J Vet Sci.
2017 Jun;18(2):159-167. 10.4142/jvs.2017.18.2.159.
Immunogenicity of recombinant Lactobacillus plantarum NC8 expressing goose parvovirus VP2 gene in BALB/c mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Animal Science and Technology, Jilin Provincial Engineering Research Center of Animal Probiotics, Jilin Agricultural University, Changchun 130118, China. yangguilian@jlau.edu.cn, wangchunfeng@jlau.edu.cn
- 2Shandong Baolai-leelai Bioengineering Co. Ltd, Taian 271000, China.
- KMID: 2412568
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2017.18.2.159
Abstract
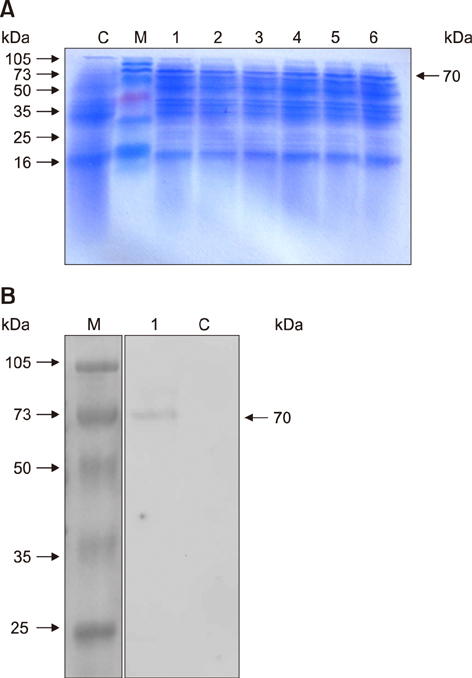
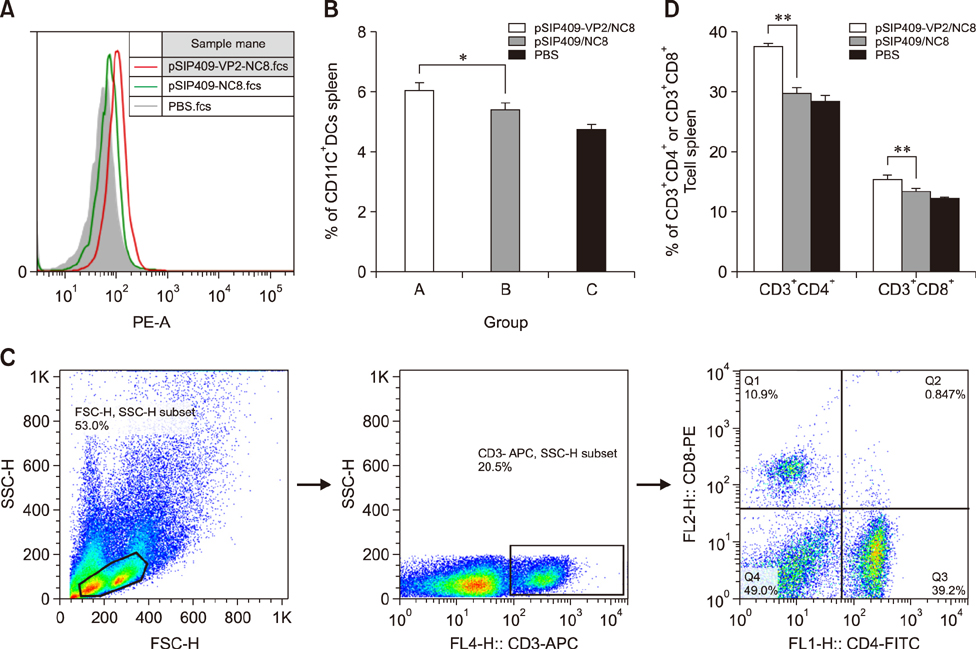
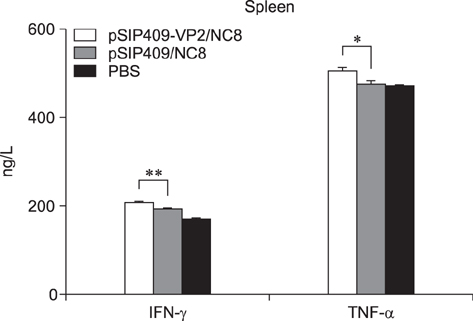
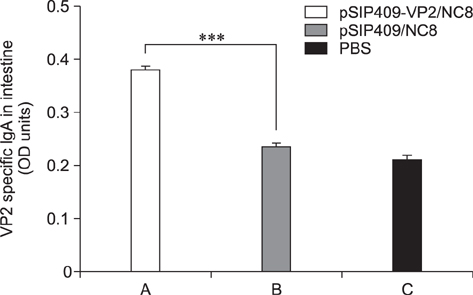
- Goose parvovirus (GPV) continues to be a threat to goose farms and has significant economic effects on the production of geese. Current commercially available vaccines only rarely prevent GPV infection. In our study, Lactobacillus (L.) plantarum NC8 was selected as a vector to express the VP2 gene of GPV, and recombinant L. plantarum pSIP409-VP2/NC8 was successfully constructed. The molecular weight of the expressed recombinant protein was approximately 70 kDa. Mice were immunized with a 2 × 109 colony-forming unit/200 µL dose of the recombinant L. plantarum strain, and the ratios and numbers of CD11câº, CD3âºCD4âº, CD3âºCD8âº, and interferon gamma- and tumor necrosis factor alpha-expressing spleen lymphocytes in the pSIP409-VP2/NC8 group were higher than those in the control groups. In addition, we assessed the capacity of L. plantarum SIP409-VP2/NC8 to induce secretory IgA production. We conclude that administered pSIP409-VP2/NC8 leads to relatively extensive cellular responses. This study provides information on GPV infection and offers a clear framework of options available for GPV control strategies.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Female
Genes, Viral/genetics
Immunity, Cellular/immunology
Immunoglobulin A, Secretory/immunology
