J Vet Sci.
2017 Dec;18(4):439-447. 10.4142/jvs.2017.18.4.439.
A serine/threonine phosphatase 1 of Streptococcus suis type 2 is an important virulence factor
- Affiliations
-
- 1Zhejiang University Institute of Preventive Veterinary Medicine and Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, Hangzhou 310058, China. whfang@zju.edu.cn
- 2Center for Synthetic Biology Engineering Research, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen 518055, China.
- KMID: 2398502
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2017.18.4.439
Abstract
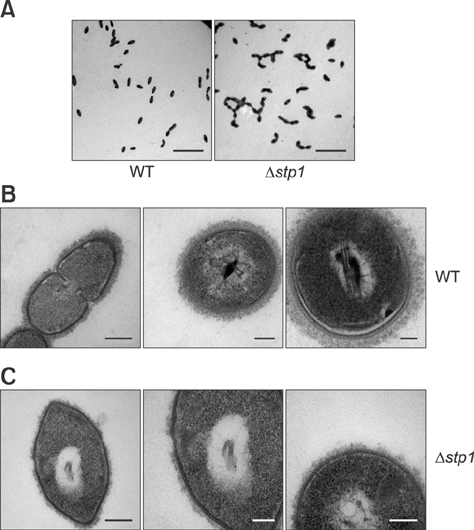
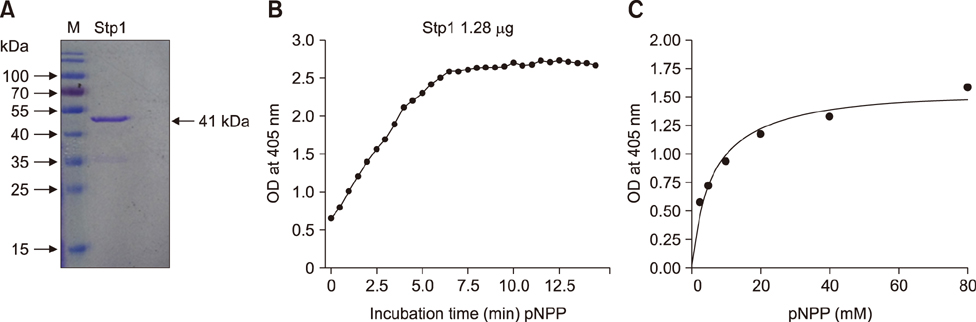
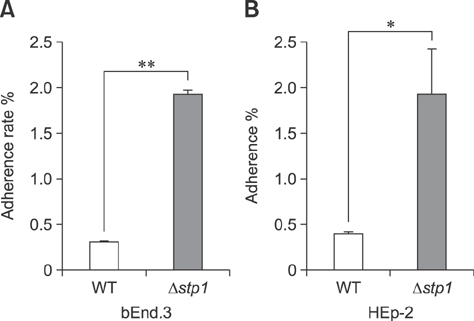
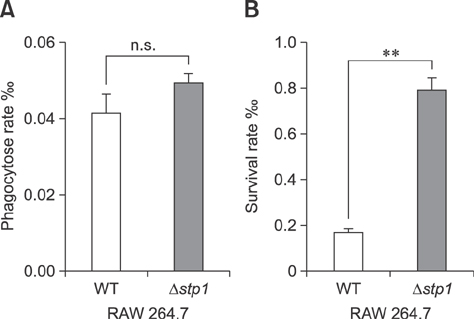
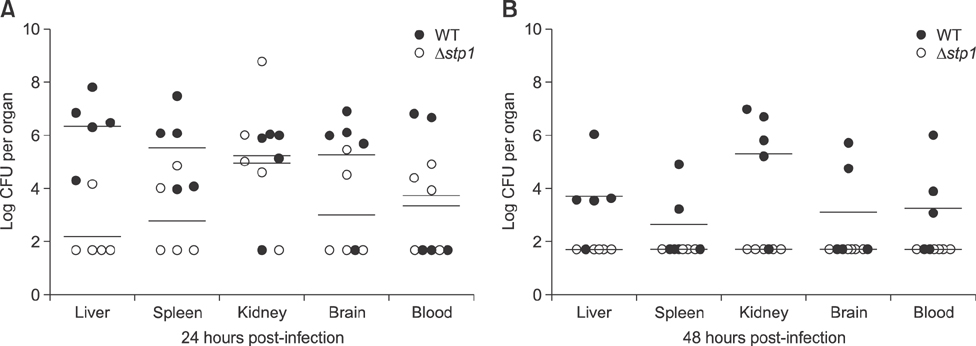
- Streptococcus suis is regarded as one of the major pathogens of pigs, and Streptococcus suis type 2 (SS2) is considered a zoonotic bacterium based on its ability to cause meningitis and streptococcal toxic shock-like syndrome in humans. Many bacterial species contain genes encoding serine/threonine protein phosphatases (STPs) responsible for dephosphorylation of their substrates in a single reaction step. This study investigated the role of stp1 in the pathogenesis of SS2. An isogenic stp1 mutant (Δstp1) was constructed from SS2 strain ZJ081101. The Δstp1 mutant exhibited a significant increase in adhesion to HEp-2 and bEnd.3 cells as well as increased survival in RAW264.7 cells, as compared to the parent strain. Increased survival in macrophage cells might be related to resistance to reactive oxygen species since the Δstp1 mutant was more resistant than its parent strain to paraquat-induced oxidative stress. However, compared to parent strain virulence, deletion of stp1 significantly attenuated virulence of SS2 in mice, as shown by the nearly double lethal dose 50 value and the lower bacterial load in organs and blood in the murine model. We conclude that Stp1 has an essential role in SS2 virulence.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Agarwal S, Agarwal S, Jin H, Pancholi P, Pancholi V. Serine/threonine phosphatase (SP-STP), secreted from Streptococcus pyogenes, is a pro-apoptotic protein. J Biol Chem. 2012; 287:9147–9167.
