Prog Med Phys.
2017 Mar;28(1):22-26. 10.14316/pmp.2017.28.1.22.
Development of an Analytic Software Using Pencil Beam Scanning Proton Beam
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Bio-convergence Engineering, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. physicist.chung@gmail.com
- KMID: 2382801
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2017.28.1.22
Abstract
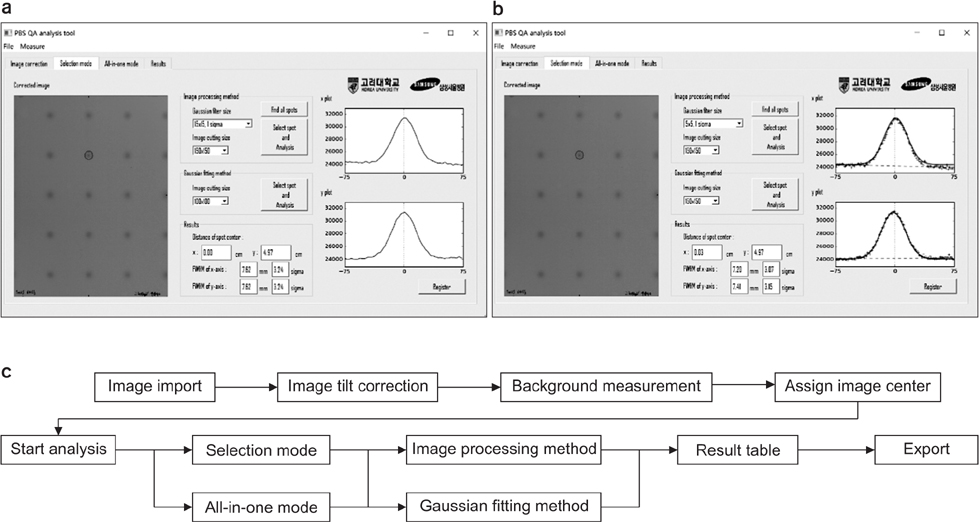
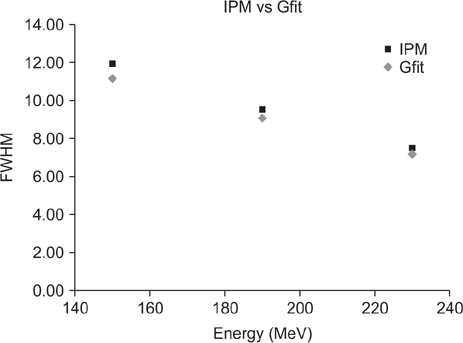
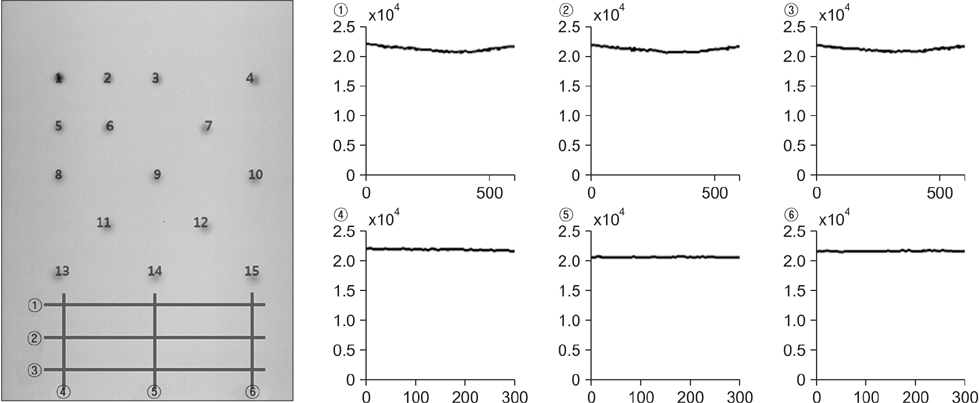
- We have developed an analytic software that can easily analyze the spot position and width of proton beam therapy nozzles in a periodic quality assurance. The developed software consists of an image processing method that conducts an analysis using center-of-spot geometry and a Gaussian fitting method that conducts an analysis through Gaussian fitting. By using the software, an analysis of 210 proton spots with energies 150, 190, and 230 MeV showed a deviation of approximately 3% from the mean. The software we developed to analyze proton spot positions and widths provides an accurate analysis and reduces the time for analysis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jermann M. Particle therapy statistics in 2014. Int J Particle Ther. 2015; 2:50–54.
Article2. ICRU. Clinical Proton Dosimetry, Part I: Beam Production, Beam Delivery and Measurement of Absorbed Dose. ICRU Report. Bethesda. ICRU;1998.3. Maughan RL, Farr JB. Proton and Charge Part icle Radiotherapy. Philadelphia: Williams & Wilkins;2007.4. Moyers MF. Modern Technology of Radiation Oncology. Medical Physics: Madison;1999.5. Arjomandy B, Sahoo N, Zhu XR, Zullo JR, Wu RY, Zhu M, et al. An overview of the comprehensive proton therapy machine quality assurance procedures implemented at The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Proton Therapy Center-Houston. Med Phys. 2009; 36:2269–2282.6. Reinhardt S, Hillbrand M, Wilkens JJ, Assmann W. Comparison of Gafchromic EBT2 and EBT3 films for clinical photon and proton beams. Med Phys. 2012; 39:5257–5262.
Article7. Guo H. A simple algorithm for fitting a Gaussian function. IEEE Sign Proc Mag. 2011; 28:134–137.
Article8. Chung K, Han Y, Ahn SH, Kim JS, Nonaka H. Commissioning and validation of a dedicated scanning nozzle at Samsung Proton Therapy Center. Prog Med Phys. 2016; 27:267–271.
Article9. Chung K, Han Y, Kim J, Ahn SH, Ju SG, Jung SH, et al. The first private-hospital based proton therapy center in Korea: Status of the Proton Therapy Center at Samsung Medical Center. Radiat Oncol J. 2015; 33:337–343.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Pilot Study of the Scanning Beam Quality Assurance Using Machine Log Files in Proton Beam Therapy
- Proton Therapy Review: Proton Therapy from a Medical
- A Monte Carlo Simulation Study of a Therapeutic Proton Beam Delivery System Using the Geant4 Code
- Commissioning and Validation of a Dedicated Scanning Nozzle at Samsung Proton Therapy Center
- Proton Beam Therapy