Lactobacillus plantarum/genetics/*immunology/virology
Mice
Mice, Inbred BALB C
Organisms, Genetically Modified
Parvoviridae Infections/prevention & control/veterinary
Parvovirinae/*genetics
Recombinant Proteins/immunology
Vaccines, Synthetic/immunology/pharmacology
Viral Proteins/genetics/*immunology
Viral Vaccines/immunology/pharmacology
Immunoglobulin A, Secretory
Recombinant Proteins
Vaccines, Synthetic
Viral Proteins
Viral Vaccines
Figure
Reference
-
1. Axelsson L, Lindstad G, Naterstad K. Development of an inducible gene expression system for Lactobacillus sakei . Lett Appl Microbiol. 2003; 37:115–120.
Article2. Axelsson L, Rud I, Naterstad K, Blom H, Renckens B, Boekhorst J, Kleerebezem M, van Hijum S, Siezen RJ. Genome sequence of the naturally plasmid-free Lactobacillus plantarum strain NC8 (CCUG 61730). J Bacteriol. 2012; 194:2391–2392.
Article3. Banchereau J, Steinman RM. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature. 1998; 392:245–252.
Article4. Brown KE, Green SW, Young NS. Goose parvovirus—an autonomous member of the dependovirus genus. Virology. 1995; 210:283–291.
Article5. Chen Z, Li C, Zhu Y, Wang B, Meng C, Liu G. Immunogenicity of virus-like particles containing modified goose parvovirus VP2 protein. Virus Res. 2012; 169:306–309.
Article6. Cho HJ, Kim JY, Lee Y, Kim JM, Kim YB, Chun T, Oh YK. Enhanced humoral and cellular immune responses after sublingual immunization against human papillomavirus 16 L1 protein with adjuvants. Vaccine. 2010; 28:2598–2606.
Article7. de Roock S, van Elk M, van Dijk MEA, Timmerman HM, Rijkers GT, Prakken BJ, Hoekstra MO, de Kleer IM. Lactic acid bacteria differ in their ability to induce functional regulatory T cells in humans. Clin Exp Allergy. 2010; 40:103–110.
Article8. Dicks LM, Botes M. Probiotic lactic acid bacteria in the gastro-intestinal tract: health benefits, safety and mode of action. Benef Microbes. 2010; 1:11–29.
Article9. Dong H, Rowland I, Yaqoob P. Comparative effects of six probiotic strains on immune function in vitro . Br J Nutr. 2012; 108:459–470.
