J Rhinol.
2018 May;25(1):1-6. 10.18787/jr.2018.25.1.1.
Epigenetic Regulation of Nasal Polyp Formation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. lhman@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2412913
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2018.25.1.1
Abstract
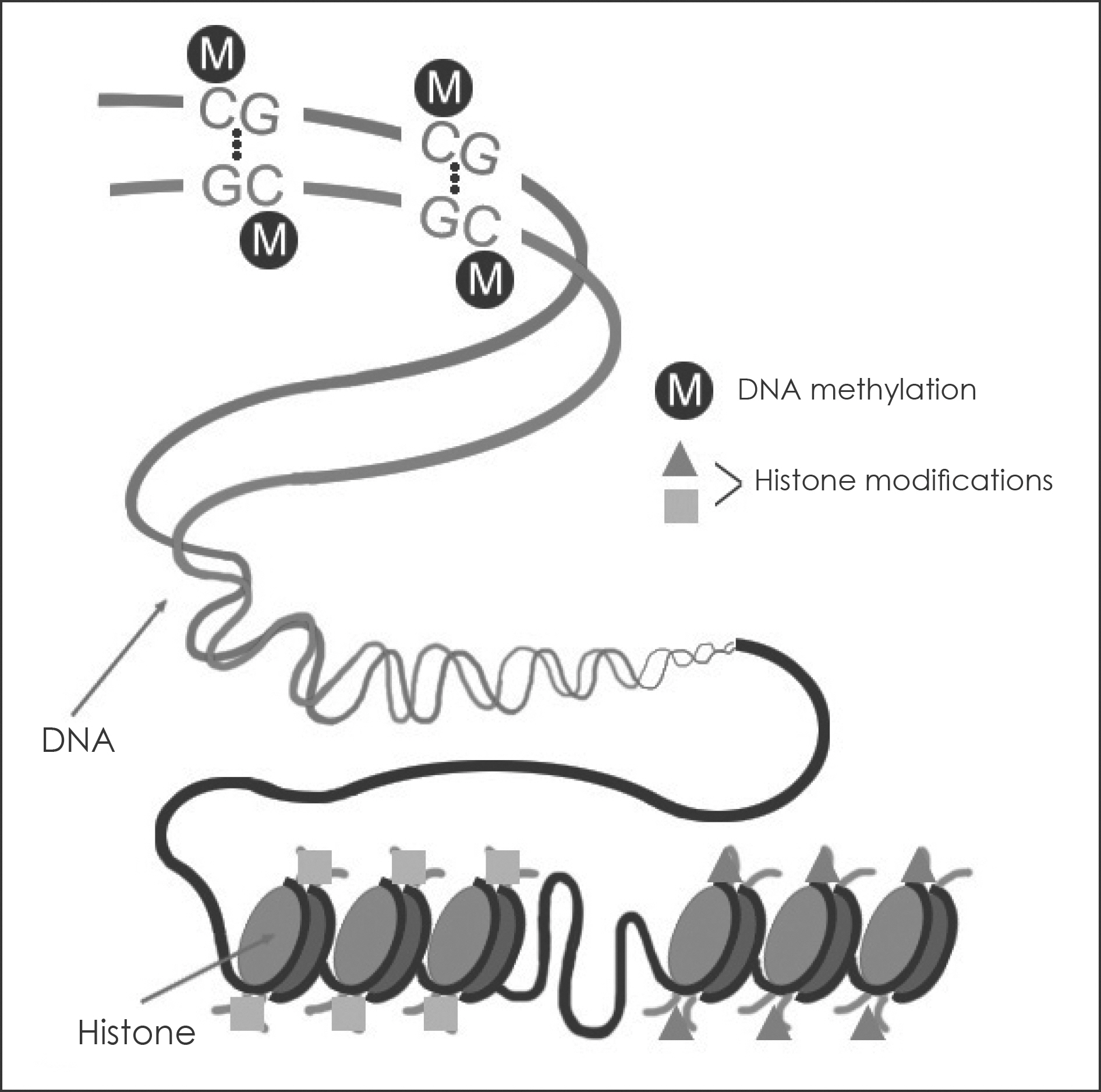
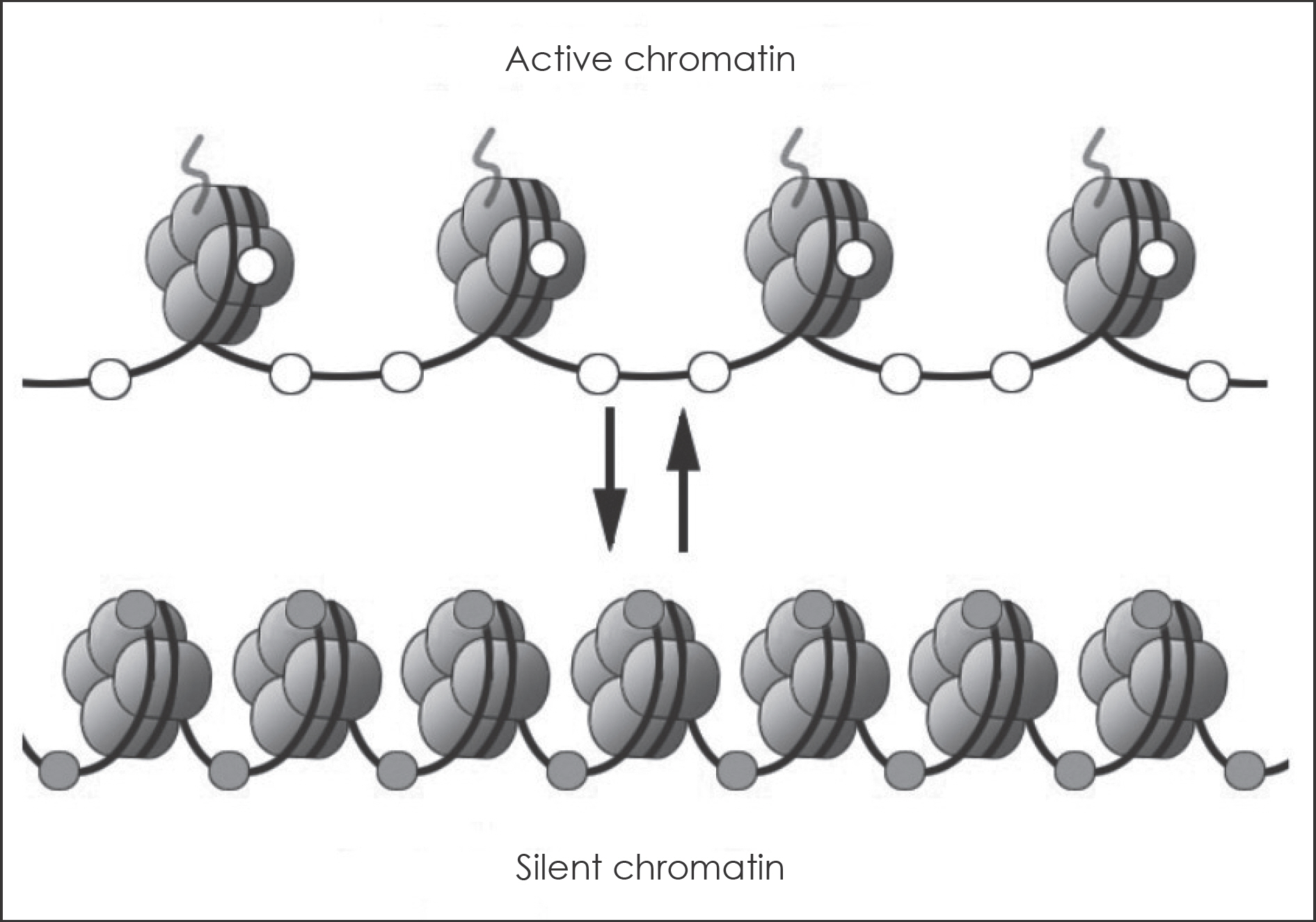
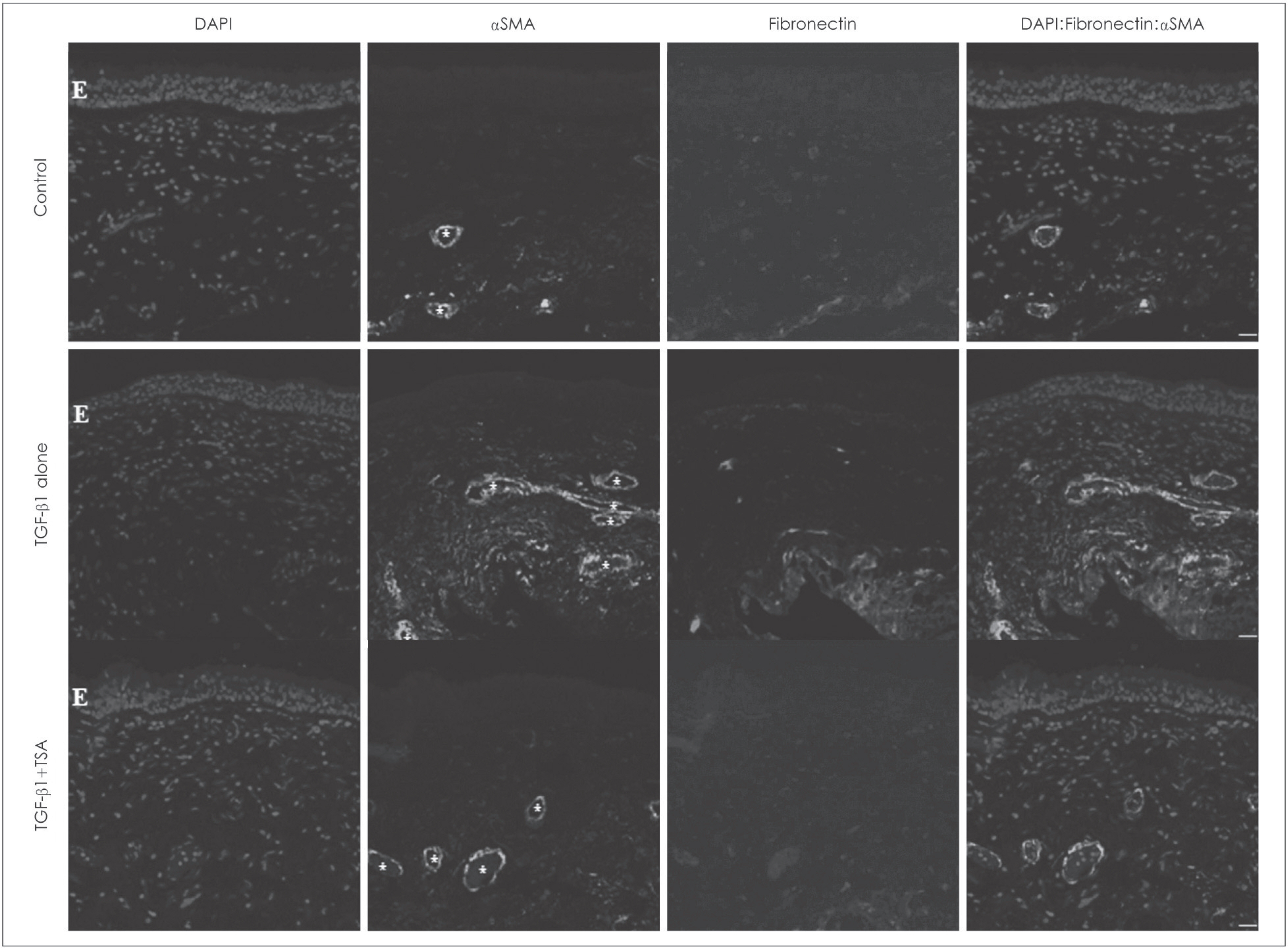
- Nasal polyposis is a multi-factorial disease associated with chronic inflammation of the paranasal sinuses. Myofibroblast differentiation and extracellular matrix (ECM) accumulation are involved in the pathogenesis of nasal polyposis. Epigenetics, DNA methylation, and chromatin modifications are critical for generating cellular diversity and for maintaining distinct gene expression profiles. Based on our recent study that evaluated the inhibitory effect of