J Korean Acad Conserv Dent.
2007 Nov;32(6):514-521.
Expression of P2X3 and its colocalization with trpv1 in the human dental pulp
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea. skykim@knu.ac.kr
Abstract
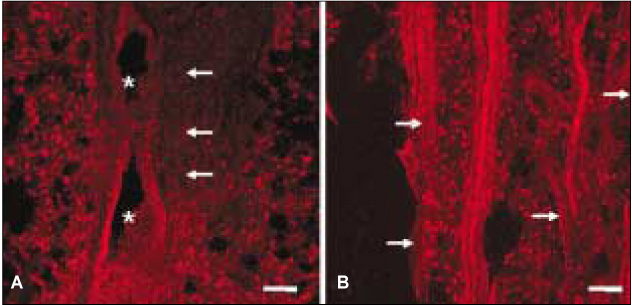
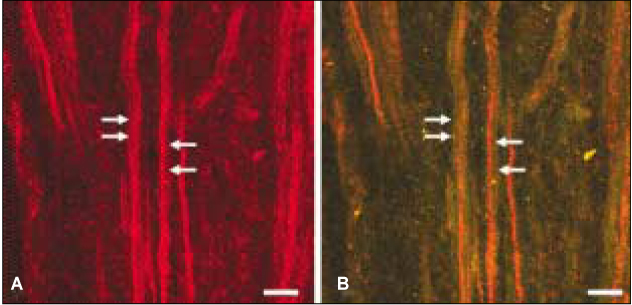
- The purinoreceptor, P2X3 is a ligand-gated cation channel activated by extracellular ATP. It has been reported that ATP can be released during inflammation and tissue damage, which in turn may activate P2X3 receptors to initiate nociceptive signals. However, little is known about the contribution of P2X3 to the dental pain during pulpal inflammation. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to investigate the expression of P2X3 and its colocalization with TRPV1 to understand the mechanism of pain transmission through P2X3 in the human dental pulp with double labeling immunofluorescence method. In the human dental pulp, intense P2X3 immunoreactivity was observed throughout the coronal and radicular pulp. Of all P2X3-positive fibers examined, 79.4% coexpressed TRPV1. This result suggests that P2X3 along with TRPV1 may be involved in the transmission of pain and potentiation of noxious stimuli during pulpal inflammation.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chen CC, Akopian AN, Sivilotti L, Colquhoun D, Burnstock G, Wood JN. A P2X purinoreceptor expressed by a subset of sensory neurons. Nature. 1995. 377(6548):428–431.
Article2. Caterina MJ, Schumacher MA, Tominaga M, Rosen TA, Levin JD, Julius D. The capsaicin receptor: A heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature. 1997. 389(6653):816–824.
Article3. Cook SP, Vulchanova L, Hargreaves KM, Wide R, McClesky EW. Distinct ATP receptors on pain-sensing and stretch-sensing neurons. Nature. 1997. 387(6632):505–508.
Article4. Dunn PM, Zhing Y, Burnstock G. P2X receptors in peripheral neurons. Prog neurobiol. 2001. 65:107–134.
Article5. North RA, Surprenant A. Pharmacology of cloned P2X receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2000. 40:563–580.
Article6. Ding Y, Cesare P, Drew L, Nikitaki D, Wood JN. ATP, P2X receptors and pain pathway. J Auton Nerv Syst. 2000. 81:289–294.7. Hamilton SG, Wade A, McMahon SB. The effect of inflammation and inflammatory mediators on nociceptive behaviour induced by ATP analogues in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1999. 126:326–332.8. Bo X, Alavi A, Xiang Z, Oglesby I, Ford A, Burnstock G. Localization of ATP-gated P2X2 and P2X3 receptor immunoreactive nerves in rat taste buds. Neuroreport. 1999. 10(5):1107–1111.9. North RA. P2X3 receptors and peripheral pain mechanism. J Physiol. 2004. 554(Pt 2):301–308.10. Llewellyn-Smith IJ, Burnstock G. Ultrastructural localization of P2X3 receptors in rat sensory neuron. Neuroreport. 1998. 9:2545–2550.
Article11. Ichikawa H, Fukunaga T, Jin HW, Fujita M, Takana-Yamamoto M, Sugimoto T. VR1- and VRL-1- and P2X3 receptor-immunoreactive innervation of the rat temporomandibular joint. Brain Res. 2004. 1008(1):131–136.12. Alavi AM, Dubyak GR, Burnstock G. Immunohistochemical evidence for ATP receptors in human dental pulp. J Dent Res. 2001. 80(2):476–483.
Article13. Renton T, Yiangou Y, Baecker PA, Ford AP, Anand P. Capsaicin receptor VR1 and ATP Purinoceptor P2X3 in painful and nonpainful human tooth pulp. J Orofac Pain. 2003. 17:245–250.14. Tominaga M, Caterina MJ, Malmberg AB, Rosen TA, Gilbert H, Skinner K, Raumann BE, Basbaum AI, Julius D. The cloned capsaicin receptor integrates multiple pain-producing stimuli. Neuron. 1998. 21:531–543.