Article10. Doron S, Gorbach SL. Probiotics: their role in the treatment and prevention of disease. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2006; 4:261–275.
Article11. Drago L, Nicola L, Iemoli E, Banfi G, De Vecchi E. Strain-dependent release of cytokines modulated by Lactobacillus salivarius human isolates in an in vitro model. BMC Res Notes. 2010; 3:44.
Article12. Drakes M, Blanchard T, Czinn S. Bacterial probiotic modulation of dendritic cells. Infect Immun. 2004; 72:3299–3309.
Article13. Eijsink VG, Brurberg MB, Middelhoven PH, Nes IF. Induction of bacteriocin production in Lactobacillus sake by a secreted peptide. J Bacteriol. 1996; 178:2232–2237.
Article14. Everson MP, Lemak DG, McDuffie DS, Koopman WJ, McGhee JR, Beagley KW. Dendritic cells from Peyer's patch and spleen induce different T helper cell responses. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1998; 18:103–115.
Article15. Foligne B, Nutten S, Grangette C, Dennin V, Goudercourt D, Poiret S, Dewulf J, Brassart D, Mercenier A, Pot B. Correlation between in vitro and in vivo immunomodulatory properties of lactic acid bacteria. World J Gastroenterol. 2007; 13:236–243.
Article16. Fukushima Y, Kawata Y, Hara H, Terada A, Mitsuoka T. Effect of a probiotic formula on intestinal immunoglobulin A production in healthy children. Int J Food Microbiol. 1998; 42:39–44.
Article17. Gilbert C, Robinson K, Le Page RW, Wells JM. Heterologous expression of an immunogenic pneumococcal type 3 capsular polysaccharide in Lactococcus lactis . Infect Immun. 2000; 68:3251–3260.
Article18. Glávits R, Zolnai A, Szabó E, Ivanics E, Zarka P, Mató T, Palya V. Comparative pathological studies on domestic geese (Anser anser domestics) and Muscovy ducks (Cairina moschata) experimentally infected with parvovirus strains of goose and Muscovy duck origin. Acta Vet Hung. 2005; 531:73–89.19. Haan L, Verweij WR, Holtrop M, Brands R, van Scharrenburg GJM, Palache AM, Agsteribbe E, Wilschut J. Nasal or intramuscular immunization of mice with influenza subunit antigen and the B subunit of Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin induces IgA- or IgG-mediated protective mucosal immunity. Vaccine. 2001; 19:2898–2907.
Article20. Huang Z, Elankumaran S, Yunus AS, Samal SK. A recombinant Newcastle disease virus (NDV) expressing VP2 protein of infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV) protects against NDV and IBDV. J Virol. 2004; 78:10054–10063.
Article21. Jansson DS, Feinstein R, Kardi V, Mató T, Palya V. Epidemiologic investigation of an outbreak of goose parvovirus infection in Sweden. Avian Dis. 2007; 51:609–613.
Article22. Kikuchi Y, Kunitoh-Asari A, Hayakawa K, Imai S, Kasuya K, Abe K, Adachi Y, Fukudome S, Takahashi Y, Hachimura S. Oral administration of Lactobacillus plantarum strain AYA enhances IgA secretion and provides survival protection against influenza virus infection in mice. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e86416.23. Liu D, Lu H, Shi K, Su F, Li J, Du R. Immunogenicity of recombinant BCGs expressing predicted antigenic epitopes of bovine viral diarrhea virus E2 gene. Res Vet Sci. 2014; 97:430–438.
Article24. López P, Gueimonde M, Margolles A, Suárez A. Distinct Bifidobacterium strains drive different immune responses in vitro. Int J Food Microbiol. 2010; 138:157–165.
Article25. Maldonado A, Ruiz-Barba JL, Jiménez-Díaz R. Purification and genetic characterization of plantaricin NC8, a novel coculture-inducible two-peptide bacteriocin from Lactobacillus plantarum NC8. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003; 69:383–389.
Article26. Mercenier A, Pavan S, Pot B. Probiotics as biotherapeutic agents: present knowledge and future prospects. Curr Pharm Des. 2003; 9:175–191.
Article27. Park MJ, General T, Lee SP. Physicochemical properties of roasted soybean flour bioconverted by solid-state fermentation using Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus plantarum . Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2012; 17:36–45.
