J Bacteriol Virol.
2018 Mar;48(1):14-22. 10.4167/jbv.2018.48.1.14.
Characterization of Specific IgA Response to Antigenic Determinants of Helicobacter pylori Urease Encoded by ureA and ureB in Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, College of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea. wklee@gnu.kr seozee@gnu.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea. wklee@gnu.kr seozee@gnu.kr
- 3Department of Pathology, College of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- 4Research Institute of Life Science, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 2409050
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2018.48.1.14
Abstract
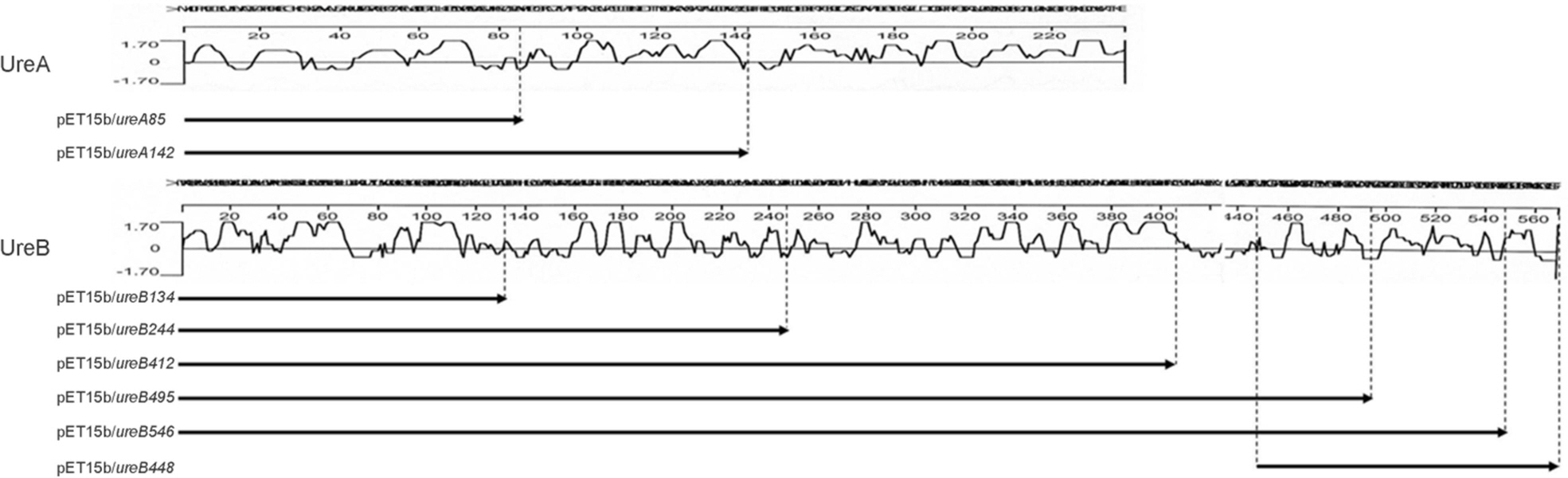
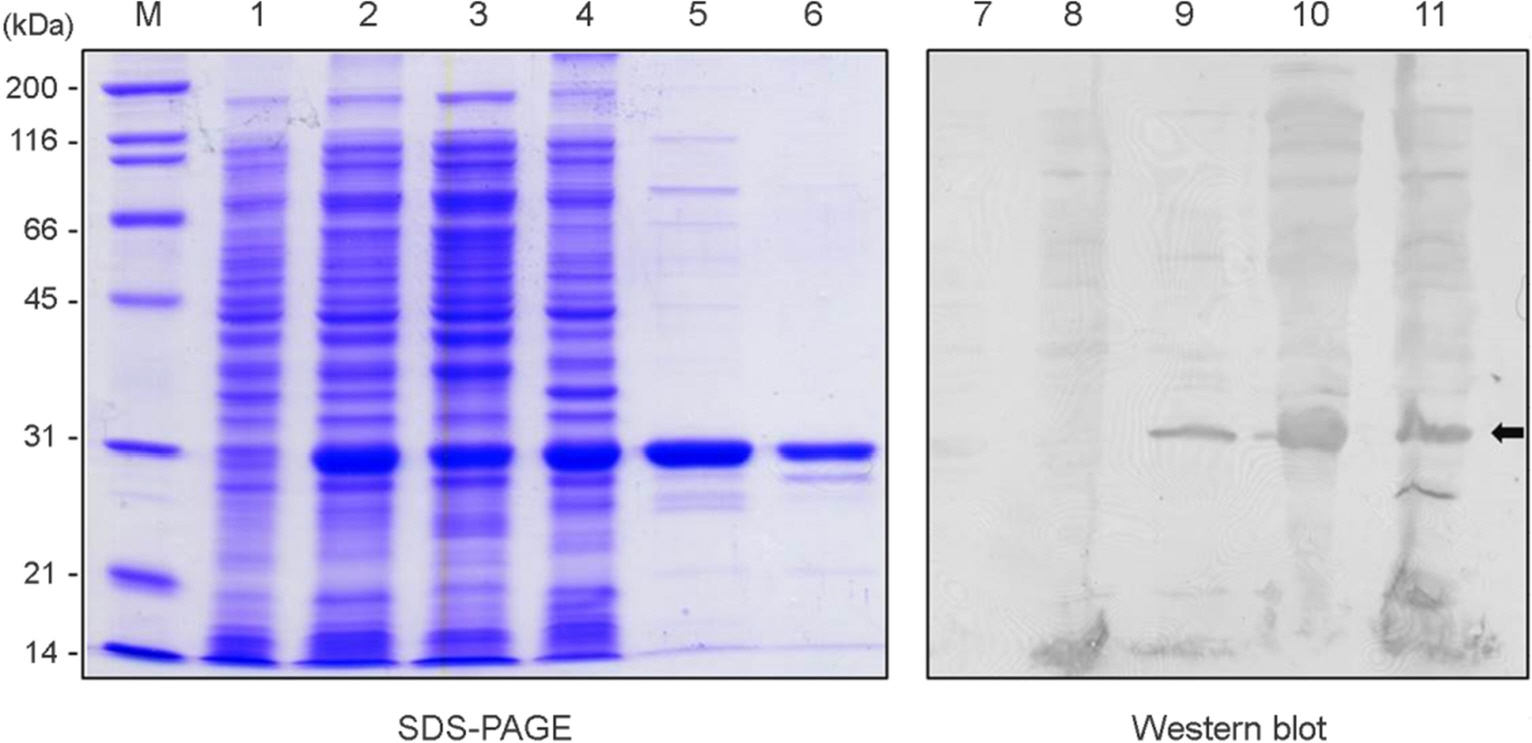
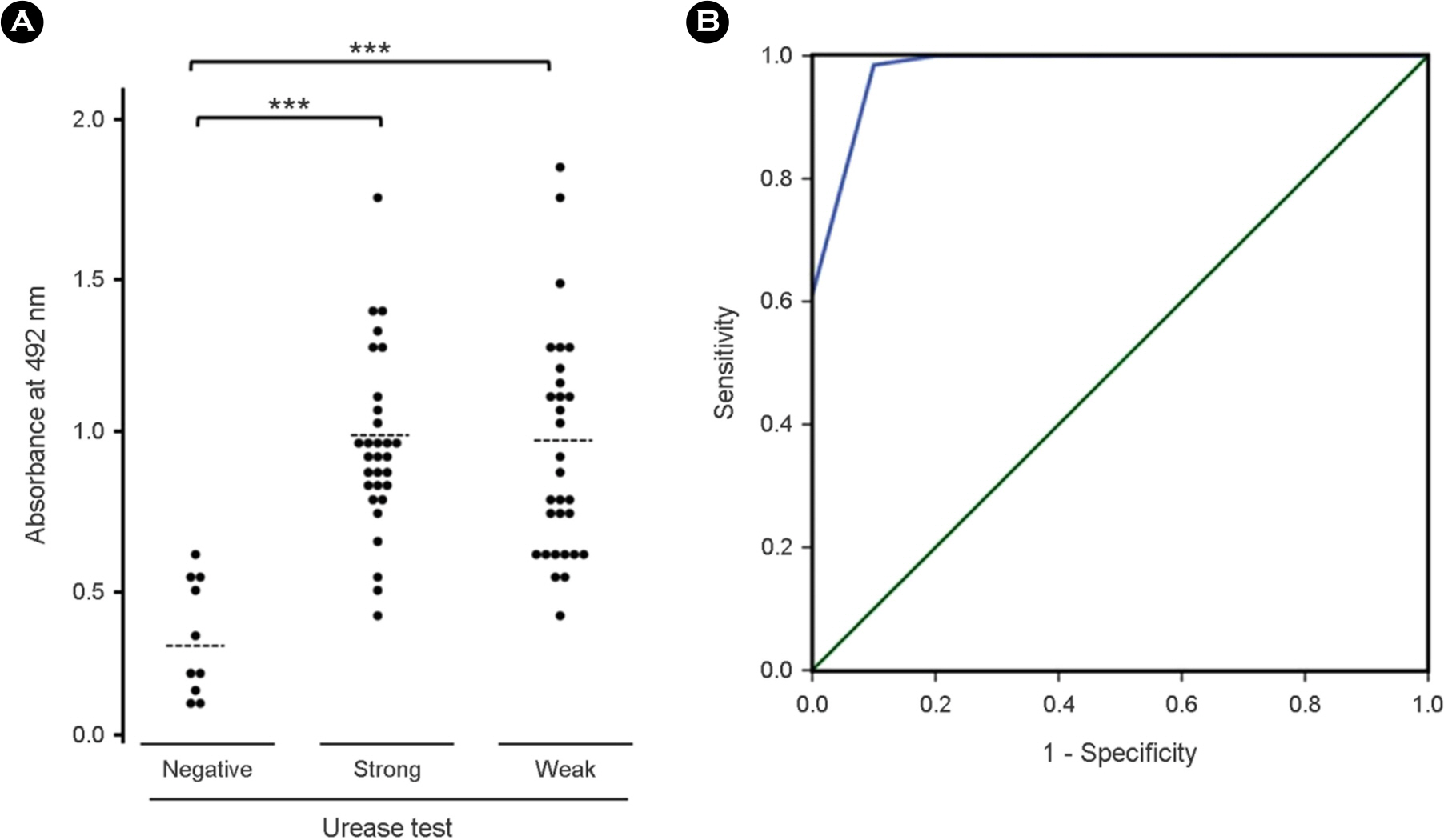
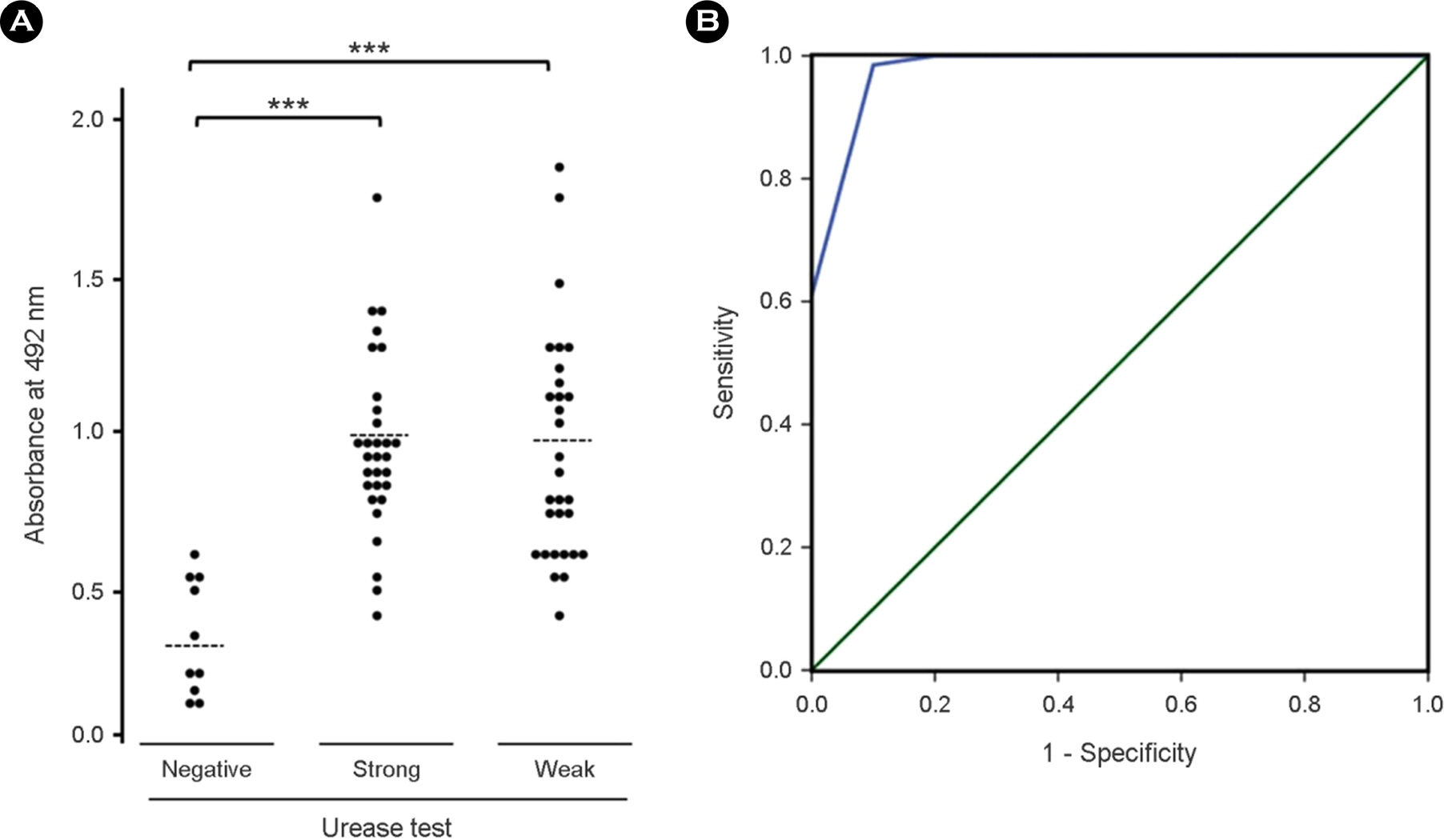
- Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), a causative agent of chronic gastritis and gastric cancer, has several virulent factors for own survival and progression toward gastric diseases in human stomach. Of those, H. pylori produces mainly urease (10~15% total protein weight) that neutralize the gastric acid for survival. Here, we identified the antigenic epitope of urease and then developed an ELISA using the antigen including the epitope of urease. We identified the antigenic epitope of urease that induces IgA antibodies in human using truncated mutants. Eight kinds of serially-truncated mutant of UreA and UreB were prepared and subjected to immunoblot using pooled sera of patients with gastric disorders. UreBEnd protein containing UreB epitope was produced and investigated its diagnostic value via ELISA in children. As a result, mutants having last 24 amino acid residues of UreB carboxyl terminus deleted did not show IgA-reactive band. The clones that contained the downstream of 448(th) amino acid in UreB showed IgA-reactive band. The serodiagnostic value of the UreBEnd recombinant protein including identified epitope was confirmed via IgA ELISA and shown to have 97% sensitivity and 100% specificity. These results demonstrated that carboxyl terminal region of UreB carries an antigenic epitope for IgA response in human. It may be useful for detecting H. pylori infection with improved test accuracy and minimum use of endoscopy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Marshall BJ, Warren JR. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet. 1984; 1:1311–5.
