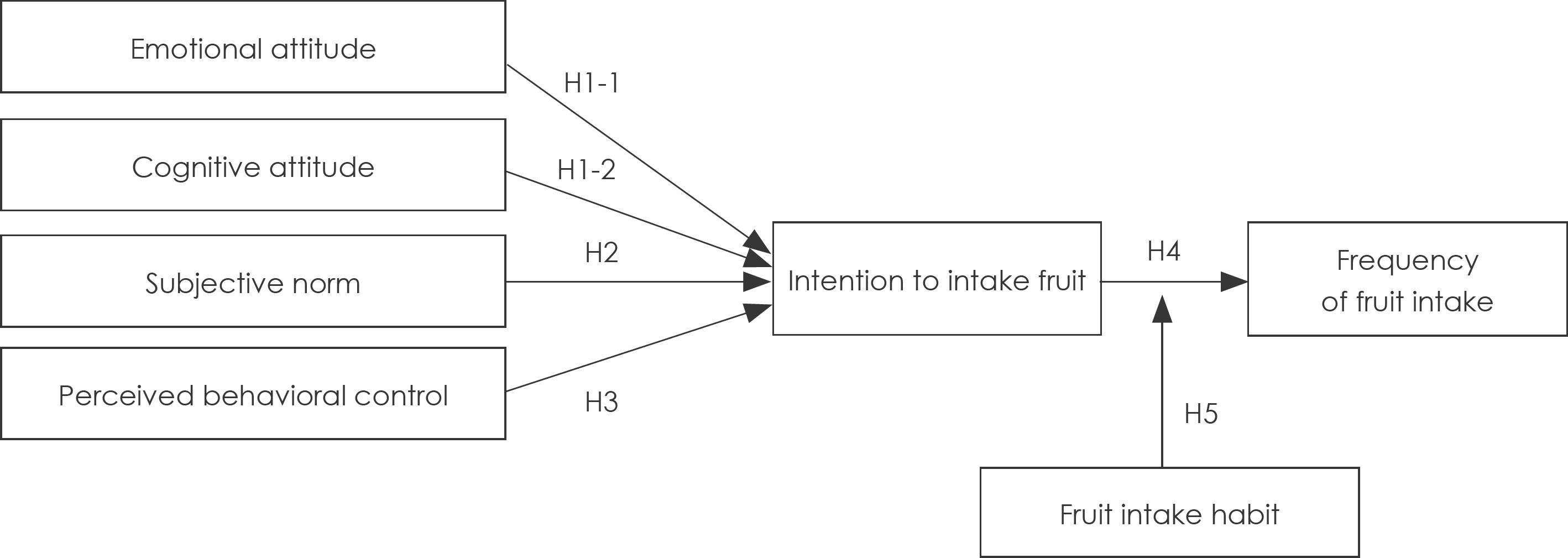
Factors influencing on intention to intake fruit: moderating effect of fruit intake habit
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nutritional Science and Food Management, Ewha Womans University, Seoul 120-750, Korea. seo@ewha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2210027
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4163/jnh.2014.47.2.134
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to identify factors affecting fruit consumption behavior by application of the Theory of Planned Behavior. In addition, this study examined the moderating effect of a fruit eating habit.
METHODS
A total of 734 consumers who have ever purchased fruit participated in this study.
RESULTS
Results of this study showed that attitudes toward fruit intake, social norms, and perceived behavioral control had significant impacts on the level of fruit intake. Fruit eating habit that showed high correlation with eating behavior was also included in the model identifying factors having an influence on fruit intake. Attitudes toward fruit intake, social norms, and perceived behavioral control had a positive influence on intention to intake fruit. Fruit eating habits played a moderating role in the relationships between intention to intake fruit and real fruit intake.
CONCLUSION
Increasing positive attitudes toward fruit intake, social norms, and perceived behavioral control would be helpful in increasing the amount of fruit intake.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea Health Statistics 2010: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V-1). Cheongwon: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2011.2. Kwon JH, Shim JE, Park MK, Paik HY. Evaluation of fruits and vegetables intake for prevention of chronic disease in Korean adults aged 30 years and over: using the Third Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES III), 2005. Korean J Nutr. 2009; 42(2):146–157.
Article3. Food and Agriculture Organization (US); World Health Organization. Fruit and vegetable for health: report of a joint FAO/WHO workshop, 1–3 September 2004, Kobe, Japan. Geneva: World Health Organization;2004.4. Carter P, Gray LJ, Troughton J, Khunti K, Davies MJ. Fruit and vegetable intake and incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and metaanalysis. BMJ. 2010; 341:c4229.
