Yonsei Med J.
2017 Jul;58(4):697-702. 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.4.697.
Low Expression of Circulating MicroRNA-34c is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, ShunDe Hospital of Southern Medical University, Foshan, China.
- 2Department of General Surgery, ShunDe Hospital of Southern Medical University, Foshan, China. xwchensdyy@163.com
- KMID: 2419073
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2017.58.4.697
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The microRNA-34 (miR-34) family is important in tumor regulation. This study aimed to investigate the association of circulating miR-34 family proteins with clinicopathological features and their prognostic value in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In this cohort study, 173 TNBC patients admitted to First People's Hospital of Shunde from May 1, 2009 to April 30, 2013 were enrolled. Meanwhile, 75 age-matched healthy women volunteers were identified as healthy controls (HCs). We examined the expression of miR-34 family (miR-34a/b/c) proteins in plasma collected from TNBC patients before any treatment was performed and from age-matched HCs using qPCR methods.
RESULTS
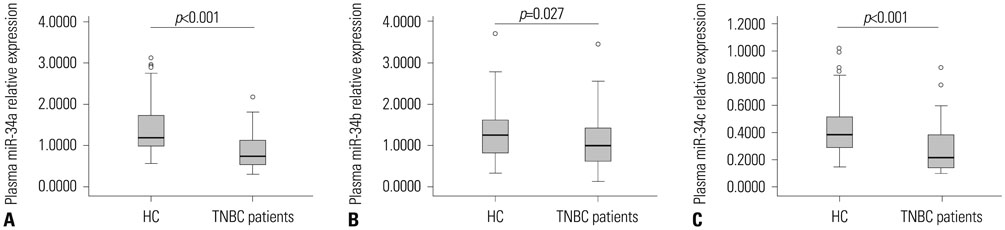
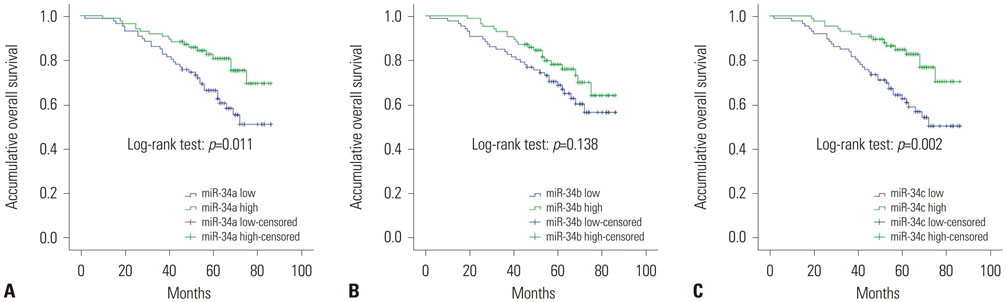
The expressions of miR-34a/34b/34c were significantly lower in TNBC patients than in HC (p<0.001, p=0.027, p<0.001, respectively). miR-34a was correlated with tumor grade (p=0.038), lymph node positive (p=0.027), distant metastasis (p=0.004), and surgery (p=0.023); miR-34b was correlated with lymph node positivity (p=0.027); and miR-34c was correlated with tumor grade (p=0.017) and distant metastasis (p<0.001). Kaplan-Meier curve analysis displayed low expression of miR-34a as associated with worse overall survival (OS) (p=0.011), as well as miR-34c low expression (p=0.002). In addition, univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression was performed, and low expression of miR-34c (p=0.011) was found to be an independent risk factor for OS, as well as tumor grade (p=0.013), lymph node positive (p=0.050), and distant metastasis (p=0.021).
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, this study demonstrated reduced miR-34a/c expression is highly associated with tumor progression and indicated worse prognosis. Also, miR-34c was an independent risk factor for OS in TNBC patients.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Cohort Studies
Factor Analysis, Statistical
Female
*Gene Expression Regulation, Neoplastic
Humans
Kaplan-Meier Estimate
MicroRNAs/*blood/*genetics/metabolism
Middle Aged
Multivariate Analysis
Neoplasm Staging
Prognosis
Proportional Hazards Models
Risk Factors
Triple Negative Breast Neoplasms/*blood/*genetics/pathology
MicroRNAs
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Notch1 in Tumor Microvascular Endothelial Cells and Tumoral miR-34a as Prognostic Markers in Locally Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Dongmin Kim, Jieun Lee, Jun Kang, Sung Hun Kim, Tae-Kyung Yoo, Sooeun Oh, Ahwon Lee
J Breast Cancer. 2019;22(4):562-578. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2019.22.e56.