Trichostatin A on myofibroblast differentiation in nasal polyposis, we hypothesized that HDAC inhibition is associated with myofibroblast differentiation and extracellular matrix accumulation in nasal polyposis and suggested that Trischostatin A may be useful as an inhibitor of nasal polyp growth and thus has potential to be used as a novel treatment option for nasal polyposis. In this review, we present general concept of epigenetics and results of recent research that elucidate the role of epigenetics in the pathogenesis of nasal polyps.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Bird A. Perceptions of epigenetics. Nature. 2007. 447:396–8.
Article2). Fraga MF., Ballestar E., Paz MF., Ropero S., Setien F., Ballestar ML, et al. Epigenetic differences arise during the lifetime of monozygotic twins. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2005. 102:10604–9.3). Kaminsky ZA., Tang T., Wang SC., Ptak C., Oh GH., Wong AH, et al. DNA methylation profiles in monozygotic and dizygotic twins. Nature genetics. 2009. 41:240–5.
Article4). Portela A., Esteller M. Epigenetic modifications and human disease. Nature Biotechnology. 2010. 28:1057–68.
Article5). Straussman R., Nejman D., Roberts D., Steinfeld I., Blum B., Benvenisty N, et al. Developmental programming of CpG island methylation profiles in the human genome. Nature Structural & Molecular biology. 2009. 16:564–71.
Article6). Luger K., Mäder AW., Richmond RK., Sargent DF., Richmond TJ. Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 Å resolution. Nature. 1997. 389:251–60.7). Karlić R., Chung H-R., Lasserre J., Vlahoviček K., Vingron M. Histone modification levels are predictive for gene expression. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2010. 107:2926–31.
