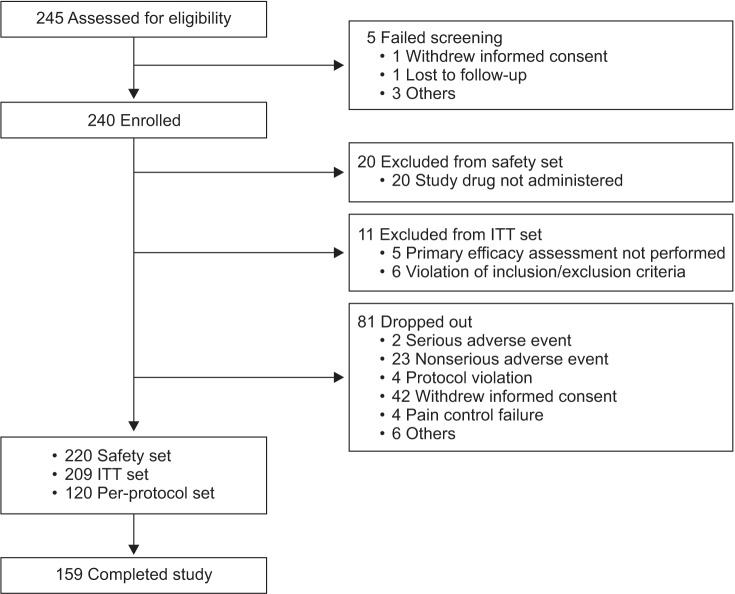
Clin Orthop Surg.
2018 Mar;10(1):33-40. 10.4055/cios.2018.10.1.33.
Analgesic Efficacy and Safety of Prolonged-Release Oxycodone/Naloxone in Korean Patients with Chronic Pain from Spinal Disorders
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sungsoo.chung@samsung.com
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Dong-A University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 4Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul Spine Institute, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- 8Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea.
- 9Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Cheongju, Korea.
- 10Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri, Korea.
- 11Mundipharma Korea Ltd., Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2405480
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.1.33
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
A prolonged-release formulation of oxycodone/naloxone has been shown to be effective in European populations for the management of chronic moderate to severe pain. However, no clinical data exist for its use in Korean patients. The objective of this study was to assess efficacy and safety of prolonged-release oxycodone/naloxone in Korean patients for management of chronic moderate-to-severe pain.
METHODS
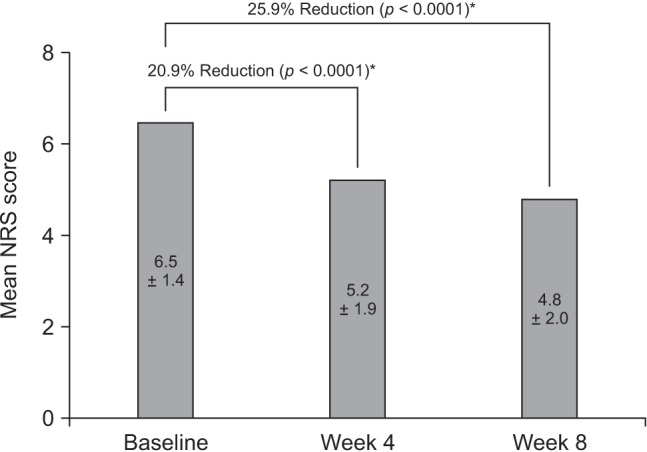
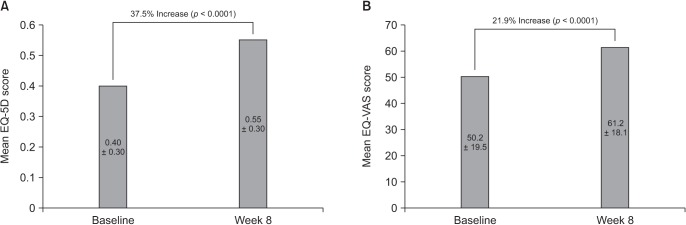
In this multicenter, single-arm, open-label, phase IV study, Korean adults with moderate-to-severe spinal disorder-related pain that was not satisfactorily controlled with weak opioids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs received prolonged-release oral oxycodone/naloxone at a starting dose of 10/5 mg/day (maximum 80/40 mg/day) for 8 weeks. Changes in pain intensity and quality of life (QoL) were measured using a numeric rating scale (NRS, 0-10) and the Korean-language EuroQol-five dimensions questionnaire, respectively.
