Prog Med Phys.
2017 Dec;28(4):144-148. 10.14316/pmp.2017.28.4.144.
Dosimetric Impact of Ti Mesh on Proton Beam Therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Proton Therapy Center, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea. dongho@ncc.re.kr
- KMID: 2401375
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2017.28.4.144
Abstract
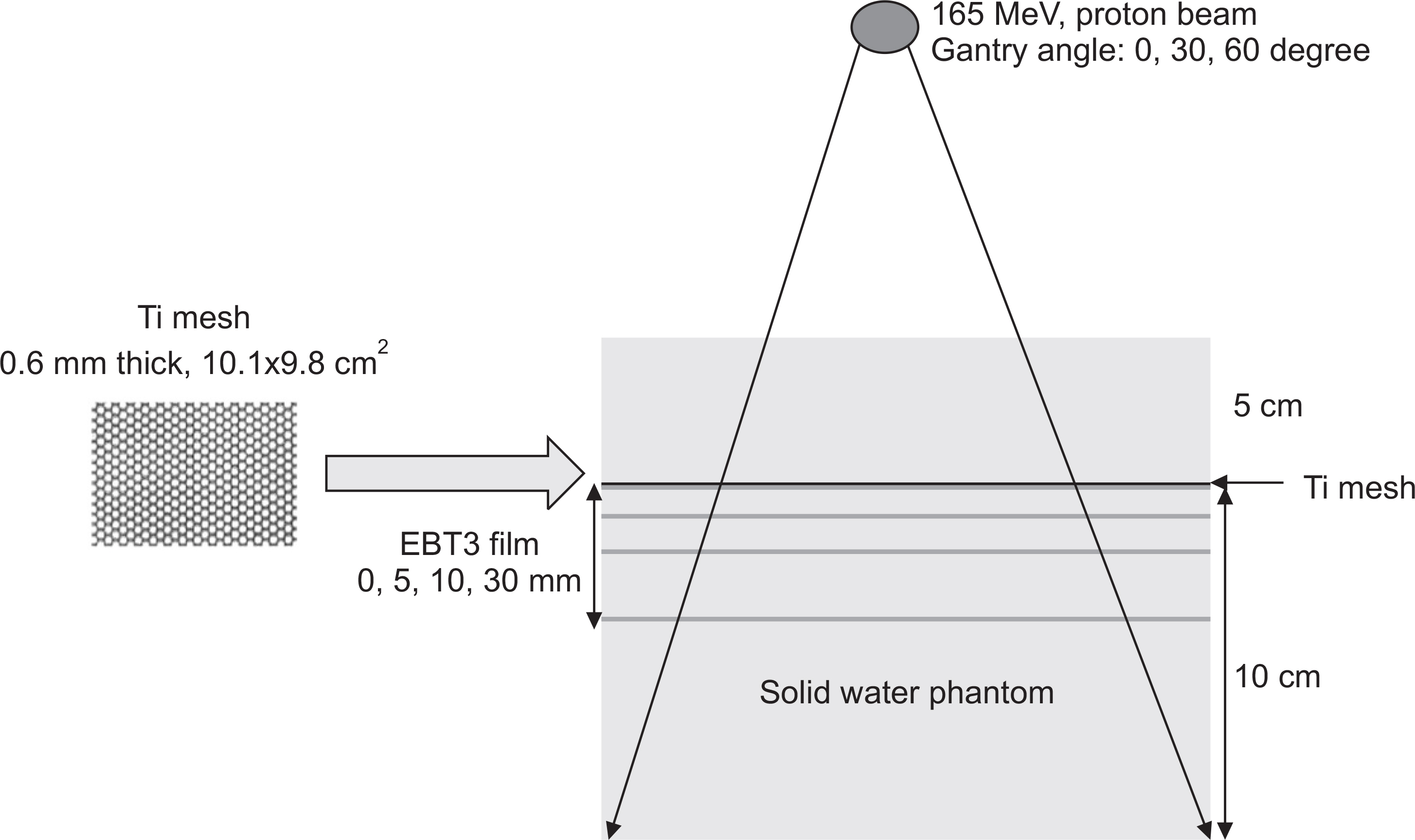
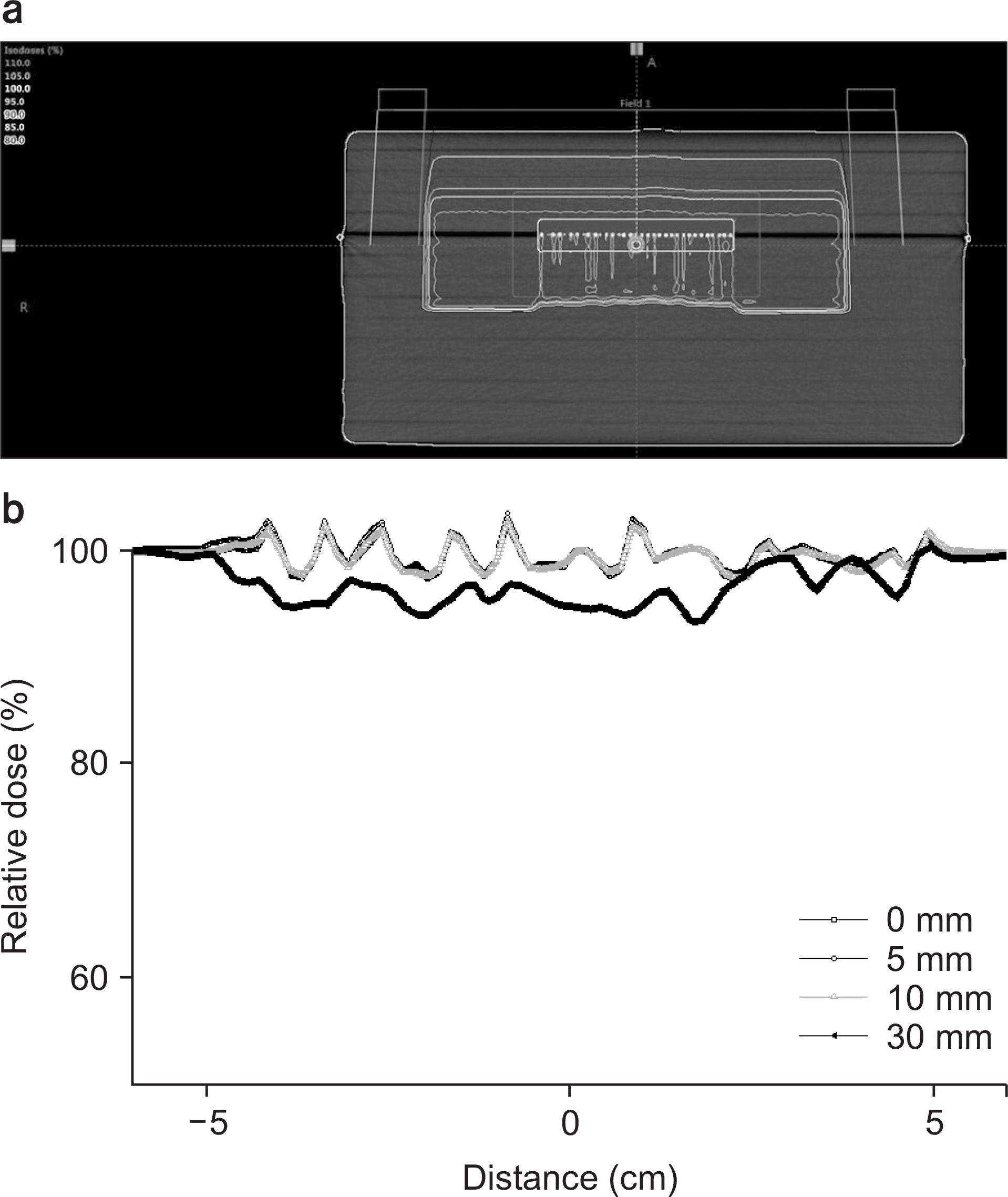
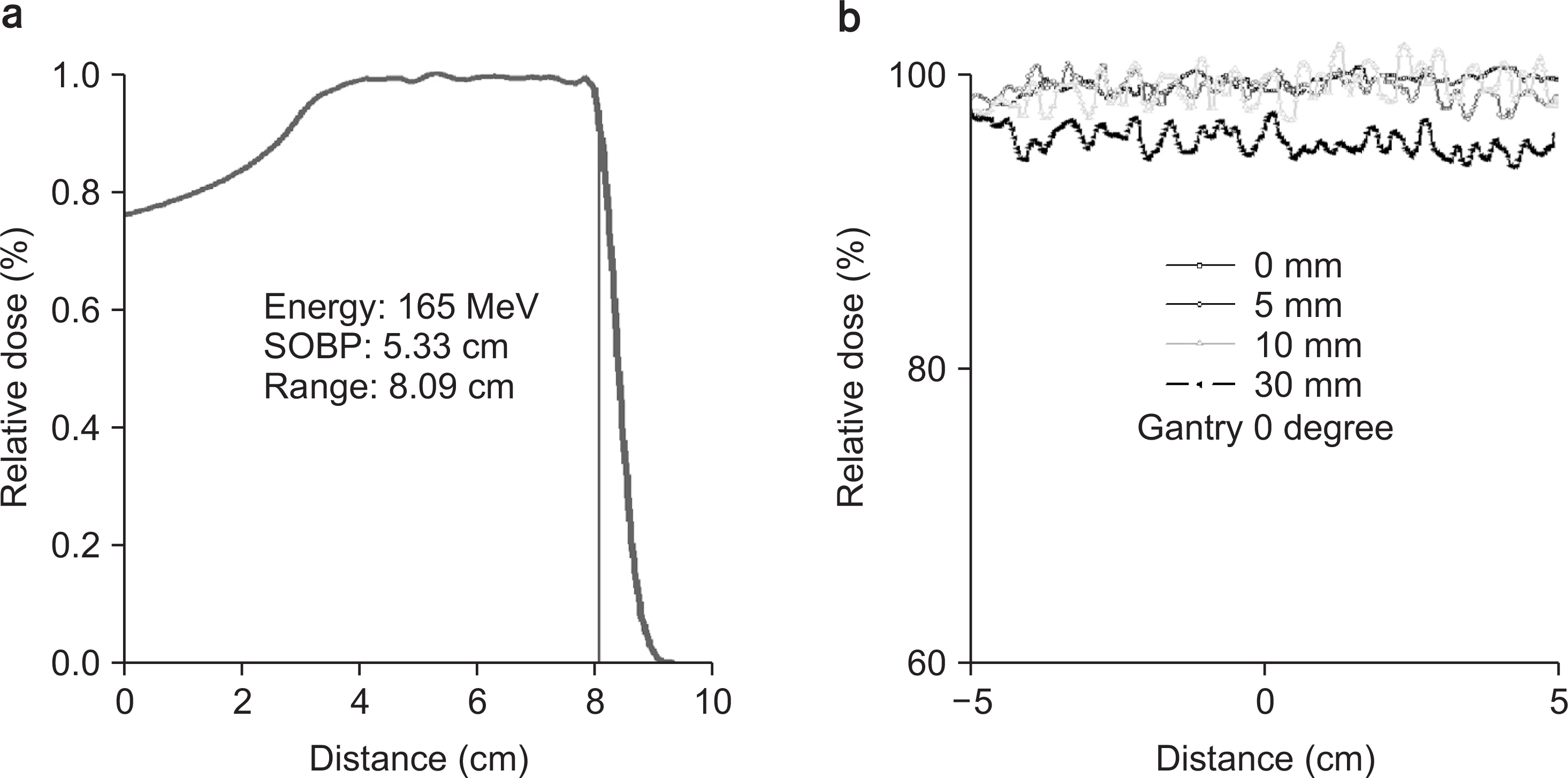
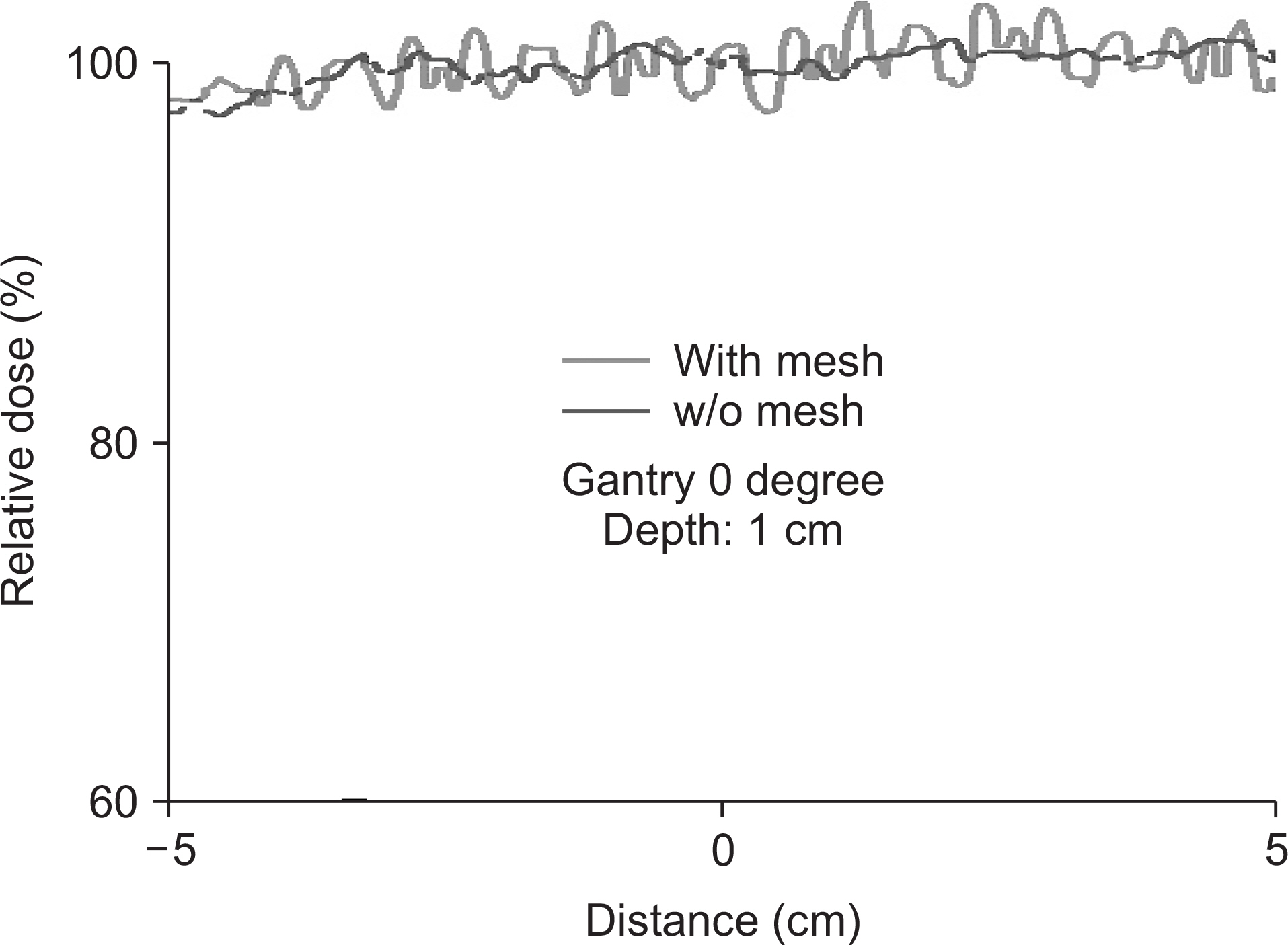
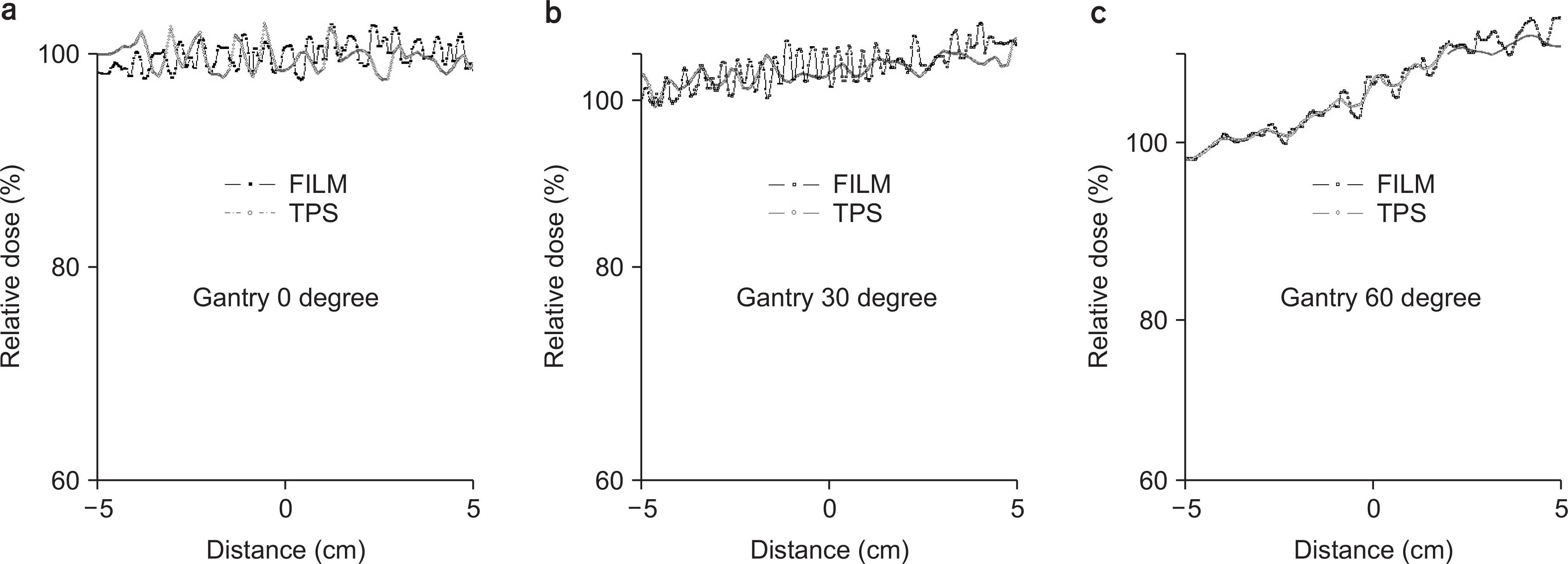
- When a high density metallic implant is placed in the path of the proton beam, spatial heterogeneity can be caused due to artifacts in