Article2. Archambaud C, Nahori MA, Pizarro-Cerda J, Cossart P, Dussurget O. Control of Listeria superoxide dismutase by phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 2006; 281:31812–31822.3. Barford D, Das AK, Egloff MP. The structure and mechanism of protein phosphatases: insights into catalysis and regulation. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1998; 27:133–164.
Article4. Baums CG, Valentin-Weigand P. Surface-associated and secreted factors of Streptococcus suis in epidemiology, pathogenesis and vaccine development. Anim Health Res Rev. 2009; 10:65–83.
Article5. Burnside K, Lembo A, de Los Reyes M, Iliuk A, BinhTran NT, Connelly JE, Lin WJ, Schmidt BZ, Richardson AR, Fang FC, Tao WA, Rajagopal L. Regulation of hemolysin expression and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus by a serine/threonine kinase and phosphatase. PLoS One. 2010; 5:e11071.6. Bus JS, Gibson JE. Paraquat: model for oxidant-initiated toxicity. Environ Health Perspect. 1984; 55:37–46.
Article7. Cameron DR, Ward DV, Kostoulias X, Howden BP, Moellering RC Jr, Eliopoulos GM, Peleg AY. Serine/threonine phosphatase Stp1 contributes to reduced susceptibility to vancomycin and virulence in Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 2012; 205:1677–1687.
Article8. Cybulski RJ Jr, Sanz P, Alem F, Stibitz S, Bull RL, O'Brien AD. Four superoxide dismutases contribute to Bacillus anthracis virulence and provide spores with redundant protection from oxidative stress. Infect Immun. 2009; 77:274–285.
Article9. Dong W, Ma J, Zhu Y, Zhu J, Yuan L, Wang Y, Xu J, Pan Z, Wu Z, Zhang W, Lu C, Yao H. Virulence genotyping and population analysis of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 isolates from China. Infect Genet Evol. 2015; 36:483–489.
Article10. Feng Y, Zhang H, Wu Z, Wang S, Cao M, Hu D, Wang C. Streptococcus suis infection: an emerging/reemerging challenge of bacterial infectious diseases? Virulence. 2014; 5:477–497.11. Gaidenko TA, Kim TJ, Price CW. The PrpC serine-threonine phosphatase and PrkC kinase have opposing physiological roles in stationary-phase Bacillus subtilis cells. J Bacteriol. 2002; 184:6109–6114.
Article12. Grenier D, Bodet C. Streptococcus suis stimulates ICAM-1 shedding from microvascular endothelial cells. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2008; 54:271–276.
Article13. Haas B, Vaillancourt K, Bonifait L, Gottschalk M, Grenier D. Hyaluronate lyase activity of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 and modulatory effects of hyaluronic acid on the bacterium's virulence properties. BMC Res Notes. 2015; 8:722.
Article14. Han H, Liu C, Wang Q, Xuan C, Zheng B, Tang J, Yan J, Zhang J, Li M, Cheng H, Lu G, Gao GF. The two-component system Ihk/Irr contributes to the virulence of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 strain 05ZYH33 through alteration of the bacterial cell metabolism. Microbiology. 2012; 158:1852–1866.
Article15. Houde M, Gottschalk M, Gagnon F, Van Calsteren MR, Segura M. Streptococcus suis capsular polysaccharide inhibits phagocytosis through destabilization of lipid microdomains and prevents lactosylceramide-dependent recognition. Infect Immun. 2012; 80:506–517.
Article16. Jin H, Pancholi V. Identification and biochemical characterization of a eukaryotic-type serine/threonine kinase and its cognate phosphatase in Streptococcus pyogenes: their biological functions and substrate identification. J Mol Biol. 2006; 357:1351–1372.
Article17. Ju CX, Gu HW, Lu CP. Characterization and functional analysis of atl, a novel gene encoding autolysin in Streptococcus suis. J Bacteriol. 2012; 194:1464–1473.
Article18. Kennelly PJ. Protein kinases and protein phosphatases in prokaryotes: a genomic perspective. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2002; 206:1–8.
Article19. Li J, Tan C, Zhou Y, Fu S, Hu L, Hu J, Chen H, Bei W. The two-component regulatory system CiaRH contributes to the virulence of Streptococcus suis 2. Vet Microbiol. 2011; 148:99–104.
