Lab Anim Res.
2017 Jun;33(2):92-97. 10.5625/lar.2017.33.2.92.
Effect of ionizing radiation at low dose on transgenerational carcinogenesis by epigenetic regulation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute of Medical Science, Kangwon National University, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Animal Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea. mjlee@kangwon.ac.kr
- 3Hugene bio, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2407421
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2017.33.2.92
Abstract
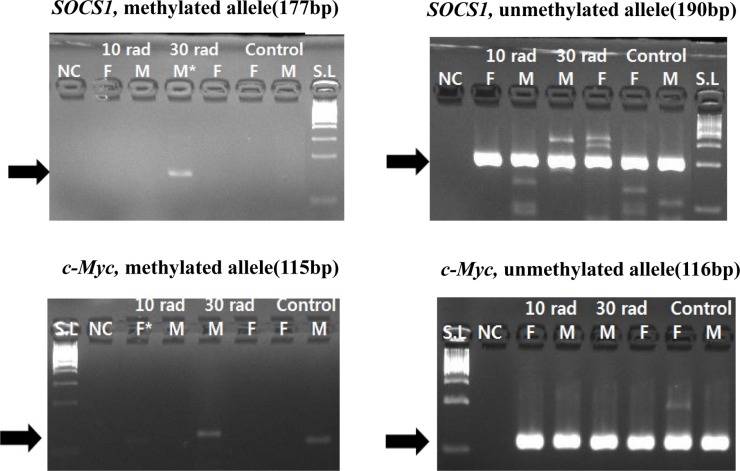
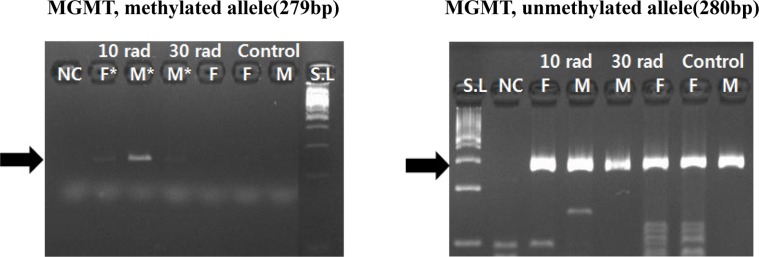
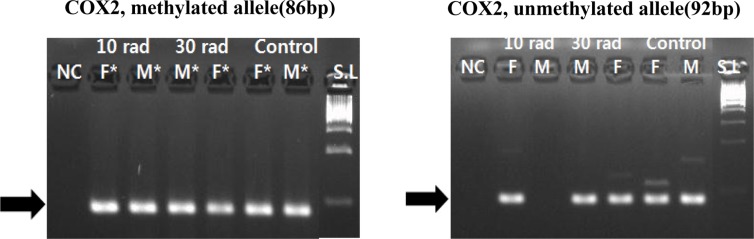
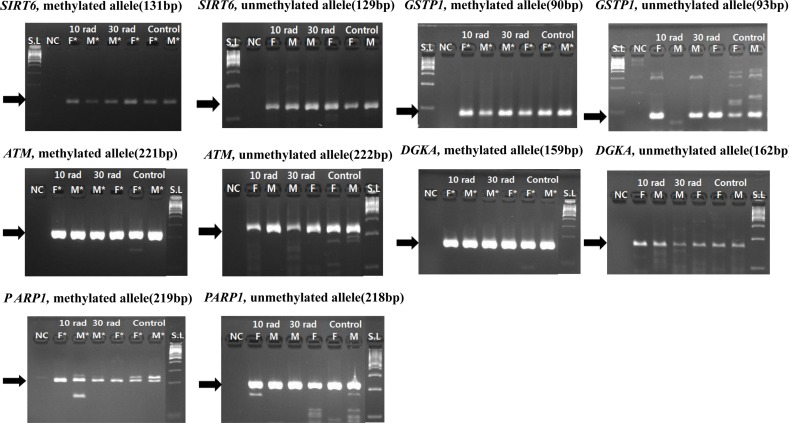
- The objective of this study was to determine the effect of ionizing radiation (IR) exposure of parents on carcinogenesis of the next generation focusing on the epigenetic perspective to clarify the relationship between radiation dose and carcinogenesis in F1 generation SD rats. F1 generations from pregnant rats (F0) who were exposed to gamma rays were divided into three groups according to the dose of radiation: 10 rad, 30 rad, and untreated. They were intraperitoneally injected with 50 mg/kg of diethylnitrosamine (DEN). Carcinogenesis was analyzed by examining expression levels of tumor suppressor genes (TSG) and other related genes by methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction (MSP). DNA methylation in liver tissues was evaluated to discern epigenetic regulation of transgenerational carcinogenesis vulnerability following IR exposure. Numerous studies have proved that transcriptional inactivation due to hypermethylation of TSG preceded carcinogenesis. Results of this study revealed hypermethylation of tumor suppressor gene SOCS1 in group treated with 30 rad. In addition, genes related to DNA damage response pathway (GSTP1, ATM, DGKA, PARP1, and SIRT6) were epigenetically inactivated in all DEN treated groups. In the case of proto-oncogene c-Myc, DNA hypermethylation was identified in the group with low dose of IR (10 rad). Results of this study indicated that each TSG had different radiation threshold level (dose-independent way) and DEN treatment could affect DNA methylation profile irrelevant of ionizing radiation dose.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Little JB. Radiation carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 2000; 21(3):397–404. PMID: 10688860.
