J Breast Cancer.
2015 Sep;18(3):249-255. 10.4048/jbc.2015.18.3.249.
Potential Prognostic Value of Histone Deacetylase 6 and Acetylated Heat-Shock Protein 90 in Early-Stage Breast Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. inah228@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Breast Care Center, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2407572
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2015.18.3.249
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) is an enzyme that deacetylates heat-shock protein 90 (HSP90). Many studies have investigated the role of HDAC6 and HSP90 in tumorigenesis and in the prognosis of cancer patients. This study aimed to evaluate the prognostic value of HDAC6 and acetylated HSP90 (acetyl-HSP90) in a cohort of breast cancer patients.
METHODS
Immunohistochemical analysis of 314 surgical specimens obtained from patients with invasive breast cancer was carried out to assess standard pathologic factors and the expression of HDAC6 and acetyl-HSP90. Statistical analyses were performed to determine the association between HDAC6, acetyl-HSP90, and conventional clinicopathological factors, and the prognostic values of these factors were evaluated.
RESULTS
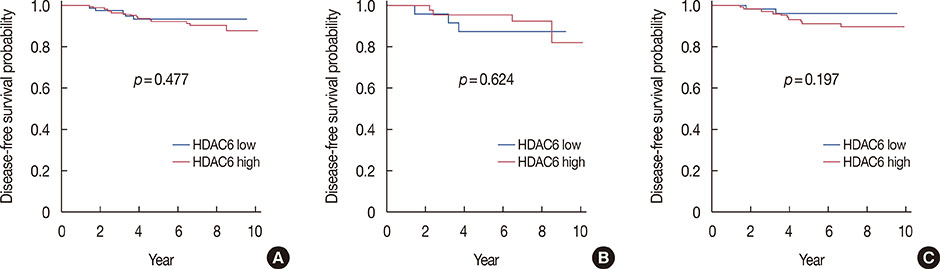
HDAC6 expression did not show any correlation with other clinicopathological factors, but acetyl-HSP90 was significantly correlated with histologic grade (p=0.001) and the Ki-67 index (p=0.015). HDAC6 and acetyl-HSP90 expression were significantly associated with each other (p=0.047). Although HDAC6 was not prognostic for disease-free survival (DFS), some patients with high expression of HDAC6 experienced recurrence 5 years after diagnosis, while there was no recurrent disease after 5 years in those with low expression. Acetyl-HSP90 was significantly associated with the DFS of all patients (p=0.016) and with high HDAC6 expression (p=0.017), but not with low expression.
CONCLUSION
Expression of HDAC6 and acetyl-HSP90 are correlated. HDAC6 is proposed to be a possible predictive marker of late recurrence, and acetyl-HSP90 has prognostic value in predicting the DFS of breast cancer patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cai FF, Kohler C, Zhang B, Wang MH, Chen WJ, Zhong XY. Epigenetic therapy for breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2011; 12:4465–4487.
Article2. Nwabo Kamdje AH, Seke Etet PF, Vecchio L, Tagne RS, Amvene JM, Muller JM, et al. New targeted therapies for breast cancer: a focus on tumor microenvironmental signals and chemoresistant breast cancers. World J Clin Cases. 2014; 2:769–786.
Article3. Duong V, Bret C, Altucci L, Mai A, Duraffourd C, Loubersac J, et al. Specific activity of class II histone deacetylases in human breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2008; 6:1908–1919.
Article4. Beliakoff J, Whitesell L. Hsp90: an emerging target for breast cancer therapy. Anticancer Drugs. 2004; 15:651–662.
Article5. Aldana-Masangkay GI, Sakamoto KM. The role of HDAC6 in cancer. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011; 2011:875824.
Article6. Lee YS, Lim KH, Guo X, Kawaguchi Y, Gao Y, Barrientos T, et al. The cytoplasmic deacetylase HDAC6 is required for efficient oncogenic tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2008; 68:7561–7569.
Article7. Yoshida M, Furumai R, Nishiyama M, Komatsu Y, Nishino N, Horinouchi S. Histone deacetylase as a new target for cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2001; 48:Suppl 1. S20–S26.
Article8. Zhang Z, Yamashita H, Toyama T, Sugiura H, Omoto Y, Ando Y, et al. HDAC6 expression is correlated with better survival in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2004; 10:6962–6968.
Article9. Saji S, Kawakami M, Hayashi S, Yoshida N, Hirose M, Horiguchi S, et al. Significance of HDAC6 regulation via estrogen signaling for cell motility and prognosis in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Oncogene. 2005; 24:4531–4539.
