J Pathol Transl Med.
2018 Jan;52(1):14-20. 10.4132/jptm.2017.10.17.
The Significance of TROP2 Expression in Predicting BRAF Mutations in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Korea Cancer Center Hospital, Seoul, Korea. tontos016@naver.com
- 2Laboratory of Radiation Exposure and Therapeutics, National Radiation Emergency Medical Center, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2403253
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.10.17
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Trophoblast antigen 2 (TROP2) is a human trophoblast cell-surface glycoprotein that is overexpressed in several types of epithelial cancers, and is suggested to be associated with an unfavorable prognosis. BRAF mutations are the most common genetic alteration in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC). We evaluated the correlation between TROP2 expression and BRAF mutation in PTC.
METHODS
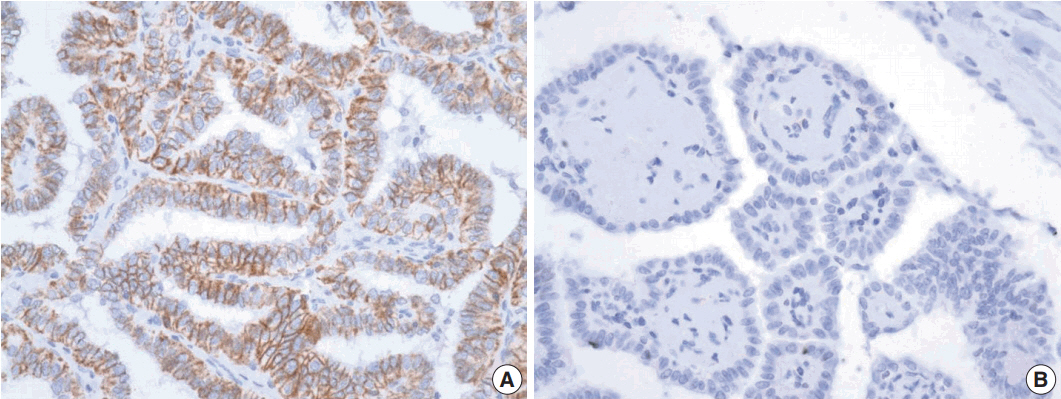
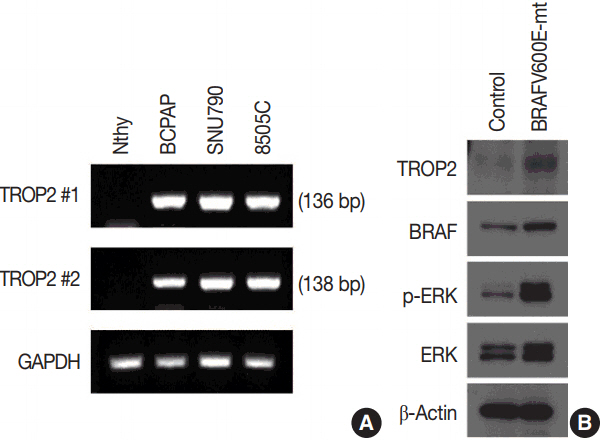
First, we carried out pyrosequencing for BRAF mutations and immunohistochemistry for TROP2 expression with a tissue microarray consisting of 52 PTC cases. Membranous staining in at least 5% of tumor cells was designated as positive staining and we analyzed the relationship between TROP2 expression and diverse clinicopathological factors, including BRAF mutation. Second, we tested TROP2 mRNA expression in three thyroid cancer cell lines with BRAF mutations (BCPAP, SNU790, and 8505C) and a normal thyroid cell line. Additionally, we checked TROP2 protein levels in a normal thyroid cell line after introduction of the BRAF V600E mutation.
RESULTS
In this study, 21 of 26 cases with BRAF mutation showed TROP2 immunoreactivity, whereas all 26 cases without BRAF mutation showed no immunoreactivity for TROP2 with a statistically significant difference (p<.001). Upregulation of TROP2 mRNA was observed in all three thyroid cancer cell lines, but not in the normal thyroid cell line. Interestingly, however, the TROP2 expression was increased in the normal thyroid cell line after introduction of the BRAF V600E mutation.
CONCLUSIONS
Based on these results, we concluded that TROP2 expression is significantly associated with BRAF mutation and that TROP2 immunohistochemistry could be used for predicting BRAF mutations or diagnosing papillary thyroid carcinoma.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011; 61:69–90.