Article28. Poonia B, Dunn PA, Lu H, Jarosinski KW, Schat KA. Isolation and molecular characterization of a new Muscovy duck parvovirus from Muscovy ducks in the USA. Avian Pathol. 2006; 35:435–441.
Article29. Schultz M, Veltkamp C, Dieleman LA, Grenther WB, Wyrick PB, Tonkonogy SL, Sartor RB. Lactobacillus plantarum 299V in the treatment and prevention of spontaneous colitis in interleukin-10-deficient mice. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2002; 8:71–80.
Article30. Shi SH, Yang WT, Yang GL, Cong YL, Huang HB, Wang Q, Cai RP, Ye LP, Hu JT, Zhou JY, Wang CF, Li Y. Immunoprotection against influenza virus H9N2 by the oral administration of recombinant Lactobacillus plantarum NC8 expressing hemagglutinin in BALB/c mice. Virology. 2014; 464-465:166–176.
Article31. Sørvig E, Grönqvist S, Naterstad K, Mathiesen G, Eijsink VGH, Axelsson L. Construction of vectors for inducible gene expression in Lactobacillus sakei and L plantarum. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2003; 229:119–126.32. Sørvig E, Mathiesen G, Naterstad K, Eijsink VGH, Axelsson L. High-level, inducible gene expression in Lactobacillus sakei and Lactobacillus plantarum using versatile expression vectors. Microbiology. 2005; 151:2439–2449.
Article33. Spath K, Heinl S, Grabherr R. Direct cloning in Lactobacillus plantarum: electroporation with non-methylated plasmid DNA enhances transformation efficiency and makes shuttle vectors obsolete. Microb Cell Fact. 2012; 11:141.34. Tannock GW. A special fondness for lactobacilli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004; 70:3189–3194.35. Wang J, Cong Y, Yin R, Feng N, Yang S, Xia X, Xiao Y, Wang W, Liu X, Hu S, Ding C, Yu S, Wang C, Ding Z. Generation and evaluation of a recombinant genotype VII Newcastle disease virus expressing VP3 protein of goose parvovirus as a bivalent vaccine in goslings. Virus Res. 2015; 203:77–83.
Article36. Wang S, Cheng XX, Chen SY, Zhu XL, Chen SL, Lin FQ, Li ZL. Genetic characterization of a potentially novel goose parvovirus circulating in Muscovy duck flocks in Fujian province, China. J Vet Med Sci. 2013; 75:1127–1130.
Article37. Wang Z, Yu Q, Gao J, Yang Q. Mucosal and systemic immune responses induced by recombinant Lactobacillus spp. expressing the hemagglutinin of the avian influenza virus H5N1. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012; 19:174–179.
Article38. Xin KQ, Hoshino Y, Toda Y, Igimi S, Kojima Y, Jounai N, Ohba K, Kushiro A, Kiwaki M, Hamajima K, Klinman D, Okuda K. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of orally administered recombinant Lactococcus lactis expressing surface-bound HIV Env. Blood. 2003; 102:223–228.
Article39. Zhang Y, Li Y, Liu M, Zhang D, Guo D, Liu C, Zhi H, Wang X, Li G, Li N, Liu S, Xiang W, Tong G. Development and evaluation of a VP3-ELISA for the detection of goose and Muscovy duck parvovirus antibodies. J Virol Methods. 2010; 163:405–409.
Article40. Zhu Y, Zhou Z, Huang Y, Yu R, Dong S, Li Z, Zhang Y. Identification of a recombinant Muscovy duck parvovirus (MDPV) in Shanghai, China. Vet Microbiol. 2014; 174:560–564.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Immunogenicity of a Canine Parvovirus 2 Capsid Antigen (VP2-S1) surface-expressed on Lactobacillus casei
- Cloning and Recombinant Protein Expression of VP2 Gene of Human Parvovirus B19
- Adhesion Activity of Lactobacillus plantarum PM 008 Isolated from Kimchi on the Intestine of Mice
- Expression of the VP2 protein of feline panleukopenia virus in insect cells and use thereof in a hemagglutination inhibition assay
- Evaluation of modified vaccinia virus Ankara expressing VP2 protein of infectious bursal disease virus as an immunogen in chickens