Article15. Davis JB, Gray J, Gunthorpe MJ, Hatcher JP, Davey PT, Overend P, Harris MH, Latcham J, Clapham C, Atkinson K, Hugfes SA, Rance K, Grau E, Harper AJ, Pugf PL, Rogers DC, Bingham S, Randall A, Sheardown SA. Vanilloid receptor-1 is essential for inflammatory thermal hyperalgesia. Nature. 2000. 405:183–187.
Article16. Kim YK, Ma SK, Jin MU, Kim SK, Bae YC. The ultrastructure of TRPV1-positive nerve terminals in the human tooth pulp. Korean J Anat. 2006. 39(4):297–303.17. Kim YK, Kim SK. Immunocytochemical study on the expression of TRPV1 in the human dental pulp. J Korean Acad Endod. 2007. 8(1):79–87.18. Guo A, Vulchanova L, Wang J, Li X, Elde R. Immunocytochemical localization of the vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1): relationship to neuropeptides, the P2X3 purinoreceptor and IB4 binding sites. Eur J Neurosci. 1999. 11:946–958.
Article19. Ichikawa H, Sugimoto T. The co-expression of P2X3 receptors with VR1 and VRL-1 in the rat trigeminal ganglion. Brain Res. 2004. 998:130–135.
Article20. Kim YS, Paik SK, Cho YS, Shin HS, Bae JY, Moritani M, Yoshida A, Ahn DK, Valtschanoff J, Hwang SJ, Moon C, Bae YC. Expression of P2X3 receptor in the trigeminal sensory nuclei of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 2008. 506:627–639.
Article21. Bradbury EJ, Burnstock G, McMahon SB. The expression of P2X3 purinoreceptors in sensory neurons: effects of axotomy and glial derived neurotrophic factor. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1998. 12:256–268.
Article22. Brady CM, Apostolidis A, Yiangou Y, Baecker PA, Ford AP, Freeman A, Jacques TS, Fowler CJ, Anand P. P2X3-immunoreactive nerve fibers in neurogenic detrusor overactivity and the effect of intravesical resiniferatoxin. Eur Urol. 2004. 46:247–253.
Article23. Eriksson J, Bongenhielm U, Kidd E, Matthews B, Fried K. Distribution of P2X3 receptors in the rat trigeminal ganglion after inferior alveolar nerve injury. Neurosci lett. 1998. 254:37–40.
Article24. Bae YC, Ihn HJ, Park MJ, Ottersen OP, Moritani M, Yoshida A, Shigenaga Y. Identification of signal substances in synapses made between primary afferents and their associated axon terminals in the rat trigeminal sensory nuclei. J Comp Neurol. 2000. 418:299–309.
Article25. Johnson MD, Yee AG. Ultrastructure of electrophysiologically-characterized synapses formed by serotonergic raphe neurons in culture. Neuroscience. 1995. 67:609–623.
Article26. Tachibana M, Wenthold RJ, Morioka H, Petralia RS. Light and electron microscopic immunocytochemical localizaation of AMPA-selective glutamate receptors in the rat spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 1994. 344:431–454.
Article27. Jin YH, bailey TW, Li BY, Schild JH, Andresen MC. Purinergic and Vanilloid receptor activation releases glutamate from separate cranial afferent terminals in nucleus tractus solitatius. J Neurosci. 2004. 24(20):4709–4717.
Article28. Kim S. Neurovascular interaction in the dental pulp in health and inflammation. J Endod. 1990. 16:48–53.
Article29. Foreman JC, Jordan CC. Neurogenic inflammation. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1984. 5:116–119.
Article30. Barclay J, Patel S, Dorn G, Wotherspoon G, Moffatt S, Eunson L, Abdel'al S, Natt F, Hall J, Winter J, Bevans S, Wishart W, Fox A, Ganju P. Functional downregulation of P2X3 receptor subunit in rat sensory neurons reveals a significant role in chronic neuropathic and inflammatory pain. J Neurosci. 2002. 22(18):8139–8147.
Article31. Honore P, Mikusa J, Bianchi B, McDonald H, Cartmell J, Faltynek C, Jarvis MF. TNP-ATP, a potent P2X3 receptor antagonist, block acetic acid-induced abdominal constriction in mice: comparison with reference analgesics. Pain. 2002. 96:99–105.
Article32. Paukert M, Osteroth R, Geisler HS, Brandle U, Glowatzki E, Ruppersberg JP, Grunder S. Inflammatory mediators potentiate ATP-gated channels through the P2X3 subunit. J Biol Chem. 2001. 276:21077–21082.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Ultrastructure of TRPV1-positive Nerve Terminals in the Human Tooth Pulp
- Eugenol Inhibits ATP-induced P2X Currents in Trigeminal Ganglion Neurons
- Characterization of Human Dental Pulp Cells from Supernumerary Teeth by Using Flow Cytometry Analysis
- Effect of hypoxia on angiogenesis-related proteins in human dental pulp cells
- Dlx3 and Dlx5 Inhibit Adipogenic Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells