J Breast Cancer.
2014 Jun;17(2):143-148.
miR-205 and miR-200c: Predictive Micro RNAs for Lymph Node Metastasis in Triple Negative Breast Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, GATA Haydarpasa Training Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey. patologub@gmail.com
Abstract
- PURPOSE
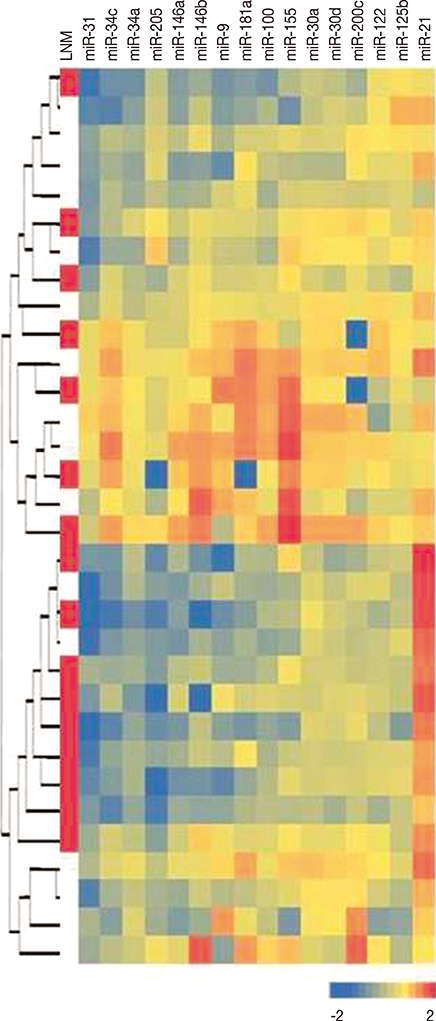
We examined expression profiles of 16 micro RNAs (miRNAs) in triple negative breast cancers to identify their potential as biomarkers for lymph node metastasis.
METHODS
The expression profiles of miR-9, miR-21, miR-30a, miR-30d, miR-31, miR-34a, miR-34c, miR-100, miR-122, miR-125b, miR-146a, miR-146b, miR-155, miR-181a, miR-200c, and miR-205 were examined by using real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction in tumor samples and corresponding benign breast tissues. Their associations with histopathological features and prognostic parameters were assessed.
RESULTS
When compared with the expression in benign breast tissues, seven of the miRNAs (miR-31, miR-205, miR-34a, miR-146a, miR-125b, miR-34c, and miR-181a) were downregulated more than 1.5-fold in tumor tissues, whereas, only miR-21 was found to be upregulated more than 1.5-fold in tumor tissues. Although miR-200c levels were decreased only 1.12-fold in tumor tissues, the reduced expressions of miR-200c and miR-205 were significantly associated with lymph node metastasis (p=0.021 and p=0.016, respectively).
CONCLUSION
Our results demonstrate that miR-205 and miR-200c expression levels may be useful in predicting lymph node metastasis in triple negative breast cancer patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fabian MR, Sonenberg N. The mechanics of miRNA-mediated gene silencing: a look under the hood of miRISC. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012; 19:586–593.
Article2. Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006; 103:2257–2261.
Article3. Tang J, Ahmad A, Sarkar FH. The role of microRNAs in breast cancer migration, invasion and metastasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2012; 13:13414–13437.
Article4. Harris L, Fritsche H, Mennel R, Norton L, Ravdin P, Taube S, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology 2007 update of recommendations for the use of tumor markers in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:5287–5312.
Article5. Dawson SJ, Provenzano E, Caldas C. Triple negative breast cancers: clinical and prognostic implications. Eur J Cancer. 2009; 45:Suppl 1. 27–40.
Article6. Rakha EA, Reis-Filho JS, Ellis IO. Basal-like breast cancer: a critical review. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:2568–2581.
Article7. Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001; 25:402–408.
Article8. Valastyan S, Reinhardt F, Benaich N, Calogrias D, Szász AM, Wang ZC, et al. A pleiotropically acting microRNA, miR-31, inhibits breast cancer metastasis. Cell. 2009; 137:1032–1046.
Article9. Augoff K, McCue B, Plow EF, Sossey-Alaoui K. miR-31 and its host gene lncRNA LOC554202 are regulated by promoter hypermethylation in triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 2012; 11:5.
Article10. Wu H, Zhu S, Mo YY. Suppression of cell growth and invasion by miR-205 in breast cancer. Cell Res. 2009; 19:439–448.
Article11. Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G, et al. The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 2008; 10:593–601.
Article12. Radojicic J, Zaravinos A, Vrekoussis T, Kafousi M, Spandidos DA, Stathopoulos EN. MicroRNA expression analysis in triple-negative (ER, PR and Her2/neu) breast cancer. Cell Cycle. 2011; 10:507–517.
Article13. Savad S, Mehdipour P, Miryounesi M, Shirkoohi R, Fereidooni F, Mansouri F, et al. Expression analysis of MiR-21, MiR-205, and MiR-342 in breast cancer in Iran. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012; 13:873–877.
Article14. Wellner U, Schubert J, Burk UC, Schmalhofer O, Zhu F, Sonntag A, et al. The EMT-activator ZEB1 promotes tumorigenicity by repressing stemness-inhibiting microRNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 2009; 11:1487–1495.
Article15. Wu X, Somlo G, Yu Y, Palomares MR, Li AX, Zhou W, et al. De novo sequencing of circulating miRNAs identifies novel markers predicting clinical outcome of locally advanced breast cancer. J Transl Med. 2012; 10:42.
Article16. Roth C, Rack B, Müller V, Janni W, Pantel K, Schwarzenbach H. Circulating microRNAs as blood-based markers for patients with primary and metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2010; 12:R90.
Article17. Lee JA, Lee HY, Lee ES, Kim I, Bae JW. Prognostic implications of microRNA-21 overexpression in invasive ductal carcinomas of the breast. J Breast Cancer. 2011; 14:269–275.
Article18. Ouzounova M, Vuong T, Ancey PB, Ferrand M, Durand G, Le-Calvez Kelm F, et al. MicroRNA miR-30 family regulates non-attachment growth of breast cancer cells. BMC Genomics. 2013; 14:139.
Article19. Zeng RC, Zhang W, Yan XQ, Ye ZQ, Chen ED, Huang DP, et al. Down-regulation of miRNA-30a in human plasma is a novel marker for breast cancer. Med Oncol. 2013; 30:477.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Significance of MicroRNA Let-7b, miR-30c, and miR-200c Expression in Breast Cancers
- LncRNA DLG1-AS1 Promotes Cancer Cell Proliferation in Triple Negative Breast Cancer by Downregulating miR-203
- Low Expression of Circulating MicroRNA-34c is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Advantages of Restoring miR-205-3p Expression for Better Prognosis of Gastric Cancer via Prevention of Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition
- MicroRNA-200c as a Prognostic Biomarker for Pancreatic Cancer