Ann Dermatol.
2018 Jun;30(3):284-289. 10.5021/ad.2018.30.3.284.
Both Educational Lectures and Reference Photographs Are Necessary to Improve the Accuracy and Reliability of Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) Assessment: Results from Korean Nation-Wide PASI Educational Workshop
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. swyoun@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2419168
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2018.30.3.284
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Accurate assessment of the severity of psoriasis is important in daily practice and clinical studies. However, the assessment of psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) reflects the physician's experience, and thus evaluations by physicians are inherently subjective, with intra-rater and inter-rater variability.
OBJECTIVE
To elucidate the effectiveness of PASI educational lectures and the use of reference photographs on the improvement of accuracy and reliability in PASI assessments and to develop effective educational programs for PASI assessments.
METHODS
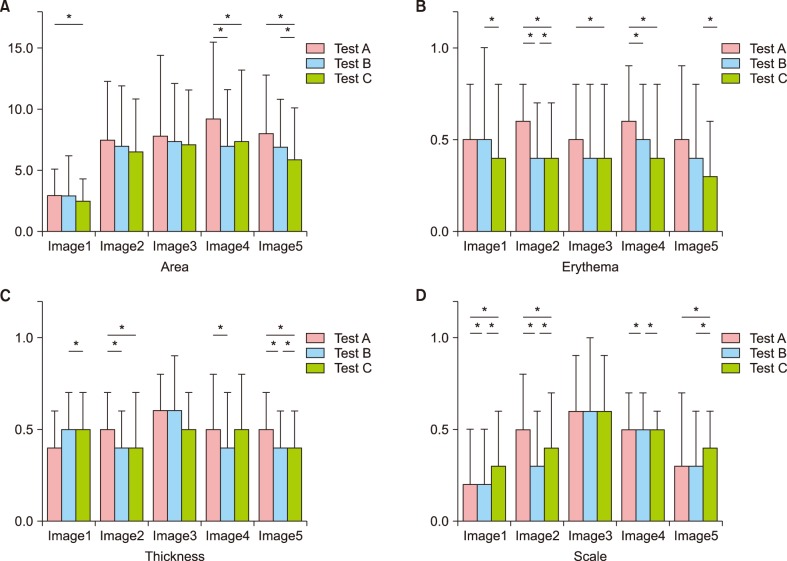
We performed a before-and-after comparison study during nation-wide PASI educational workshops. The participants were asked to assess the severity components of PASI (erythema, thickness, scale, and affected area) three times: in the test administered before an educational lecture, the test immediately after the lecture, and lastly the test with the use of reference photographs. The improvement of accuracy and reliability was analyzed by comparing the results of three tests.
RESULTS
Ninety-six board-certified dermatologists and residents participated and 72 participants completed all three tests. The accuracy and reliability of the assessment of severity components of PASI increased significantly after the educational lecture and the use of reference photographs. Use of reference photographs resulted in limited improvements when the recognition of three-dimensional structures was required, such as in the assessment of thickness or scale.
CONCLUSION
Our study confirmed that the combination of standardized educational training and reference photographs can improve the accuracy and reliability of PASI assessments. Understanding how to evaluate three-dimensional psoriatic lesions can help with proper assessment of the severity of psoriasis.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Morphological Characteristics of Psoriatic Lesions Affect the Accuracy and Reliability of Severity Assessments: Proposal for New Working Criteria for the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index
Chong Won Choi, Bo Ri Kim, Seungkul Yang, Sang Woong Youn
Ann Dermatol. 2019;31(1):81-83. doi: 10.5021/ad.2019.31.1.81.
Reference
-
1. Faria JR, Aarão AR, Jimenez LM, Silva OH, Avelleira JC. Inter-rater concordance study of the PASI (Psoriasis Area and Severity Index). An Bras Dermatol. 2010; 85:625–629. PMID: 21152786.2. Armstrong AW, Parsi K, Schupp CW, Mease PJ, Duffin KC. Standardizing training for psoriasis measures: effectiveness of an online training video on Psoriasis Area and Severity Index assessment by physician and patient raters. JAMA Dermatol. 2013; 149:577–582. PMID: 23426158.3. Robinson A, Kardos M, Kimball AB. Physician Global Assessment (PGA) and Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI): why do both? A systematic analysis of randomized controlled trials of biologic agents for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012; 66:369–375. PMID: 22041254.4. Puzenat E, Bronsard V, Prey S, Gourraud PA, Aractingi S, Bagot M, et al. What are the best outcome measures for assessing plaque psoriasis severity? A systematic review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2010; 24(Suppl 2):10–16.
Article5. Youn SW, Choi CW, Kim BR, Chae JB. Reduction of inter-rater and intra-rater variability in psoriasis area and severity index assessment by photographic training. Ann Dermatol. 2015; 27:557–562. PMID: 26512170.
Article6. Robertson K, McIntosh RD, Bradley-Scott C, MacFarlane S, Rees JL. Image training, using random images of melanoma, performs as well as the ABC(D) criteria in enabling novices to distinguish between melanoma and mimics of melanoma. Acta Derm Venereol. 2014; 94:265–270. PMID: 24212235.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reduction of Inter-Rater and Intra-Rater Variability in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index Assessment by Photographic Training
- Relation between the Peripherofacial Psoriasis and Scalp Psoriasis
- A Clinical Study of Calcipotriol Ointment in the Treatment of Psoriasis Vulgaris
- A clinical study of calciportriol ointment(MC 903) in the treatment of psoriasis
- Mean Platelet Volume Is Elevated in Patients with Psoriasis Vulgaris