Prog Med Phys.
2017 Sep;28(3):129-133. 10.14316/pmp.2017.28.3.129.
A Pilot Study of the Scanning Beam Quality Assurance Using Machine Log Files in Proton Beam Therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kchung@skku.edu
- KMID: 2393374
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2017.28.3.129
Abstract
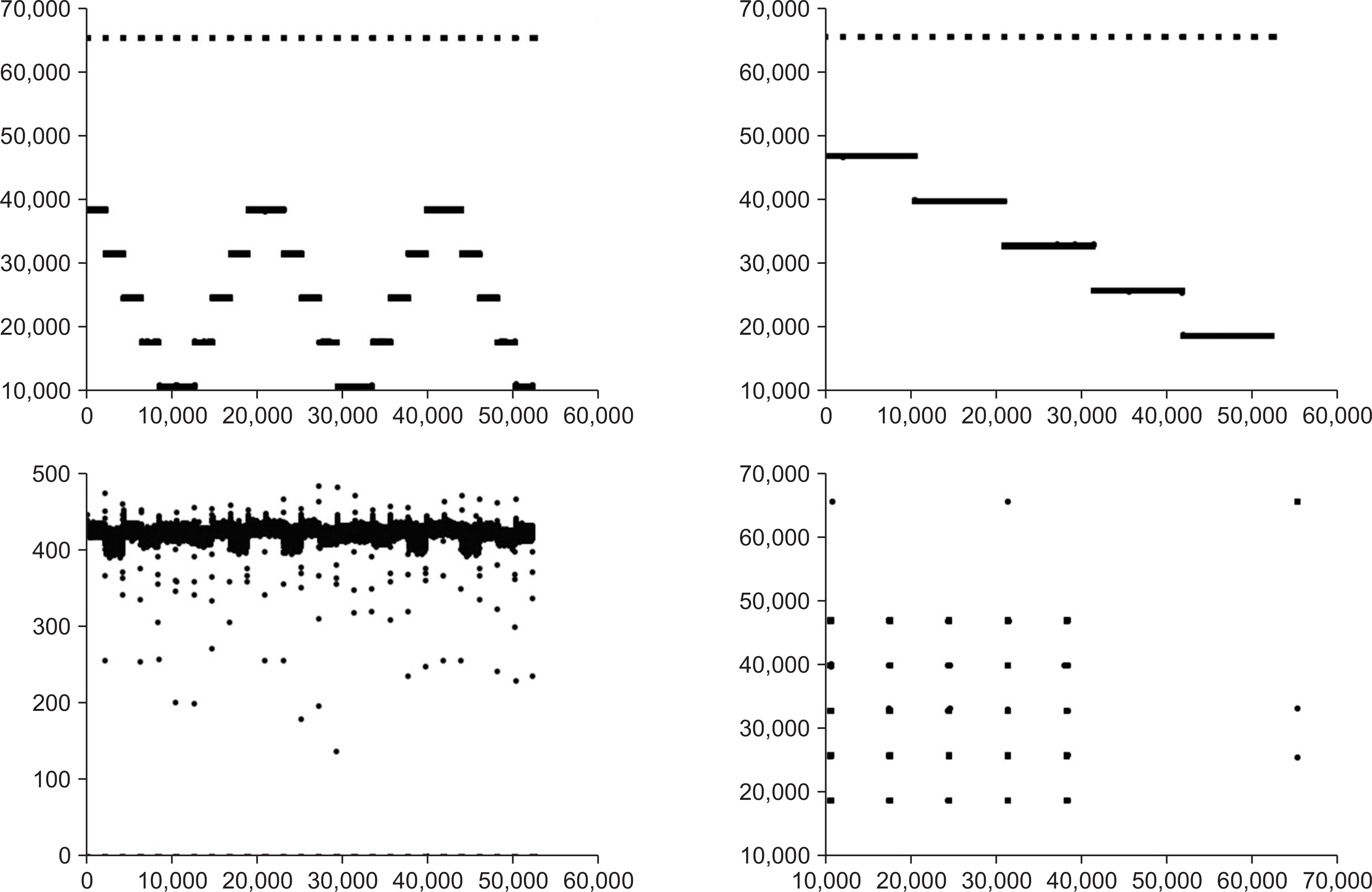
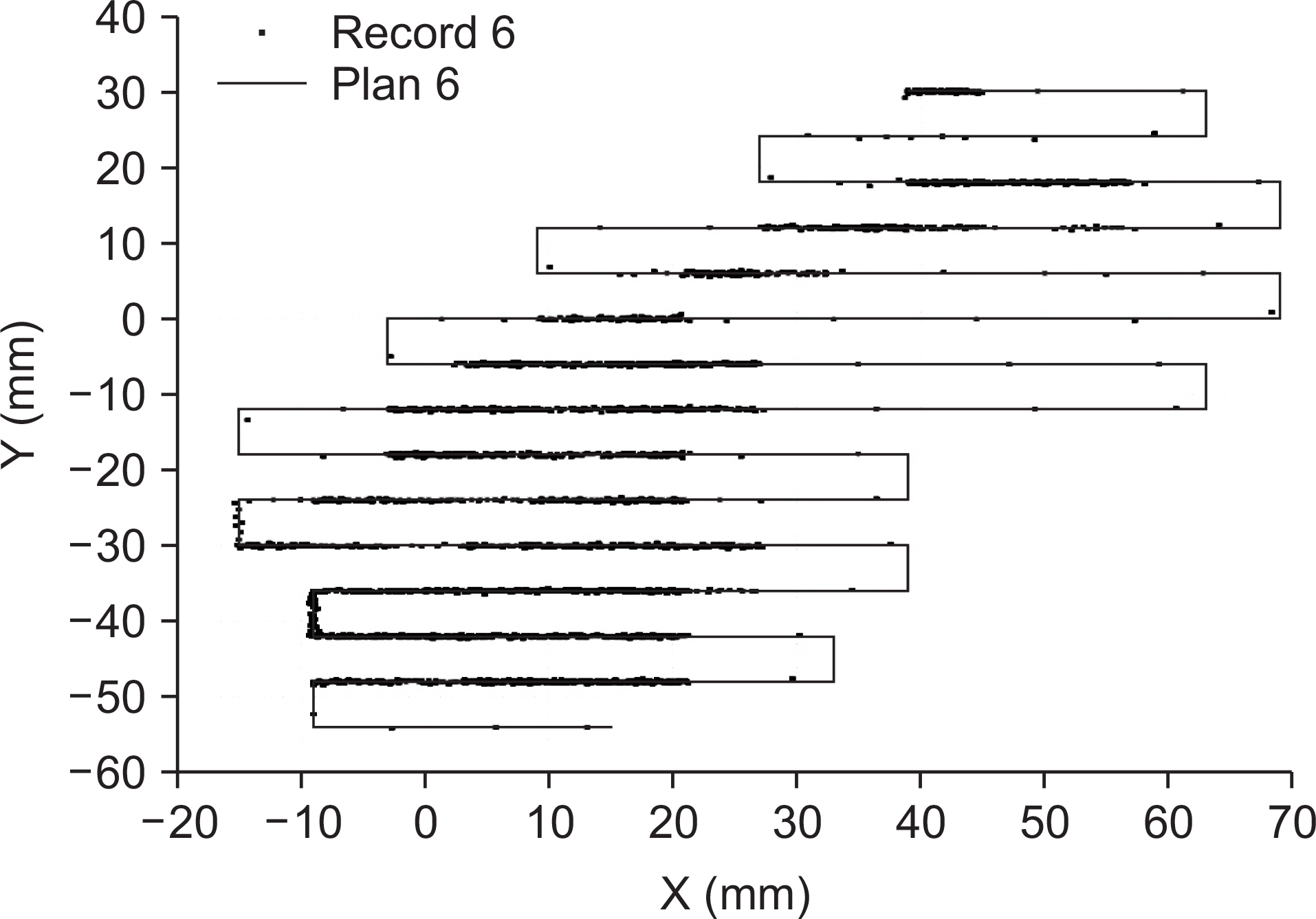
- The machine log files recorded by a scanning control unit in proton beam therapy system have been studied to be used as a quality assurance method of scanning beam deliveries. The accuracy of the data in the log files have been evaluated with a standard calibration beam scan pattern. The proton beam scan pattern has been delivered on a gafchromic film located at the isocenter plane of the proton beam treatment nozzle and found to agree within ±1.0 mm. The machine data accumulated for the scanning beam proton therapy of five different cases have been analyzed using a statistical method to estimate any systematic error in the data. The high-precision scanning beam log files in line scanning proton therapy system have been validated to be used for off-line scanning beam monitoring and thus as a patient-specific quality assurance method. The use of the machine log files for patient-specific quality assurance would simplify the quality assurance procedure with accurate scanning beam data.
Figure
Reference
-