Article2). Jones KR, Whitmire JM, Merrell DS. A Tale of Two Toxins: Helicobacter pyloriCagA and VacA Modulate Host Pathways that Impact Disease. Front Microbiol. 2010; 1:115.
Article3). Hatakeyama M. Helicobacter pyloriCagA and gastric cancer: a paradigm for hit-and-run carcinogenesis. Cell Host Microbe. 2014; 15:306–16.4). Salih BA. Helicobacter pyloriinfection in developing countries: the burden for how long? Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2009; 15:201–7.
Article5). Ohkusa T, Okayasu I, Miwa H, Ohtaka K, Endo S, Sato N. Helicobacter pyloriinfection induces duodenitis and superficial duodenal ulcer in Mongolian gerbils. Gut. 2003; 52:797–803.6). Jang KM, Choe BH, Choe JY, Hong SJ, Park HJ, Chu MA, et al. Changing Prevalence of Helicobacter pyloriInfections in Korean Children with Recurrent Abdominal Pain. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2015; 18:10–6.7). Ben-Hur H, Gurevich P, Elhayany A, Avinoach I, Schneider DF, Zusman I. Transport of maternal immunoglobulins through the human placental barrier in normal pregnancy and during inflammation. Int J Mol Med. 2005; 16:401–7.
Article8). Veenendaal RA, Götz JM, Schroijen V, Kurban F, Bernards AT, Veselic M, et al. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pyloriinfection by specific gastric mucosal IgA and IgG pylori antibodies. J Clin Pathol. 1995; 48:990–3.9). IARC. Schistosomes, liver flukes and Helicobacter pylori. IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Lyon, 7–14 June 1994. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum. 1994; 61:1–241.10). Roesler BM, Rabelo-Goncalves EM, Zeitune JM. Virulence Factors of Helicobacter pylori: A Review. Clin Med Insights Gastroenterol. 2014; 7:9–17.
Article11). Wu C, Zou QM, Guo H, Yuan XP, Zhang WJ, Lu DS, et al. Expression, purification and immuno-characteristics of recombination UreB protein of H. pylori. World J Gastroenterol. 2001; 7:389–93.12). Hu LT, Mobley HL. Purification and N-terminal analysis of urease from Helicobacter pylori. Infect Immun. 1990; 58:992–8.
Article13). Seo JH, Park JS, Yeom JS, Lim JY, Park CH, Woo HO, et al. Correlation between positive rate and number of biopsy samples on urease test in childhood Helicobacter pyloriinfection. J Korean Med Sci. 2014; 29:106–9.14). Baik SC, Youn HS, Chung MH, Lee WK, Cho MJ, Ko GH, et al. Increased oxidative DNA damage in Helicobacter pylori-infected human gastric mucosa. Cancer Res. 1996; 56:1279–82.15). Ha NC, Oh ST, Sung JY, Cha KA, Lee MH, Oh BH. Supramolecular assembly and acid resistance of Helicobacter pylori urease. Nat Struct Biol. 2001; 8:505–9.16). Minkara MS, Ucisik MN, Weaver MN, Merz KM Jr. Molecular Dynamics Study of Helicobacter pyloriUrease. J Chem Theory Comput. 2014; 10:1852–62.17). Ghalehnoei H, Ahmadzadeh A, Farzi N, Alebouyeh M, Aghdaei HA, Azimzadeh P, et al. Relationship between ureB Sequence Diversity, Urease Activity and Genotypic Variations of Different Helicobacter pyloriStrains in Patients with Gastric Disorders. Pol J Microbiol. 2016; 65:153–9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Activation of Urease Apoprotein of Helicobacter pylori
- Purification of the urease of helicobacter pylori and production of monoclonal antibody to the urease of helicobacter pylori
- The Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori Infection
- Helicobacter pylori Stool Antigen Test for the Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection in Children
- Serologic Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori Gastritis in Children : Seroepidemiology of H. pylori in Normal School Children and Diagnostic Accuracy of IgG GAP Test in Children with Gastrointestinal Symptoms