Article2. Shvartsur A, Bonavida B. Trop2 and its overexpression in cancers: regulation and clinical/therapeutic implications. Genes Cancer. 2015; 6:84–105.3. McDougall AR, Tolcos M, Hooper SB, Cole TJ, Wallace MJ. Trop2: from development to disease. Dev Dyn. 2015; 244:99–109.
Article4. Lipinski M, Parks DR, Rouse RV, Herzenberg LA. Human trophoblast cell-surface antigens defined by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981; 78:5147–50.
Article5. Fang YJ, Lu ZH, Wang GQ, et al. Elevated expressions of MMP7, TROP2, and survivin are associated with survival, disease recurrence, and liver metastasis of colon cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2009; 24:875–84.
Article6. Fong D, Moser P, Krammel C, et al. High expression of TROP2 correlates with poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 2008; 99:1290–5.
Article7. Fong D, Spizzo G, Gostner JM, et al. TROP2: a novel prognostic marker in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Mod Pathol. 2008; 21:186–91.
Article8. Mühlmann G, Spizzo G, Gostner J, et al. TROP2 expression as prognostic marker for gastric carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 2009; 62:152–8.9. Guan GF, Zhang DJ, Wen LJ, et al. Prognostic value of TROP2 in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015; 8:10995–1004.10. Bignotti E, Todeschini P, Calza S, et al. Trop-2 overexpression as an independent marker for poor overall survival in ovarian carcinoma patients. Eur J Cancer. 2010; 46:944–53.
Article11. Bignotti E, Zanotti L, Calza S, et al. Trop-2 protein overexpression is an independent marker for predicting disease recurrence in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma. BMC Clin Pathol. 2012; 12:22.
Article12. Addati T, Achille G, Centrone M, et al. TROP-2 expression in papillary thyroid cancer: a preliminary cyto-histological study. Cytopathology. 2015; 26:303–11.
Article13. Simms A, Jacob RP, Cohen C, Siddiqui MT. TROP-2 expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma: potential diagnostic utility. Diagn Cytopathol. 2016; 44:26–31.14. Liu H, Shi J, Lin F. The potential diagnostic utility of TROP-2 in thyroid neoplasms. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2017; 25:525–33.
Article15. Xing M. BRAF mutation in thyroid cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005; 12:245–62.16. Schweppe RE, Klopper JP, Korch C, et al. Deoxyribonucleic acid profiling analysis of 40 human thyroid cancer cell lines reveals cross-contamination resulting in cell line redundancy and misidentification. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008; 93:4331–41.
Article17. Koh CS, Ku JL, Park SY, et al. Establishment and characterization of cell lines from three human thyroid carcinomas: responses to all-trans-retinoic acid and mutations in the BRAF gene. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2007; 264:118–27.
Article18. Busca R, Abbe P, Mantoux F, et al. Ras mediates the cAMP-dependent activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) in melanocytes. EMBO J. 2000; 19:2900–10.
Article19. Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature. 2002; 417:949–54.20. Peyssonnaux C, Eychène A. The Raf/MEK/ERK pathway: new concepts of activation. Biol Cell. 2001; 93:53–62.
Article21. Cubas R, Zhang S, Li M, Chen C, Yao Q. Trop2 expression contributes to tumor pathogenesis by activating the ERK MAPK pathway. Mol Cancer. 2010; 9:253.
Article22. Ahmed N, Oliva K, Wang Y, Quinn M, Rice G. Downregulation of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor expression inhibits Erk signalling with concomitant suppression of invasiveness due to loss of uPAR-beta1 integrin complex in colon cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 2003; 89:374–84.23. Fang JY, Richardson BC. The MAPK signalling pathways and colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2005; 6:322–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expressions of miRNAs in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma and Their Associations with the BRAFV600EMutation and Clinicopathological Features.
- Osteopontin expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma and its relationship with the BRAF mutation and tumor characteristics
- Concurrent Medullay and Papillary Carcinoma of the Thyroid
- A Case of Multifocal Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Consisting of One Encapsulated Follicular Variant with BRAF K601E Mutation and Three Conventional Types with BRAF V600E Mutation
- Clinicopathological Features of Rare BRAF Mutations in Korean Thyroid Cancer Patients