Article2. Brenner DJ, Doll R, Goodhead DT, Hall EJ, Land CE, Little JB, Lubin JH, Preston DL, Preston RJ, Puskin JS, Ron E, Sachs RK, Samet JM, Setlow RB, Zaider M. Cancer risks attributable to low doses of ionizing radiation: assessing what we really know. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003; 100(24):13761–13766. PMID: 14610281.
Article3. Modan B. Low-dose radiation carcinogenesis. Eur J Cancer. 1992; 28(6-7):1010–1012.
Article4. Dasenbrock C, Tillmann T, Ernst H, Behnke W, Kellner R, Hagemann G, Kaever V, Kohler M, Rittinghausen S, Mohr U, Tomatis L. Maternal effects and cancer risk in the progeny of mice exposed to X-rays before conception. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2005; 56(6):351–360. PMID: 15945274.
Article5. Jones PA. DNA methylation errors and cancer. Cancer Res. 1996; 56(11):2463–2467. PMID: 8653676.6. Gonzalo S. Epigenetic alterations in aging. J Appl Physiol. 2010; 109(2):586–597. PMID: 20448029.
Article7. Klose RJ, Bird AP. Genomic DNA methylation: the mark and its mediators. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006; 31(2):89–97. PMID: 16403636.
Article8. Counts JL, Goodman JI. Alterations in DNA methylation may play a variety of roles in carcinogenesis. Cell. 1995; 83(1):13–15. PMID: 7553865.
Article9. Zingg JM, Jones PA. Genetic and epigenetic aspects of DNA methylation on genome expression, evolution, mutation and carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 1997; 18(5):869–882. PMID: 9163670.
Article10. Lillycrop KA, Slater-Jefferies JL, Hanson MA, Godfrey KM, Jackson AA, Burdge GC. Induction of altered epigenetic regulation of the hepatic glucocorticoid receptor in the offspring of rats fed a protein-restricted diet during pregnancy suggests that reduced DNA methyltransferase-1 expression is involved in impaired DNA methylation and changes in histone modifications. Br J Nutr. 2007; 97(6):1064–1073. PMID: 17433129.
Article11. Liu WB, Liu JY, Ao L, Zhou ZY, Zhou YH, Cui ZH, Cao J. Epigenetic silencing of cell cycle regulatory genes during 3-methylcholanthrene and diethylnitrosamine-induced multistep rat lung cancer. Mol Carcinog. 2010; 49(6):556–565. PMID: 20512841.
Article12. Bird AP. DNA methylation and the frequency of CpG in animal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980; 8(7):1499–1504. PMID: 6253938.
Article13. Liu WB, Ao L, Zhou ZY, Cui ZH, Zhou YH, Yuan XY, Xiang YL, Cao J, Liu JY. CpG island hypermethylation of multiple tumor suppressor genes associated with loss of their protein expression during rat lung carcinogenesis induced by 3-methylcholanthrene and diethylnitrosamine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010; 402(3):507–514. PMID: 20970405.
Article14. Phillips T. The role of methylation in gene expression. Nat Educ. 2008; 1(1):116.16. Saha A, Wittmeyer J, Cairns BR. Chromatin remodelling: the industrial revolution of DNA around histones. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006; 7(6):437–447. PMID: 16723979.
Article17. Santos-Rosa H, Schneider R, Bannister AJ, Sherriff J, Bernstein BE, Emre NC, Schreiber SL, Mellor J, Kouzarides T. Active genes are tri-methylated at K4 of histone H3. Nature. 2002; 419(6905):407–411. PMID: 12353038.
Article18. Liu WB, Liu JY, Ao L, Zhou ZY, Zhou YH, Cui ZH, Yang H, Cao J. Dynamic changes in DNA methylation during multistep rat lung carcinogenesis induced by 3-methylcholanthrene and diethylnitrosamine. Toxicol Lett. 2009; 189(1):5–13. PMID: 19409458.
Article19. Kim TY, Jong HS, Song SH, Dimtchev A, Jeong SJ, Lee JW, Kim TY, Kim NK, Jung M, Bang YJ. Transcriptional silencing of the DLC-1 tumor suppressor gene by epigenetic mechanism in gastric cancer cells. Oncogene. 2003; 22(25):3943–3951. PMID: 12813468.
Article20. Oue N, Sentani K, Yokozaki H, Kitadai Y, Ito R, Yasui W. Promoter methylation status of the DNA repair genes hMLH1 and MGMT in gastric carcinoma and metaplastic mucosa. Pathobiology. 2001; 69(3):143–149. PMID: 11872960.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Low-dose Gamma-irradiation Effect on Early Stage Development and Lifespan in Various Strains of Drosophila melanogaster
- Epigenetic profiling to environmental stressors in model and non-model organisms: Ecotoxicology perspective
- Current status of medical radiation exposure and regulation efforts
- Risk assessment from heterogeneous energy deposition in tissue. theproblem of effects from low doses of ionizing radiation
- Genetic and epigenetic alterations of colorectal cancer