Article10. Yoshida N, Omoto Y, Inoue A, Eguchi H, Kobayashi Y, Kurosumi M, et al. Prediction of prognosis of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer with combination of selected estrogen-regulated genes. Cancer Sci. 2004; 95:496–502.
Article11. Rey M, Irondelle M, Waharte F, Lizarraga F, Chavrier P. HDAC6 is required for invadopodia activity and invasion by breast tumor cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 2011; 90:128–135.
Article12. Goetz MP, Toft DO, Ames MM, Erlichman C. The Hsp90 chaperone complex as a novel target for cancer therapy. Ann Oncol. 2003; 14:1169–1176.
Article13. Whitesell L, Lin NU. HSP90 as a platform for the assembly of more effective cancer chemotherapy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012; 1823:756–766.
Article14. Ferrarini M, Heltai S, Zocchi MR, Rugarli C. Unusual expression and localization of heat-shock proteins in human tumor cells. Int J Cancer. 1992; 51:613–619.
Article15. Pick E, Kluger Y, Giltnane JM, Moeder C, Camp RL, Rimm DL, et al. High HSP90 expression is associated with decreased survival in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2007; 67:2932–2937.
Article16. Kovacs JJ, Murphy PJ, Gaillard S, Zhao X, Wu JT, Nicchitta CV, et al. HDAC6 regulates Hsp90 acetylation and chaperone-dependent activation of glucocorticoid receptor. Mol Cell. 2005; 18:601–607.
Article17. Rao R, Fiskus W, Yang Y, Lee P, Joshi R, Fernandez P, et al. HDAC6 inhibition enhances 17-AAG: mediated abrogation of Hsp90 chaperone function in human leukemia cells. Blood. 2008; 112:1886–1893.
Article18. Bali P, Pranpat M, Bradner J, Balasis M, Fiskus W, Guo F, et al. Inhibition of histone deacetylase 6 acetylates and disrupts the chaperone function of heat shock protein 90: a novel basis for antileukemia activity of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280:26729–26734.
Article19. Meng Q, Chen X, Sun L, Zhao C, Sui G, Cai L. Carbamazepine promotes Her-2 protein degradation in breast cancer cells by modulating HDAC6 activity and acetylation of Hsp90. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011; 348:165–171.
Article20. Hyun CL, Lee HE, Kim KS, Kim SW, Kim JH, Choe G, et al. The effect of chromosome 17 polysomy on HER-2/neu status in breast cancer. J Clin Pathol. 2008; 61:317–321.
Article21. Song CH, Park SY, Eom KY, Kim JH, Kim SW, Kim JS, et al. Potential prognostic value of heat-shock protein 90 in the presence of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase overexpression or loss of PTEN, in invasive breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res. 2010; 12:R20.
Article22. Minucci S, Pelicci PG. Histone deacetylase inhibitors and the promise of epigenetic (and more) treatments for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006; 6:38–51.23. Li Y, Shin D, Kwon SH. Histone deacetylase 6 plays a role as a distinct regulator of diverse cellular processes. FEBS J. 2013; 280:775–793.24. Inoue A, Yoshida N, Omoto Y, Oguchi S, Yamori T, Kiyama R, et al. Development of cDNA microarray for expression profiling of estrogen-responsive genes. J Mol Endocrinol. 2002; 29:175–192.
Article25. Hayashi S, Yamaguchi Y. Estrogen signaling and prediction of endocrine therapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2005; 56:Suppl 1. 27–31.
Article26. Sabnis GJ, Goloubeva O, Chumsri S, Nguyen N, Sukumar S, Brodie AM. Functional activation of the estrogen receptor-α and aromatase by the HDAC inhibitor entinostat sensitizes ER-negative tumors to letrozole. Cancer Res. 2011; 71:1893–1903.27. Krämer OH, Mahboobi S, Sellmer A. Drugging the HDAC6-HSP90 interplay in malignant cells. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2014; 35:501–509.
Article28. Abduljabbar R, Negm OH, Lai CF, Jerjees DA, Al-Kaabi M, Hamed MR, et al. Clinical and biological significance of glucocorticoid receptor (GR) expression in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015; 150:335–346.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Traditional and Novel Mechanisms of Heat Shock Protein 90 (HSP90) Inhibition in Cancer Chemotherapy Including HSP90 Cleavage
- Molecular markers associated with radiation resistance and new molecular agents
- HDAC1 Expression in Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of the Breast and Its Value as a Good Prognostic Factor
- Elevated N1-Acetylspermidine Levels in Doxorubicintreated MCF-7 Cancer Cells: Histone Deacetylase 10 Inhibition with an N1-Acetylspermidine Mimetic
- Expression of Heat Shock Protein 70 m-RNA in Rat Bladder Overdistended by Diuresis