three dimensional (3D) computed tomography (CT) scans. These artifacts result in range uncertainty in dose calculation in treatment planning system (TPS). And this uncertainty may cause significant underdosing to the target volume or overdosing to normal tissue beyond the target. In clinical cases, metal implants must be placed in the beam path in order to preserve organ at risk (OARs) and increase target coverage for tumors. So we should introduce Ti-mesh. In this paper, we measured the lateral dose profile for proton beam using an EBT3 film to confirm dosimetric impact of Ti-mesh when the Ti-mesh plate was placed in the proton beam pathway. The effect of Ti-mesh on the proton beam was investigated by comparing the lateral dose profile calculated from TPS with the film-measured value under the same conditions.
Figure
Reference
-
1.Ming Yang, X Ronald Zhu, Peter C Park. Comprehensive analysis of proton range uncertainties related to patient stopping-power-ratio estimation using the stoichiometric calibration. Physics in Medicine and Biology. 2012. 57:4095–4115.2.Kassim I., Joosten H., Barnhoorn JC., Heijmen BJ., Dirkx ML. Implications of artifacts reduction in the planning CT originated from the implanted fiducial markers. Medical Dosimetry. 2011. 36(2):119–25.3.Yazdi M., Gingras L., Beaulieu L. An adaptive approach to metal artifact reduction in helical computed tomography for