Article5. Ford ES, Mokdad AH. Fruit and vegetable consumption and diabetes mellitus incidence among U.S. adults. Prev Med. 2001; 32(1):33–39.
Article6. Appel LJ, Champagne CM, Harsha DW, Cooper LS, Obarzanek E, Elmer PJ, Stevens VJ, Vollmer WM, Lin PH, Svetkey LP, Stedman SW, Young DR. Writing Group of the PREMIER Collaborative Research Group. Effects of comprehensive lifestyle modification on blood pressure control: main results of the PREMIER clinical trial. JAMA. 2003; 289(16):2083–2093.
Article7. Utsugi MT, Ohkubo T, Kikuya M, Kurimoto A, Sato RI, Suzuki K, Metoki H, Hara A, Tsubono Y, Imai Y. Fruit and vegetable consumption and the risk of hypertension determined by self measurement of blood pressure at home: the Ohasama study. Hypertens Res. 2008; 31(7):1435–1443.
Article8. Buijsse B, Feskens EJ, Schulze MB, Forouhi NG, Wareham NJ, Sharp S, Palli D, Tognon G, Halkjaer J, Tj⊘nneland A, Jakobsen MU, Overvad K, van der A DL, Du H, S⊘rensen TI, Boeing H. Fruit and vegetable intakes and subsequent changes in body weight in European populations: results from the project on Diet, Obesity, and Genes (DiOGenes). Am J Clin Nutr. 2009; 90(1):202–209.
Article9. Epstein LH, Gordy CC, Raynor HA, Beddome M, Kilanowski CK, Paluch R. Increasing fruit and vegetable intake and decreasing fat and sugar intake in families at risk for childhood obesity. Obes Res. 2001; 9(3):171–178.
Article10. Dauchet L, Amouyel P, Hercberg S, Dallongeville J. Fruit and vegetable consumption and risk of coronary heart disease: a metaanalysis of cohort studies. J Nutr. 2006; 136(10):2588–2593.
Article11. Nikolić M, Nikić D, Petrović B. Fruit and vegetable intake and the risk for developing coronary heart disease. Cent Eur J Public Health. 2008; 16(1):17–20.
Article12. Bazzano LA, He J, Ogden LG, Loria CM, Vupputuri S, Myers L, Whelton PK. Fruit and vegetable intake and risk of cardiovascular disease in US adults: the first National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Epidemiologic Follow-up Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002; 76(1):93–99.
Article13. Boggs DA, Palmer JR, Wise LA, Spiegelman D, Stampfer MJ, Adams-Campbell LL, Rosenberg L. Fruit and vegetable intake in relation to risk of breast cancer in the Black Women's Health Study. Am J Epidemiol. 2010; 172(11):1268–1279.
Article14. Freedman ND, Park Y, Subar AF, Hollenbeck AR, Leitzmann MF, Schatzkin A, Abnet CC. Fruit and vegetable intake and head and neck cancer risk in a large United States prospective cohort study. Int J Cancer. 2008; 122(10):2330–2336.
Article15. Millen AE, Subar AF, Graubard BI, Peters U, Hayes RB, Weiss-feld JL, Yokochi LA, Ziegler RG. PLCO Cancer Screening Trial Project Team. Fruit and vegetable intake and prevalence of colorectal adenoma in a cancer screening trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007; 86(6):1754–1764.16. Johnston KL, White KM. Binge-drinking: A test of the role of group norms in the Theory of Planned Behaviour. Psychol Health. 2003; 18(1):63–77.
Article17. Tuu HH, Olsen SO, Thao DT, Anh NT. The role of norms in explaining attitudes, intention and consumption of a common food (fish) in Vietnam. Appetite. 2008; 51(3):546–551.
Article18. Rhodes RE, De Bruijn GJ. Automatic and motivational correlates of physical activity: does intensity moderate the relationship? Behav Med. 2010; 36(2):44–52.
Article19. Godin G, Amireault S, Béllanger-Gravel A, Vohl MC, Pélrusse L, Guillaumie L. Prediction of daily fruit and vegetable consumption among overweight and obese individuals. Appetite. 2010; 54(3):480–484.
Article20. Guillaumie L, Godin G, Vézina-Im LA. Psychosocial determinants of fruit and vegetable intake in adult population: a systematic review. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2010; 7:12.