RESULTS
Among 209 patients assessed for efficacy, the mean NRS pain score was reduced by 25.9% between baseline and week 8 of treatment (p < 0.0001). There was also a significant improvement in QoL from baseline to week 8 (p < 0.0001). The incidence of adverse drug reactions was 27.7%, the most common being nausea, constipation, and dizziness; 77.9% of these adverse drug reactions had resolved or were resolving at the end of the study.
CONCLUSIONS
Prolonged-release oxycodone/naloxone provided significant and clinically relevant reductions in pain intensity and improved QoL in Korean patients with chronic spinal disorders. (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01811238)
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hoy D, Brooks P, Blyth F, Buchbinder R. The epidemiology of low back pain. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2010; 24(6):769–781. PMID: 21665125.
Article2. Manchikanti L, Singh V, Datta S, Cohen SP, Hirsch JA;. Comprehensive review of epidemiology, scope, and impact of spinal pain. Pain Physician. 2009; 12(4):E35–E70. PMID: 19668291.3. Jhun HJ, Park JY. Estimated number of Korean adults with back pain and population-based associated factors of back pain: data from the fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009; 46(5):443–450. PMID: 20041054.4. Ko SB, Lee SW. Prevalence of spondylolysis and its relationship with low back pain in selected population. Clin Orthop Surg. 2011; 3(1):34–38. PMID: 21369476.
Article5. Andrew R, Derry S, Taylor RS, Straube S, Phillips CJ. The costs and consequences of adequately managed chronic non-cancer pain and chronic neuropathic pain. Pain Pract. 2014; 14(1):79–94. PMID: 23464879.
Article6. Hong JH, Kim HD, Shin HH, Huh B. Assessment of depression, anxiety, sleep disturbance, and quality of life in patients with chronic low back pain in Korea. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2014; 66(6):444–450. PMID: 25006368.
Article7. Langley PC. The prevalence, correlates and treatment of pain in the European Union. Curr Med Res Opin. 2011; 27(2):463–480. PMID: 21194390.
Article8. Argoff CE, Viscusi ER. The use of opioid analgesics for chronic pain: minimizing the risk for harm. Am J Gastroenterol Suppl. 2014; 2(1):3–8. PMID: 25207607.
Article9. Park HJ, Moon DE. Pharmacologic management of chronic pain. Korean J Pain. 2010; 23(2):99–108. PMID: 20556211.
Article10. Han T. Opioids in cancer and non-cancer pain management in Korea: the past, present and future. Eur J Pain. 2001; 5(Suppl A):73–78. PMID: 11798222.
Article11. Lee J, Yoon JS, Lee JH, et al. Clinical usefulness of long-term application of fentanyl matrix in chronic non-cancer pain: improvement of pain and physical and emotional functions. Clin Orthop Surg. 2016; 8(4):465–474. PMID: 27904731.
Article12. Chou R, Qaseem A, Snow V, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of low back pain: a joint clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians and the American Pain Society. Ann Intern Med. 2007; 147(7):478–491. PMID: 17909209.
Article13. Coyne KS, LoCasale RJ, Datto CJ, Sexton CC, Yeomans K, Tack J. Opioid-induced constipation in patients with chronic noncancer pain in the USA, Canada, Germany, and the UK: descriptive analysis of baseline patient-reported outcomes and retrospective chart review. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2014; 6:269–281. PMID: 24904217.