radiation therapy treatment planning: experimental and clinical studies. International Journal of Radiation Oncology∗Biology∗Physics. 2005. 62(4):1224–31.4.H Lin, X Ding, L Yin, H Zhai. The effects of titanium mesh on passive-scattering proton dose. Physics in Medicine and Biology. 2014. 59:N81–N89.5.Patone H., Barker J., Roberge D. Effects of neurosurgical titanium mesh on radiation dose. Medical Dosimetry. 2006. 31:298–301.
Article6.Reinhardt S., Hillbrand M., Wilkens J., Assmann W. Comparison of Gafchromic EBT2 and EBT3 films for clinical photon and proton beams. Medical Physics. 2012. 39:5257–5262.
Article7.SW Kang, JB Chung. Evaluation of dual-channel compound method for EBT3 film dosimetry. Progress in Medical Physics. 2017. 28(1):16–21.8.Hertanto A., Zhang QH., Hu YC., Dzyubak O., Rimmer A., Mageras G. Reduction of irregular Breathing artifacts in respiration-correlated CT images using a respiratory motion model. Medical Physics. 2012. 39:3070–3079.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Proton Therapy Review: Proton Therapy from a Medical
- A Pilot Study of the Scanning Beam Quality Assurance Using Machine Log Files in Proton Beam Therapy
- Feasibility Test of Flat-Type Faraday Cup for UltrahighDose-Rate Transmission Proton Beam Therapy
- Dosimetric Influence of Implanted Gold Markers in Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer
- Proton Beam Therapy