Cancer Res Treat.
2018 Jul;50(3):658-669. 10.4143/crt.2017.134.
BCL2 Regulation according to Molecular Subtype of Breast Cancer by Analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas Database
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. kiterius@snu.ac.kr
- 2Division of Clinical Bioinformatics, Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Biostatistics, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Pathology, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Radiology, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Internal Medicine, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2417855
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2017.134
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We investigated B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL2) regulation across DNA, RNA, protein, and methylation status according to molecular subtype of breast cancer using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We analyzed clinical and biological data on 1,096 breast cancers from the TCGA database. Biological data included reverse phase protein array (RPPA), mRNA sequencing (mRNA-seq), mRNA microarray, methylation, copy number alteration linear, copy number alteration nonlinear, and mutation data.
RESULTS
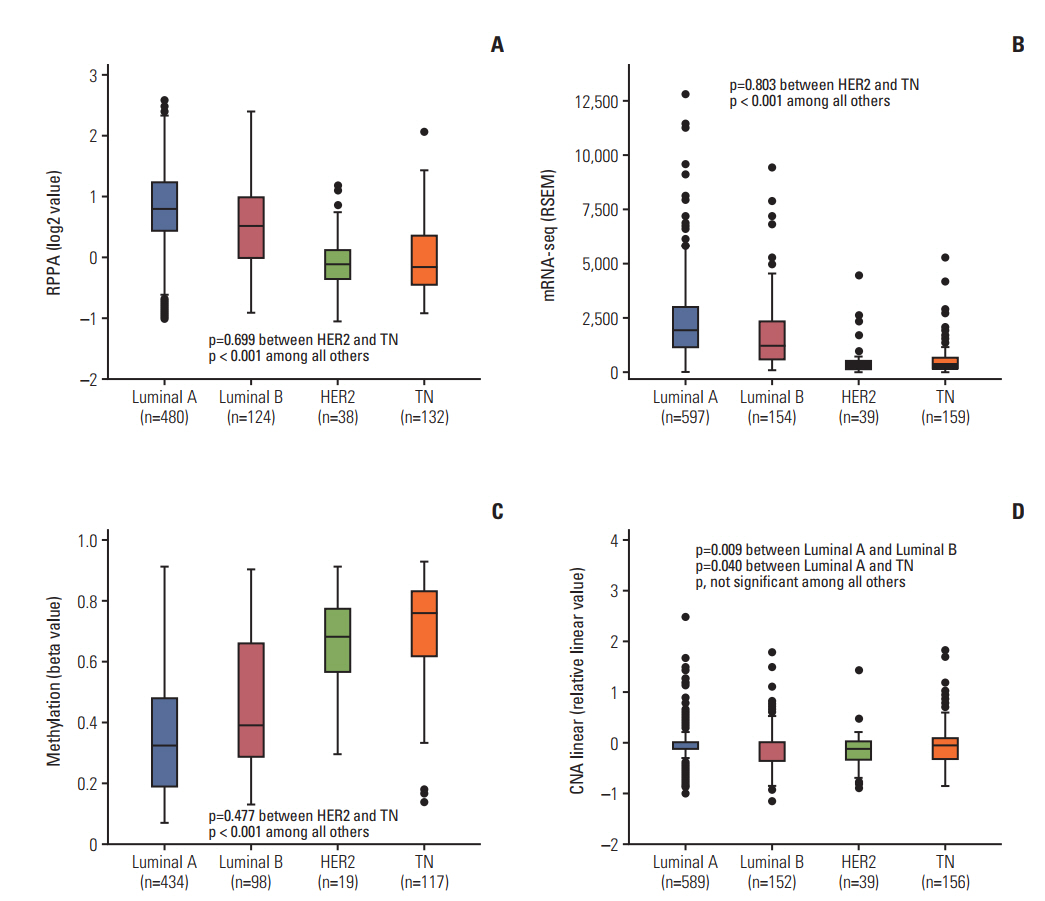
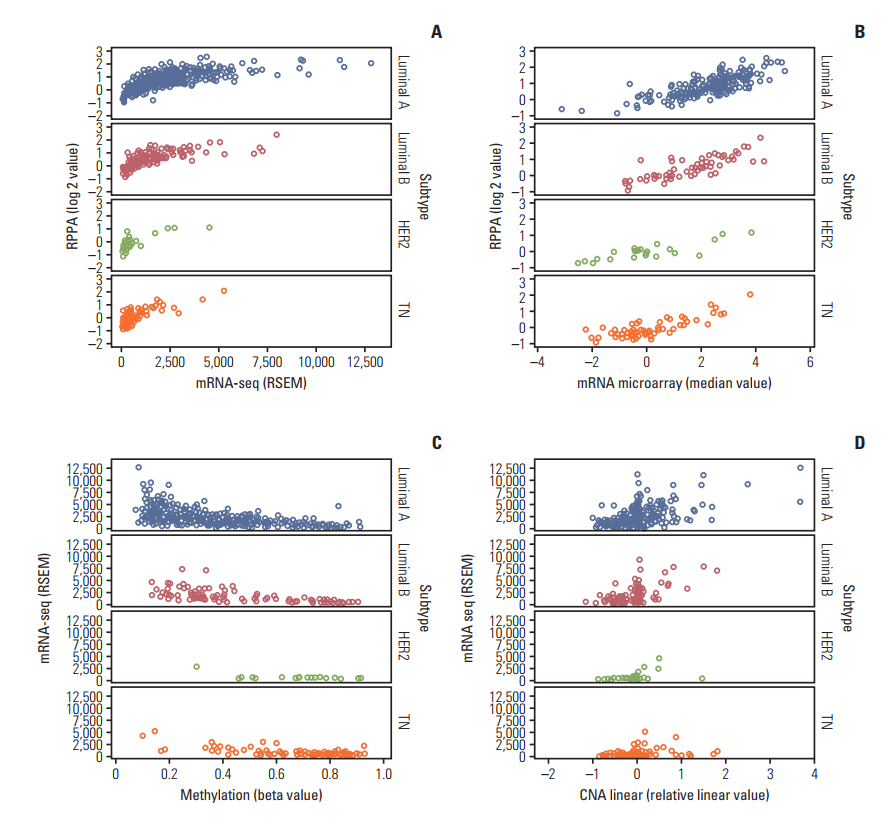
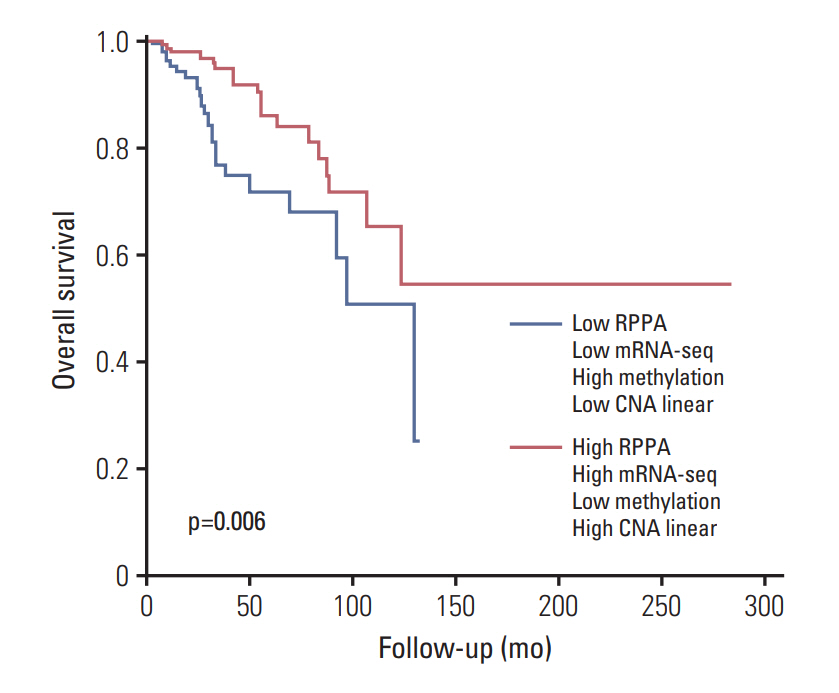
The luminal A and luminal B subtypes showed upregulated expression of RPPA and mRNAseq and hypomethylation compared to the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) and triple-negative subtypes (all p < 0.001). No mutations were found in any subjects. High mRNA-seq and high RPPA were strongly associated with positive estrogen receptor, positive progesterone receptor (all p < 0.001), and negative HER2 (p < 0.001 and p=0.002, respectively). Correlation analysis revealed a strong positive correlation between protein and mRNA levels and a strong negative correlation between methylation and protein and mRNA levels (all p < 0.001). The high BCL2 group showed superior overall survival compared to the low BCL2 group (p=0.006).