Article21. Zoellner J, Krzeski E, Harden S, Cook E, Allen K, Estabrooks PA. Qualitative application of the theory of planned behavior to understand beverage consumption behaviors among adults. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2012; 112(11):1774–1784.
Article22. Chen MF. Consumer attitudes and purchase intentions in relation to organic foods in Taiwan: Moderating effects of food-related personality traits. Food Qual Prefer. 2007; 18(7):1008–1021.
Article23. De Bruijn GJ, Kremers SPJ, De Vet EE, De Nooijer J, Van Mechelen W, Brug J. Does habit strength moderate the intention-behaviour relationship in the Theory of Planned Behaviour? The case of fruit consumption. Psychol Health. 2007; 22(8):899–916.
Article24. Arvola A, Vassallo M, Dean M, Lampila P, Saba A, Lähteenmä-ki L, Shepherd R. Predicting intentions to purchase organic food: the role of affective and moral attitudes in the Theory of Planned Behaviour. Appetite. 2008; 50(2–3):443–454.
Article25. Latimer AE, Martin Ginis KA. The importance of subjective norms for people who care what others think of them. Psychol Health. 2005; 20(1):53–62.
Article26. Manstead AS, van Eekelen SA. Distinguishing between perceived behavioral control and self-efficacy in the domain of academic achievement intentions and behaviors. J Appl Soc Psychol. 1998; 28(15):1375–1392.
Article27. Povey R, Conner M, Sparks P, James R, Shepherd R. Application of the theory of planned behaviour to two dietary behaviours: roles of perceived control and self-efficacy. Br J Health Psychol. 2000; 5(2):121–139.
Article28. Sparks P, Guthrie CA, Shepherd R. The dimensional structure of the perceived behavioral control construct. J Appl Soc Psychol. 1997; 27(5):418–438.29. Aarts H, Paulussen T, Schaalma H. Physical exercise habit: on the conceptualization and formation of habitual health behaviours. Health Educ Res. 1997; 12(3):363–374.
Article30. Bamberg S, Ajzen I, Schmidt P. Choice of travel mode in the theory of planned behavior: The roles of past behavior, habit, and reasoned action. Basic Appl Soc Psych. 2003; 25(3):175–187.
Article31. Brug J, De Vet E, De Nooijer J, Verplanken B. Predicting fruit consumption: cognitions, intention, and habits. J Nutr Educ Behav. 2006; 38(2):73–81.
Article32. Reinaerts E, De Nooijer J, Candel M, De Vries N. Explaining school children's fruit and vegetable consumption: the contributions of availability, accessibility, exposure, parental consumption and habit in addition to psychosocial factors. Appetite. 2007; 48(2):248–258.
Article33. Kothe EJ, Mullan BA, Butow P. Promoting fruit and vegetable consumption. Testing an intervention based on the theory of planned behaviour. Appetite. 2012; 58(3):997–1004.
Article34. Sjoberg S, Kim K, Reicks M. Applying the theory of planned behavior to fruit and vegetable consumption by older adults. J Nutr Elder. 2004; 23(4):35–46.
Article35. Cha MH, Kim YK. Consumers'purchasing intentions of organic foods in relation to the perceived health concerns, healthy eating practices and attitudes, and food choice motives. Korean J Community Nutr. 2009; 14(3):286–294.36. Verplanken B, Orbell S. Reflections on past behavior: a self-report index of habit strength. J Appl Soc Psychol. 2003; 33(6):1313–1330.37. De Bruijn GJ. Understanding college students'fruit consumption. Integrating habit strength in the theory of planned behaviour. Appetite. 2010; 54(1):16–22.38. Ahn Y, Kim KW. Beliefs regarding vegetable consumption, self-efficacy and eating behaviors according to the stages of change in vegetable consumption among college students. Korean J Community Nutr. 2012; 17(1):1–13.
Article39. Emanuel AS, McCully SN, Gallagher KM, Updegraff JA. Theory of planned behavior explains gender difference in fruit and vegetable consumption. Appetite. 2012; 59(3):693–697.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- How much fruit should diabetic patients eat?
- Analysis of socio-demographic and dietary factors associated with fruit and vegetable consumption among Korean adolescents: use of data from the 7th and 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016–2019)
- Fruit Intake and Changes of Cardio-Metabolic Risk Factors in People with Obesity
- Intake of Fruit and Glycemic Control in Korean Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Intake of Fruits for Diabetics: Why and How Much?