Article20. Li M, Wang C, Feng Y, Pan X, Cheng G, Wang J, Ge J, Zheng F, Cao M, Dong Y, Liu D, Wang J, Lin Y, Du H, Gao GF, Wang X, Hu F, Tang J. SalK/SalR, a two-component signal transduction system, is essential for full virulence of highly invasive Streptococcus suis serotype 2. PLoS One. 2008; 3:e2080.21. Martinez MA, Das K, Saikolappan S, Materon LA, Dhandayuthapani S. A serine/threonine phosphatase encoded by MG_207 of Mycoplasm genitalium is critical for its virulence. BMC Microbiol. 2013; 13:44.
Article22. Neiss WF. Electron staining of the cell surface coat by osmium-low ferrocyanide. Histochemistry. 1984; 80:231–242.
Article23. Osaki M, Arcondéguy T, Bastide A, Touriol C, Prats H, Trombe MC. The StkP/PhpP signaling couple in Streptococcus pneumoniae: cellular organization and physiological characterization. J Bacteriol. 2009; 191:4943–4950.
Article24. Pereira SFF, Goss L, Dworkin J. Eukaryote-like serine/threonine kinases and phosphatases in bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011; 75:192–212.
Article25. Pullen KE, Ng HL, Sung PY, Good MC, Smith SM, Alber T. An alternate conformation and a third metal in PstP/Ppp, the M. tuberculosis PP2C-family Ser/Thr protein phosphatase. Structure. 2004; 12:1947–1954.
Article26. Rajagopal L, Clancy A, Rubens CE. A eukaryotic type serine/threonine kinase and phosphatase in Streptococcus agalactiae reversibly phosphorylate an inorganic pyrophosphatase and affect growth, cell segregation, and virulence. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278:14429–14441.
Article27. Rajagopal L, Vo A, Silvestroni A, Rubens CE. Regulation of purine biosynthesis by a eukaryotic-type kinase in Streptococcus agalactiae. Mol Microbiol. 2005; 56:1329–1346.
Article28. Rajala RVS, Kanan Y, Anderson RE. Photoreceptor neuroprotection: regulation of Akt activation through serine/threonine phosphatases, PHLPP and PHLPPL. In : Rickman CB, LaVail MM, Anderson RE, Grimm C, Hollyfield J, Ash J, editors. Retinal Degenerative Diseases: Mechanisms and Experimental Thergpy. London: Springer;2016. p. 419–424. (Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Vol. 854).29. Segura M, Gottschalk M. Streptococcus suis interactions with the murine macrophage cell line J774: adhesion and cytotoxicity. Infect Immun. 2002; 70:4312–4322.
Article30. Takamatsu D, Osaki M, Sekizaki T. Construction and characterization of Streptococcus suis-Escherichia coli shuttle cloning vectors. Plasmid. 2001; 45:101–113.
Article31. Takamatsu D, Osaki M, Sekizaki T. Thermosensitive suicide vectors for gene replacement in Streptococcus suis. Plasmid. 2001; 46:140–148.
Article32. Tang Y, Zhang X, Wu W, Lu Z, Fang W. Inactivation of the sodA gene of Streptococcus suis type 2 encoding superoxide dismutase leads to reduced virulence to mice. Vet Microbiol. 2012; 158:360–366.
Article33. Tang Y, Zhao H, Wu W, Wu D, Li X, Fang W. Genetic and virulence characterization of Streptococcus suis type 2 isolates from swine in the provinces of Zhejiang and Henan, China. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2011; 56:541–548.
Article34. Ulijasz AT, Falk SP, Weisblum B. Phosphorylation of the RitR DNA-binding domain by a Ser-Thr phosphokinase: implications for global gene regulation in the streptococci. Mol Microbiol. 2009; 71:382–390.
Article35. van Samkar A, Brouwer MC, Schultsz C, van der Ende A, van de Beek D. Streptococcus suis Meningitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015; 9:e0004191.36. Zhao Y, Liu G, Li S, Wang M, Song J, Wang J, Tang J, Li M, Hu F. Role of a type IV-like secretion system of Streptococcus suis 2 in the development of streptococcal toxic shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 2011; 204:274–281.
Article37. Zhu H, Huang D, Zhang W, Wu Z, Lu Y, Jia H, Wang M, Lu C. The novel virulence-related gene stp of Streptococcus suis serotype 9 strain contributes to a significant reduction in mouse mortality. Microb Pathog. 2011; 51:442–453.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Identification of a Novel Putative Protein Serine / Threonine Kinase, PK38, in Normal Human Keratinocytes
- Action Mechanisms of Hormone Binding to Cell Surface Receptors: 3) TGF-beta; Binding to Serine-threonine Kinase Receptors and Action Mechanisms
- A Case of Streptococcus suis Infection Causing Pneumonia with Empyema in Korea
- A Case of Life-Threating Streptococcus suis Infection Presented as Septic Shock and Multiple Abscesses
- Meningitis Caused by Streptococcus suis: Case Report and Review of the Literature