CONCLUSION
The regulation of BCL2 was mainly associated with methylation across the molecular subtypes of breast cancer, and luminal A and luminal B subtypes showed upregulated expression of BCL2 protein, mRNA, and hypomethylation. Although copy number alteration may have played a minor role, mutation status was not related to BCL2 regulation. Upregulation of BCL2 was associated with superior prognosis than downregulation of BCL2.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Breast Neoplasms*
Breast*
DNA
Down-Regulation
Estrogens
Gene Expression Regulation
Genome*
Humans
Lymphoma, B-Cell
Methylation
Phenobarbital
Prognosis
Protein Array Analysis
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
Receptors, Progesterone
RNA
RNA, Messenger
Up-Regulation
DNA
Estrogens
Phenobarbital
RNA
RNA, Messenger
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
Receptors, Progesterone
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ebrahim AS, Sabbagh H, Liddane A, Raufi A, Kandouz M, Al-Katib A. Hematologic malignancies: newer strategies to counter the BCL-2 protein. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016; 142:2013–22.
Article2. Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A, Adams JM. Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family: implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014; 15:49–63.
Article3. Tsujimoto Y, Finger LR, Yunis J, Nowell PC, Croce CM. Cloning of the chromosome breakpoint of neoplastic B cells with the t(14;18) chromosome translocation. Science. 1984; 226:1097–9.
Article4. Cleary ML, Smith SD, Sklar J. Cloning and structural analysis of cDNAs for bcl-2 and a hybrid bcl-2/immunoglobulin transcript resulting from the t(14;18) translocation. Cell. 1986; 47:19–28.
Article5. Tzifi F, Economopoulou C, Gourgiotis D, Ardavanis A, Papa-georgiou S, Scorilas A. The role of BCL2 family of apoptosis regulator proteins in acute and chronic leukemias. Adv Hematol. 2012; 2012:524308.
Article6. Martin B, Paesmans M, Berghmans T, Branle F, Ghisdal L, Mascaux C, et al. Role of Bcl-2 as a prognostic factor for survival in lung cancer: a systematic review of the literature with meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. 2003; 89:55–64.
Article7. Cheng H, Wang X, Li T, Chen L. Bcl-2 expression and patient survival in gastric cancer: a systematic review of the literature with meta-analysis. Med Oncol. 2015; 32:389.
Article8. Zhao L, Yu N, Guo T, Hou Y, Zeng Z, Yang X, et al. Tissue biomarkers for prognosis of prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014; 23:1047–54.
Article9. Correia C, Lee SH, Meng XW, Vincelette ND, Knorr KL, Ding H, et al. Emerging understanding of Bcl-2 biology: implications for neoplastic progression and treatment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015; 1853:1658–71.
Article10. Delbridge AR, Grabow S, Strasser A, Vaux DL. Thirty years of BCL-2: translating cell death discoveries into novel cancer therapies. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016; 16:99–109.