Article8). Bhaumik SR., Smith E., Shilatifard A. Covalent modifications of histones during development and disease pathogenesis. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology. 2007. 14:1008–16.
Article9). Schones DE., Cui K., Cuddapah S., Roh TY., Barski A., Wang Z, et al. Dynamic regulation of nucleosome positioning in the human genome. Cell. 2008. 132:887–98.
Article10). Chodavarapu RK., Feng S., Bernatavichute YV., Chen PY., Stroud H., Yu Y, et al. Relationship between nucleosome positioning and DNA methylation. Nature. 2010. 466:388–92.
Article11). Getun IV., Wu ZK., Khalil AM., Bois PR. Nucleosome occupancy landscape and dynamics at mouse recombination hotspots. EMBO reports. 2010. 11:555–60.
Article12). Lee SH. The Pathogenesis of Nasal Polyp. Journal of Rhinology. 2005. 12:6.13). Wang QP., Escudier E., Roudot-Thoraval F., Samad IAA., Peynègre R., Coste A. Myofibroblast Accumulation Induced by Transforming Growth Factor-β Is Involved in the Pathogenesis of Nasal Polyps. The Laryngoscope. 1997. 107:926–31.
Article14). Nakagawa HY., Nakai Yoshiaki., Shigeta Toshinobu., Takashima Tadayoshi., Zenju Takeda Takayuki. Comparative assessment of cell proliferation and accumulation of extracellular matrix in nasal polyps. Acta Oto-Laryngologica. 1998. 118:205–8.
Article15). Nonaka M., Pawankar R., Fukumoto A., Yagi T. Heterogeneous response of nasal and lung fibroblasts to transforming growth factor-β1. Clinical & Experimental Allergy. 2008. 38:812–21.
Article16). Pawankar R. Nasal polyposis: an update. Current Opinion in Allergy And Clinical Immunology. 2003. 3:1–6.
Article17). Bhavsar P., Ahmad T., Adcock IM. The role of histone deacetylases in asthma and allergic diseases. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2008. 121:580–4.
Article18). Noh H., Oh EY., Seo JY., Yu MR., Kim YO., Ha H, et al. Histone deacetylase-2 is a key regulator of diabetes-and transforming growth factor-β1-induced renal injury. American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology. 2009. 297:F729–39.19). Komorowsky C., Ocker M., Goppelt-Struebe M. Differential regulation of connective tissue growth factor in renal cells by histone deacetylase inhibitors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine. 2009. 13:2353–64.
Article20). Rombouts K., Niki T., Greenwel P., Vandermonde A., Wielant A., Hel-lemans K, et al. Trichostatin A, a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, Suppresses Collagen Synthesis and Prevents TGF-β< sub> 1</sub>-Induced Fibrogenesis in Skin Fibroblasts. Experimental Cell Research. 2002. 278:184–97.21). Ghosh AK., Mori Y., Dowling E., Varga J. Trichostatin A blocks TGF-β-induced collagen gene expression in skin fibroblasts: involvement of Sp1. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2007. 354:420–6.
Article22). Sharma A., Mehan MM., Sinha S., Cowden JW., Mohan RR. Trichostatin A inhibits corneal haze in vitro and in vivo. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 2009. 50:2695–701.
Article23). Guo W., Shan B., Klingsberg RC., Qin X., Lasky JA. Abrogation of TGF-β1-induced fibroblast-myofibroblast differentiation by histone deacetylase inhibition. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. 2009. 297:L864.
Article24). Cho JS., Moon YM., Park IH., Um JY., Moon JH., Park SJ, et al. Epigenetic regulation of myofibroblast differentiation and extracellular matrix production in nasal polyp-derived fibroblasts. Clinical & Experimental Allergy. 2012. 42:872–82.
Article25). Cho JS., Moon YM., Park IH., Um JY., Kang JH., Kim TH, et al. Effects of histone deacetylase inhibitor on extracellular matrix production in human nasal polyp organ cultures. American Journal of Rhinology & Allergy. 2013. 27:18–23.
Article26). Pérez-Novo CA., Zhang Y., Denil S., Trooskens G., De Meyer T., Van Criekinge W, et al. Staphylococcal enterotoxin B influences the DNA methylation pattern in nasal polyp tissue: a preliminary study. Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology. 2013. 9:48.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Local Production of IgE in Nasal Polyp
- Nasopharynx Obstruction by Huge Nasal Polyp with Metaplastic Ossification
- Recurrent Bacterial Meningitis Associated with Inflammatory Nasal Polyp
- Detection of Staphylococcus Aureus Exotoxins(SEA, TSST-1) in Nasal Polyp with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Patients
- Epigenetic regulation and chromatin remodeling in learning and memory