Reference
-
1. Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015; 65:87–108.
Article2. Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000; 406:747–752.
Article3. Foulkes WD, Smith IE, Reis-Filho JS. Triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:1938–1948.
Article4. Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009; 136:215–233.
Article5. Maroof H, Salajegheh A, Smith RA, Lam AK. MicroRNA-34 family, mechanisms of action in cancer: a review. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2014; 14:737–751.
Article6. Misso G, Di Martino MT, De Rosa G, Farooqi AA, Lombardi A, Campani V, et al. Mir-34: a new weapon against cancer? Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2014; 3:e194.
Article7. Rokavec M, Li H, Jiang L, Hermeking H. The p53/miR-34 axis in development and disease. J Mol Cell Biol. 2014; 6:214–230.
Article8. Garcia AI, Buisson M, Bertrand P, Rimokh R, Rouleau E, Lopez BS, et al. Down-regulation of BRCA1 expression by miR-146a and miR-146b-5p in triple negative sporadic breast cancers. EMBO Mol Med. 2011; 3:279–290.
Article9. Radojicic J, Zaravinos A, Vrekoussis T, Kafousi M, Spandidos DA, Stathopoulos EN. MicroRNA expression analysis in triple-negative (ER, PR and Her2/neu) breast cancer. Cell Cycle. 2011; 10:507–517.
Article10. He L, He X, Lim LP, de Stanchina E, Xuan Z, Liang Y, et al. A microRNA component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature. 2007; 447:1130–1134.
Article11. Corney DC, Hwang CI, Matoso A, Vogt M, Flesken-Nikitin A, Godwin AK, et al. Frequent downregulation of miR-34 family in human ovarian cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2010; 16:1119–1128.
Article12. Welch C, Chen Y, Stallings RL. MicroRNA-34a functions as a potential tumor suppressor by inducing apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. Oncogene. 2007; 26:5017–5022.
Article13. Peurala H, Greco D, Heikkinen T, Kaur S, Bartkova J, Jamshidi M, et al. MiR-34a expression has an effect for lower risk of metastasis and associates with expression patterns predicting clinical outcome in breast cancer. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e26122.
Article14. Dutta KK, Zhong Y, Liu YT, Yamada T, Akatsuka S, Hu Q, et al. Association of microRNA-34a overexpression with proliferation is cell type-dependent. Cancer Sci. 2007; 98:1845–1852.
Article15. Nugent M, Miller N, Kerin MJ. Circulating miR-34a levels are reduced in colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2012; 106:947–952.16. Javeri A, Ghaffarpour M, Taha MF, Houshmand M. Downregulation of miR-34a in breast tumors is not associated with either p53 mutations or promoter hypermethylation while it correlates with metastasis. Med Oncol. 2013; 30:413.
Article17. Tao WY, Wang CY, Sun YH, Su YH, Pang D, Zhang GQ. MicroRNA-34c suppresses breast cancer migration and invasion by targeting GIT1. J Cancer. 2016; 7:1653–1662.
Article18. Yang S, Li Y, Gao J, Zhang T, Li S, Luo A, et al. MicroRNA-34 suppresses breast cancer invasion and metastasis by directly targeting Fra-1. Oncogene. 2013; 32:4294–4303.
Article19. Achari C, Winslow S, Ceder Y, Larsson C. Expression of miR-34c induces G2/M cell cycle arrest in breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 2014; 14:538.
Article20. Yu F, Jiao Y, Zhu Y, Wang Y, Zhu J, Cui X, et al. MicroRNA 34c gene down-regulation via DNA methylation promotes self-renewal and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast tumor-initiating cells. J Biol Chem. 2012; 287:465–473.
Article21. Svoboda M, Sana J, Redova M, Navratil J, Palacova M, Fabian P, et al. MiR-34b is associated with clinical outcome in triple-negative breast cancer patients. Diagn Pathol. 2012; 7:31.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- miR-205 and miR-200c: Predictive Micro RNAs for Lymph Node Metastasis in Triple Negative Breast Cancer
- Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognosis of Early Stage Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Comparison with Non-triple Negative Group
- Treatment Outcomes of Weakly Positive Hormone Receptor Breast Cancer and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- High MicroRNA-370 Expression Correlates with Tumor Progression and Poor Prognosis in Breast Cancer
- miR-195/miR-497 Regulate CD274 Expression of Immune Regulatory Ligands in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer