J Korean Med Assoc.
2008 Jul;51(7):638-642. 10.5124/jkma.2008.51.7.638.
Proton Beam Therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Proton Therapy Center, National Cancer Center, Korea. radiopia@ncc.re.kr
- KMID: 2185914
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2008.51.7.638
Abstract
- Proton is quite different from x-ray in terms of energy emission. As it enters a cancer patient's body through skin and tissue, it releases a relatively low dose of energy before it reaches the target. It, however, hits the targeted tumor by depositing the biggest dose of energy on it, then suddenly stopping its activity afterwards. The point where the highest energy is released is called as the Bragg peak. The proton beam has many advantages over the conventional x-ray beam because the proton beam radiates primarily the tumor site, leaving the surrounding healthy tissue and organs totally unharmed or relatively less damaged. Thus, the patients can enjoy much more enhanced quality-of-life during and after the treatment as well as have a high probability to be cured from their diseases.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim DY, Kim TH. Proton therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Hepatol. 2008. 14:S2. 75–79.2. Damato B, Kacperek A, Chopra M, Campbell IR, Errington RD. Proton beam radiotherapy of choroidal melanoma: the Liverpool-Clatterbridge experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005. 62:1405–1411.
Article3. Dendale R, Lumbroso-Le Rouic L, Noel G, Feuvret L, Levy C, Delacroix S, Meyer A, Nauraye C, Mazal A, Mammar H, Garcia P, D'Hermies F, Frau E, Plancher C, Asselain B, Schlienger P, Mazeron JJ, Desjardins L. Proton beam radiotherapy for uveal melanoma: results of Curie Institut-Orsay proton therapy center (ICPO). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006. 65:780–787.
Article4. Egger E, Schalenbourg A, Zografos L, Bercher L, Boehringer T, Chamot L, Goitein G. Maximizing local tumor control and survival after proton beam radiotherapy of uveal melanoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001. 51:138–147.
Article5. Höcht S, Bechrakis NE, Nausner M, Kreusel KM, Kluge H, Heese J, Heufelder J, Cordini D, Homeyer H, Fuchs H, Martus P, Foerster MH, Wiegel T, Hinkelbein W. Proton therapy of uveal melanomas in Berlin. 5 years of experience at the Hahn-Meitner Institute. Strahlenther Onkol. 2004. 180:419–424.6. Kodjikian L, Roy P, Rouberol F, Garweg JG, Chauvel P, Manon L, Jean-Louis B, Little RE, Sasco AJ, Grange JD. Survival after proton-beam irradiation of uveal melanomas. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004. 137:1002–1010.
Article7. Zhang X, Dong L, Lee AK, Cox JD, Kuban DA, Zhu RX, Wang X, Li Y, Newhauser WD, Gillin M, Mohan R. Effect of anatomic motion on proton therapy dose distributions in prostate cancer treatment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007. 67:620–629.
Article8. Igaki H, Tokuuye K, Okumura T, Sugahara S, Kagei K, Hata M, Ohara K, Hashimoto T, Tsuboi K, Takano S, Matsumura A, Akine Y. Clinical results of proton beam therapy for skull base chordoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. 60:1120–1126.
Article9. Weber DC, Rutz HP, Pedroni ES, Bolsi A, Timmermann B, Verwey J, Lomax AJ, Goitein G. Results of spot-scanning proton radiation therapy for chordoma and chondrosarcoma of the skull base: the Paul Scherrer Institut experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005. 63:401–409.
Article10. Fitzek MM, Thornton AF, Rabinov JD, Lev MH, Pardo FS, Munzenrider JE, Okunieff P, Bussière M, Braun I, Hochberg FH, Hedley-Whyte ET, Liebsch NJ, Harsh GR 4th. Accelerated fractionated proton/photon irradiation to 90 cobalt gray equivalent for glioblastoma multiforme: results of a phase II prospective trial. J Neurosurg. 1999. 91:251–260.
Article11. Noël G, Habrand JL, Mammar H, Haie-Meder C, Pontvert D, Dederke S, Ferrand R, Beaudré A, Gaboriaud G, Boisserie G, Mazeron JJ. Highly conformal therapy using proton component in the management of meningiomas. Preliminary experience of the Centre de Protontherapie d'Orsay. Strahlenther Onkol. 2002. 178:480–485.
Article12. Slater JD, Yonemoto LT, Mantik DW, Bush DA, Preston W, Grove RI, Miller DW, Slater JM. Proton radiation for treatment of cancer of the oropharynx: early experience at Loma Linda University Medical Center using a concomitant boost technique. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005. 62:494–500.
Article13. Tokuuye K, Akine Y, Kagei K, Hata M, Hashimoto T, Mizumoto T, Ohshiro Y, Sugahara S, Ohara K, Okumura T, Kusakari J, Yoshida H, Otsuka F. Proton therapy for head and neck malignancies at Tsukuba. Strahlenther Onkol. 2004. 180:96–101.
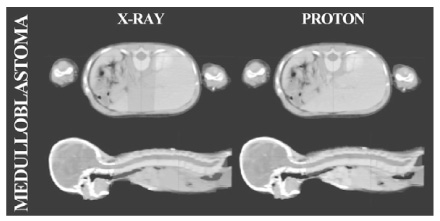
Article14. St Clair WH, Adams JA, Bues M, Fullerton BC, La Shell S, Kooy HM, Loeffler JS, Tarbell NJ. Advantage of protons compared to conventional X-ray or IMRT in the treatment of a pediatric patient with medulloblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. 58:727–734.
Article15. Lee CT, Bilton SD, Famiglietti RM, Riley BA, Mahajan A, Chang EL, Maor MH, Woo SY, Cox JD, Smith AR. Treatment planning with protons for pediatric retinoblastoma, medulloblastoma, and pelvic sarcoma: how do protons compare with other conformal techniques? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005. 63:362–372.
Article16. Hug EB, Sweeney RA, Nurre PM, Holloway KC, Slater JD, Munzenrider JE. Proton radiotherapy in management of pediatric base of skull tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002. 52:1017–1024.
Article17. Bush DA, Slater JD, Shin BB, Cheek G, Miller DW, Slater JM. Hypofractionated proton beam radiotherapy for stage I lung cancer. Chest. 2004. 126:1198–1203.
Article18. Shioyama Y, Tokuuye K, Okumura T, Kagei K, Sugahara S, Ohara K, Akine Y, Ishikawa S, Satoh H, Sekizawa K. Clinical evaluation of proton radiotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003. 56:7–13.
Article19. Nihei K, Ogino T, Ishikura S, Nishimura H. High-dose proton beam therapy for Stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006. 65:107–111.
Article20. Sugahara S, Tokuuye K, Okumura T, Nakahara A, Saida Y, Kagei K, Ohara K, Hata M, Igaki H, Akine Y. Clinical results of proton beam therapy for cancer of the esophagus. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005. 61:76–84.
Article21. Kagei K, Tokuuye K, Okumura T, Ohara K, Shioyama Y, Sugahara S, Akine Y. Long-term results of proton beam therapy for carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003. 55:1265–1271.
Article22. Chiba T, Tokuuye K, Matsuzaki Y, Sugahara S, Chuganji Y, Kagei K, Shoda J, Hata M, Abei M, Igaki H, Tanaka N, Akine Y. Proton beam therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective review of 162 patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. 11:3799–3805.
Article23. Hata M, Tokuuye K, Sugahara S, Kagei K, Igaki H, Hashimoto T, Ohara K, Matsuzaki Y, Tanaka N, Akine Y. Proton beam therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus. Cancer. 2005. 104:794–801.
Article24. Slater JD, Rossi CJ Jr, Yonemoto LT, Bush DA, Jabola BR, Levy RP, Grove RI, Preston W, Slater JM. Proton therapy for prostate cancer: the initial Loma Linda University experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. 59:348–352.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Proton Therapy Review: Proton Therapy from a Medical
- A Pilot Study of the Scanning Beam Quality Assurance Using Machine Log Files in Proton Beam Therapy
- Proton therapy: the current status of the clinical evidences
- Feasibility Test of Flat-Type Faraday Cup for UltrahighDose-Rate Transmission Proton Beam Therapy
- Dosimetric Impact of Ti Mesh on Proton Beam Therapy