Article11. Dawson SJ, Makretsov N, Blows FM, Driver KE, Provenzano E, Le Quesne J, et al. BCL2 in breast cancer: a favourable prognostic marker across molecular subtypes and independent of adjuvant therapy received. Br J Cancer. 2010; 103:668–75.
Article12. Callagy GM, Webber MJ, Pharoah PD, Caldas C. Meta-analysis confirms BCL2 is an independent prognostic marker in breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2008; 8:153.
Article13. Hwang KT, Woo JW, Shin HC, Kim HS, Ahn SK, Moon HG, et al. Prognostic influence of BCL2 expression in breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 2012; 131:E1109–19.
Article14. Hwang KT, Han W, Kim J, Moon HG, Oh S, Song YS, et al. Prognostic influence of BCL2 on molecular subtypes of breast cancer. J Breast Cancer. 2017; 20:54–64.
Article15. Seong MK, Lee JY, Byeon J, Sohn YJ, Seol H, Lee JK, et al. Bcl- 2 is a highly significant prognostic marker of hormone-receptor- positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015; 150:141–8.16. McDonnell TJ, Korsmeyer SJ. Progression from lymphoid hyperplasia to high-grade malignant lymphoma in mice transgenic for the t(14; 18). Nature. 1991; 349:254–6.17. Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, Weinstein JN, Collisson EA, Mills GB, Shaw KR, Ozenberger BA, et al. The Cancer Genome Atlas Pan-Cancer analysis project. Nat Genet. 2013; 45:1113–20.
Article18. Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2012; 490:61–70.19. Ciriello G, Gatza ML, Beck AH, Wilkerson MD, Rhie SK, Pastore A, et al. Comprehensive molecular portraits of invasive lobular breast cancer. Cell. 2015; 163:506–19.20. Chang JT, Wang F, Chapin W, Huang RS. Identification of microRNAs as breast cancer prognosis markers through The Cancer Genome Atlas. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0168284.
Article21. Ma CX, Ellis MJ. The Cancer Genome Atlas: clinical applications for breast cancer. Oncology (Williston Park). 2013; 27:1263–9.22. Bouchalova K, Kharaishvili G, Bouchal J, Vrbkova J, Megova M, Hlobilkova A. Triple negative breast cancer: BCL2 in prognosis and prediction. Review. Curr Drug Targets. 2014; 15:1166–75.23. Park SH, Kim H, Song BJ. Down regulation of bcl2 expression in invasive ductal carcinomas is both estrogen- and progesterone- receptor dependent and associated with poor prognostic factors. Pathol Oncol Res. 2002; 8:26–30.24. Bhargava V, Kell DL, van de Rijn M, Warnke RA. Bcl-2 immunoreactivity in breast carcinoma correlates with hormone receptor positivity. Am J Pathol. 1994; 145:535–40.25. Doglioni C, Dei Tos AP, Laurino L, Chiarelli C, Barbareschi M, Viale G. The prevalence of BCL-2 immunoreactivity in breast carcinomas and its clinicopathological correlates, with particular reference to oestrogen receptor status. Virchows Arch. 1994; 424:47–51.
Article26. Chen LY, Tsang JY, Ni YB, Chan SK, Chan KF, Zhang S, et al. Bcl2 and Ki67 refine prognostication in luminal breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015; 149:631–43.
Article27. Lee KH, Im SA, Oh DY, Lee SH, Chie EK, Han W, et al. Prognostic significance of bcl-2 expression in stage III breast cancer patients who had received doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel as adjuvant chemotherapy. BMC Cancer. 2007; 7:63.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prognostic influences of B-cell lymphoma 2–positive expression on late recurrence in breast cancer
- Prognostic Influence of BCL2 on Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer
- BCL2 as a Subtype-Specific Prognostic Marker for Breast Cancer
- Identification of Biomarkers for Breast Cancer Using Databases
- Downregulation of N-myc and STAT Interactor Protein Predicts Aggressive Tumor Behavior and Poor Prognosis in Invasive Ductal Carcinoma