1. RR Wilson. Radiological use of fast protons. Radiology. 1946; 47:487–91.2. Kang JK, MS Kim WI. Jang, et. al. The clinical utilization of radiation therapy in Korea between 2009 and 2013. Radiat Oncol J. 2016; 34:88–95.3. M Jermann. Particle therapy statistics in 2014. Int J Particle Ther. 2015; 2:50–4.4. H Li, N Sahoo, F Poenisch et. al. Use of treatment log files in spot scanning proton therapy as part of patient-specific quality assurance. Med Phys. 2013; 40:021703–1. -11.5. Scandurra D, Albertini F, Meer R, et al. Assessing the quality of proton PBS treatment delivery using machine log files: comprehensive analysis of clinical treatments delivered at PSI Gantry 2. Phys Med Biol. 2016; 61:1171–81.
Article6. K Chung, Y Han, J Kim et. al. The first private-hospital based proton therapy center in Korea: Status of the Proton Therapy Center at Samsung Medical Center. Radiat Oncol J. 2015; 33:337–43.7. K Chung, J Kim, DH Kim, S Ahn, Y Han. The proton therapy nozzles at Samsung Medical Center: A Monte Carlo simulation study using TOPAS. J Korean Phys Soc. 2015; 67:170–4.8. K Chung, Y Han, SH Ahn, JS Kim, H Nonaka. Commissioning and Validation of a Dedicated Scanning Nozzle at Samsung Proton Therapy Center. Prog Med Phys. 2016; 27:267–71.9. GAFChromicTM EBT3 film specifications. Available at. www.gafchromic.com.10. G Moliere. Theorie der Streuung schneller geladener Teilchen II. Mehrfach-und Vielfachstreuung. Z Naturforsch A: Phys Sci. 1948; 3a:78–97.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development of an Analytic Software Using Pencil Beam Scanning Proton Beam
- Image Based Quality Assurance of Range Compensator for Proton Beam Therapy
- Commissioning and Validation of a Dedicated Scanning Nozzle at Samsung Proton Therapy Center
- Proton Therapy Review: Proton Therapy from a Medical
- Proton Beam Therapy