Infect Chemother.
2018 Sep;50(3):274-279. 10.3947/ic.2018.50.3.274.
A Case of Life-Threating Streptococcus suis Infection Presented as Septic Shock and Multiple Abscesses
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. mdcjk@catholic.ac.kr
- 3Vaccine Bio Research Institute, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2420913
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2018.50.3.274
Abstract
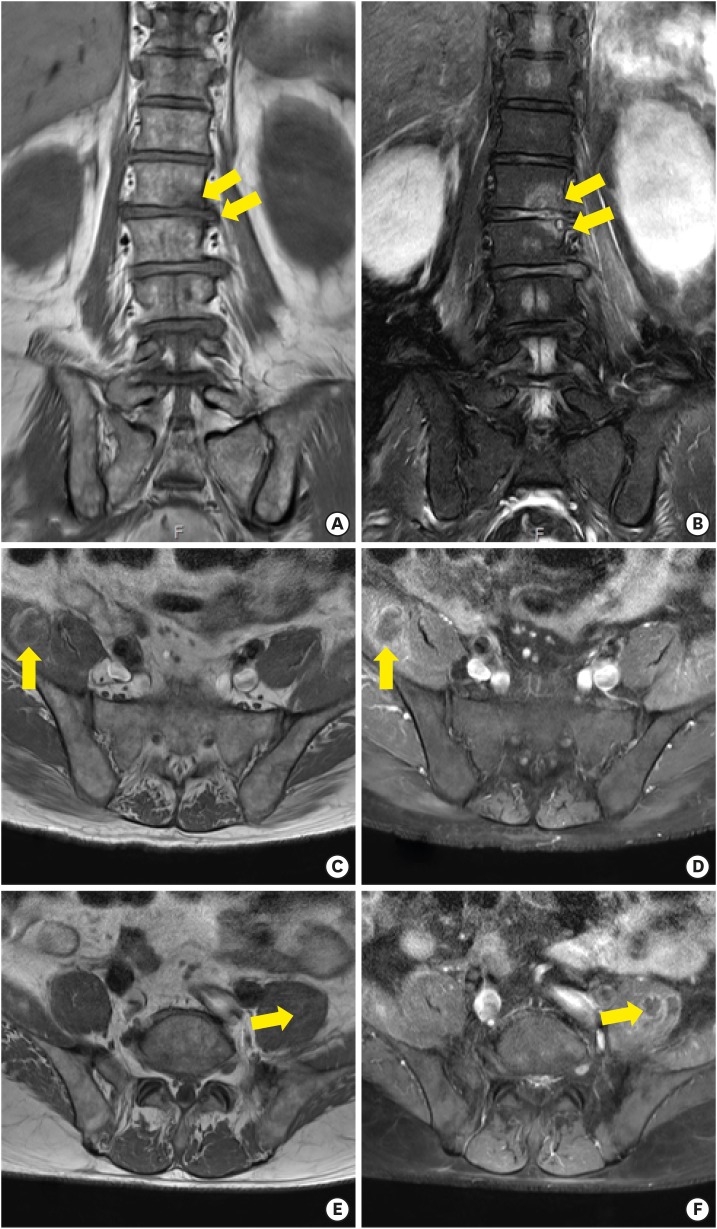
- Streptococcus suis is a zoonotic pathogen that can cause severe systemic infections in humans as well as swine. In recent decades, the number of S. suis infections in humans has increased, particularly in Southeast Asia. Although most cases of S. suis human infections are reported as sporadic, a few outbreaks have been noted. Interestingly, these outbreaks have been proposed to be associated with concomitant outbreaks in swine. In Korea, four sporadic and non-fatal cases of S. suis infection have been reported. We herein report a case of life-threating S. suis infection with sepsis for the first time in Korea. The patient was a healthy pig farmer, and the gastrointestinal tract was considered the route of infection. This case emphasized the need for awareness and recognition of S. suis as a zoonotic pathogen.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lun ZR, Wang QP, Chen XG, Li AX, Zhu XQ. Streptococcus suis: an emerging zoonotic pathogen. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007; 7:201–209. PMID: 17317601.2. Arends JP, Zanen HC. Meningitis caused by Streptococcus suis in humans. Rev Infect Dis. 1988; 10:131–137. PMID: 3353625.3. Wertheim HF, Nghia HD, Taylor W, Schultsz C. Streptococcus suis: an emerging human pathogen. Clin Infect Dis. 2009; 48:617–625. PMID: 19191650.4. Huh HJ, Park KJ, Jang JH, Lee M, Lee JH, Ahn YH, Kang CI, Ki CS, Lee NY. Streptococcus suis meningitis with bilateral sensorineural hearing loss. Korean J Lab Med. 2011; 31:205–211. PMID: 21779197.5. Choi SM, Cho BH, Choi KH, Nam TS, Kim JT, Park MS, Kim BC, Kim MK, Cho KH. Meningitis caused by Streptococcus suis: case report and review of the literature. J Clin Neurol. 2012; 8:79–82. PMID: 22523518.6. Kim H, Lee SH, Moon HW, Kim JY, Lee SH, Hur M, Yun YM. Streptococcus suis causes septic arthritis and bacteremia: phenotypic characterization and molecular confirmation. Korean J Lab Med. 2011; 31:115–117. PMID: 21474987.7. Oh YJ, Song SH. A case of Streptococcus suis infection causing pneumonia with empyema in Korea. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2012; 73:178–181.8. Greisen K, Loeffelholz M, Purohit A, Leong D. PCR primers and probes for the 16S rRNA gene of most species of pathogenic bacteria, including bacteria found in cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 1994; 32:335–351. PMID: 7512093.
Article9. van Samkar A, Brouwer MC, Schultsz C, van der Ende A, van de Beek D. Streptococcus suis meningitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015; 9:e0004191. PMID: 26505485.10. Tan JH, Yeh BI, Seet CS. Deafness due to haemorrhagic labyrinthitis and a review of relapses in Streptococcus suis meningitis. Singapore Med J. 2010; 51:e30–e33. PMID: 20358139.11. Yu H, Jing H, Chen Z, Zheng H, Zhu X, Wang H, Wang S, Liu L, Zu R, Luo L, Xiang N, Liu H, Liu X, Shu Y, Lee SS, Chuang SK, Wang Y, Xu J, Yang W. Streptococcus suis Study Groups. Human Streptococcus suis outbreak, Sichuan, China. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006; 12:914–920. PMID: 16707046.12. Han DU, Choi C, Ham HJ, Jung JH, Cho WS, Kim J, Higgins R, Chae C. Prevalence, capsular type and antimicrobial susceptibility of Streptococcus suis isolated from slaughter pigs in Korea. Can J Vet Res. 2001; 65:151–155. PMID: 11480519.13. Kim D, Han K, Oh Y, Kim CH, Kang I, Lee J, Gottschalk M, Chae C. Distribution of capsular serotypes and virulence markers of Streptococcus suis isolated from pigs with polyserositis in Korea. Can J Vet Res. 2010; 74:314–316. PMID: 21197232.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Streptococcus suis Infection Causing Pneumonia with Empyema in Korea
- Streptococcus suis Causes Septic Arthritis and Bacteremia: Phenotypic Characterization and Molecular Confirmation
- Meningitis Caused by Streptococcus suis: Case Report and Review of the Literature
- A Case of Streptococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome Caused by Group A Streptococcus Pneumonia
- Streptococcus suis causes bacterial meningitis with hearing loss in patients without direct exposure to pigs in a regional pork industry territory