Article14. Lowenstein O, Leyendecker P, Hopp M, et al. Combined prolonged-release oxycodone and naloxone improves bowel function in patients receiving opioids for moderate-to-severe non-malignant chronic pain: a randomised controlled trial. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2009; 10(4):531–543. PMID: 19243306.15. Simpson K, Leyendecker P, Hopp M, et al. Fixed-ratio combination oxycodone/naloxone compared with oxycodone alone for the relief of opioid-induced constipation in moderate-to-severe noncancer pain. Curr Med Res Opin. 2008; 24(12):3503–3512. PMID: 19032132.
Article16. Vondrackova D, Leyendecker P, Meissner W, et al. Analgesic efficacy and safety of oxycodone in combination with naloxone as prolonged release tablets in patients with moderate to severe chronic pain. J Pain. 2008; 9(12):1144–1154. PMID: 18708300.
Article17. Burness CB, Keating GM. Oxycodone/naloxone prolonged-release: a review of its use in the management of chronic pain while counteracting opioid-induced constipation. Drugs. 2014; 74(3):353–375. PMID: 24452879.
Article18. Cho YS, Lee JY, Kim HS, Kwon K. Trends in the consumption of opioid analgesics in a tertiary care hospital from 2000 to 2012. Yakhak Hoeji. 2014; 58(4):268–276.19. Chung SS, Park CK, Cho KJ, et al. A nationwide retrospective study of opioid management patterns in 2,468 patients with spinal pain in Korea. Asian Spine J. 2016; 10(6):1122–1131. PMID: 27994790.
Article20. EuroQol Group. EuroQol: a new facility for the measurement of health-related quality of life. Health Policy. 1990; 16(3):199–208. PMID: 10109801.21. Soer R, Reneman MF, Speijer BL, Coppes MH, Vroomen PC. Clinimetric properties of the EuroQol-5D in patients with chronic low back pain. Spine J. 2012; 12(11):1035–1039. PMID: 23199409.
Article22. Wild JE, Grond S, Kuperwasser B, et al. Long-term safety and tolerability of tapentadol extended release for the management of chronic low back pain or osteoarthritis pain. Pain Pract. 2010; 10(5):416–427. PMID: 20602712.
Article23. Dworkin RH, Turk DC, McDermott MP, et al. Interpreting the clinical importance of group differences in chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. Pain. 2009; 146(3):238–244. PMID: 19836888.
Article24. Dworkin RH, Turk DC, Wyrwich KW, et al. Interpreting the clinical importance of treatment outcomes in chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. J Pain. 2008; 9(2):105–121. PMID: 18055266.25. Farrar JT, Pritchett YL, Robinson M, Prakash A, Chappell A. The clinical importance of changes in the 0 to 10 numeric rating scale for worst, least, and average pain intensity: analyses of data from clinical trials of duloxetine in pain disorders. J Pain. 2010; 11(2):109–118. PMID: 19665938.
Article26. Mehta V, Alaward S, Kuravinakop S, Nikolic S. Effect of a fixed-dose opioid agonist/antagonist on constipation in patients on long-term opioids for non-malignant pain unable to tolerate laxatives. Pain Physician. 2014; 17(5):415–424. PMID: 25247899.27. Boswell K, Kwong WJ, Kavanagh S. Burden of opioid-associated gastrointestinal side effects from clinical and economic perspectives: a systematic literature review. J Opioid Manag. 2010; 6(4):269–289. PMID: 20862907.28. Kalso E, Edwards JE, Moore RA, McQuay HJ. Opioids in chronic non-cancer pain: systematic review of efficacy and safety. Pain. 2004; 112(3):372–380. PMID: 15561393.
Article29. Moore RA, McQuay HJ. Prevalence of opioid adverse events in chronic non-malignant pain: systematic review of randomised trials of oral opioids. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005; 7(5):R1046–R1051. PMID: 16207320.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Colorectal Transit and Volume During Treatment With Prolonged-release Oxycodone/Naloxone Versus Oxycodone Plus Macrogol 3350
- A new therapeutic option for postoperative pain management with oxycodone HCI injection
- Oxycodone: A New Therapeutic Option in Postoperative Pain Management
- Treatment of Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome Triggered by Oxycodone/Naloxone with Dexmedetomidine
- Comparison of the analgesic efficacy of oxycodone and fentanyl after dental surgery