Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2017 Nov;21(4):243-246. 10.14701/ahbps.2017.21.4.243.
Xanthogranulomatous pancreatitis mimicking potentially malignant pancreatic neoplasm: report of a case
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Kyungpook National University Chilgok Hospital, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. kwonhj95@naver.com
- KMID: 2397807
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2017.21.4.243
Abstract
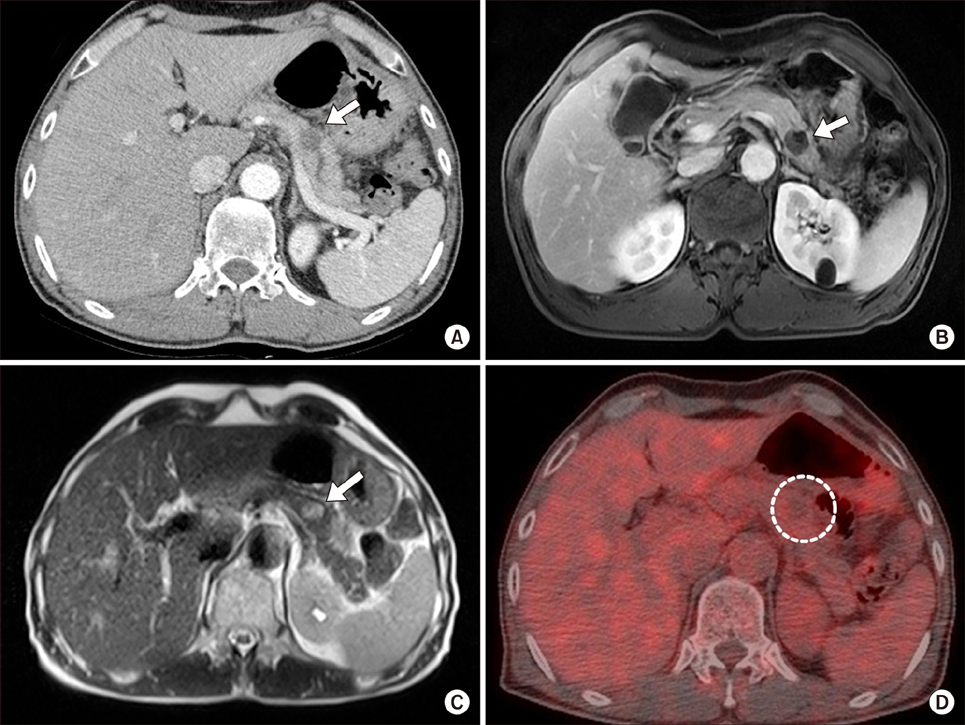
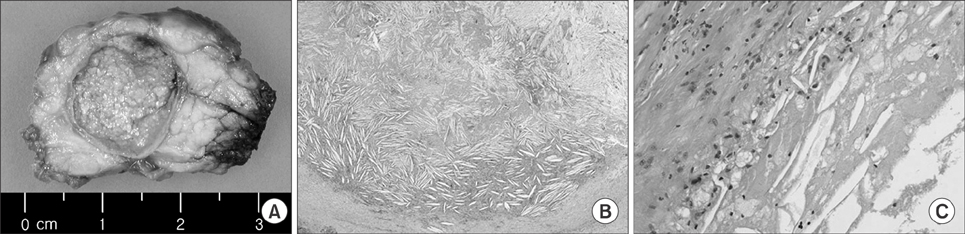
- Xanthogranulomatous pancreatitis (XGP) is a rare benign disease that may mimic or accompany other pancreatic diseases. Here we report a case of XGP initially suspected as malignant cystic neoplasm of the pancreas. A 64-year-old man had been incidentally found to have hypodense lesion at the body of pancreas during a lung cancer workup. All laboratory tests were within normal limits except that carcinoembryonic antigen was elevated to 31.3 ng/ml. Imaging study showed 1.8 cm sized, well demarcated, and low-attenuated mass on computed tomography (CT) with heterogeneously high intensity on T2-weighted images of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Under the impression of pancreas cystic neoplasm as a rare case of male solid-pseudopapillary tumor or pancreatic metastasis of lung cancer, laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy was performed. Microscopically, the mass had many foamy histiocytes with cholesterol clefts, consistent with xanthogranulomatous inflammation. Therefore, it is important to consider XGP in the differential diagnosis of pancreatic diseases.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Iyer VK, Aggarwal S, Mathur M. Xanthogranulomatous pancreatitis: mass lesion of the pancreas simulating pancreatic carcinoma--a report of two cases. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2004; 47:36–38.2. Kamitani T, Nishimiya M, Takahashi N, Shida Y, Hasuo K, Koizuka H. Xanthogranulomatous pancreatitis associated with intraductal papillary mucinous tumor. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 185:704–707.3. Nishimura M, Nishihira T, Hirose T, Ishikawa Y, Yamaoka R, Inoue H, et al. Xanthogranulomatous pancreatitis mimicking a malignant cystic tumor of the pancreas: report of a case. Surg Today. 2011; 41:1310–1313.4. Shima Y, Saisaka Y, Furukita Y, Nishimura T, Horimi T, Nakamura T, et al. Resected xanthogranulomatous pancreatitis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2008; 15:240–242.5. Iso Y, Tagaya N, Kita J, Sawada T, Kubota K. Xanthogranulomatous lesion of the pancreas mimicking pancreatic cancer. Med Sci Monit. 2008; 14:CS130–CS133.6. Ikeura T, Takaoka M, Shimatani M, Koyabu M, Kusuda T, Suzuki R, et al. Xanthogranulomatous inflammation of the peripancreatic region mimicking pancreatic cystic neoplasm. Intern Med. 2009; 48:1881–1884.7. Kim YN, Park SY, Kim YK, Moon WS. Xanthogranulomatous pancreatitis combined with intraductal papillary mucinous carcinoma in situ. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:1814–1817.8. Kim HS, Joo M, Chang SH, Song HY, Song TJ, Seo JW, et al. Xanthogranulomatous pancreatitis presents as a solid tumor mass: a case report. J Korean Med Sci. 2011; 26:583–586.9. Hanna T, Abdul-Rahman Z, Greenhalf W, Farooq A, Neoptolemos JP. Xanthogranulomatous pancreatitis associated with a mucinous cystic neoplam. Pathol Int. 2016; 66:174–176.10. Roberts KM, Parsons MA. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis: clinicopathological study of 13 cases. J Clin Pathol. 1987; 40:412–417.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Xanthogranulomatous Pancreatitis Mimicking a Pancreatic Cancer on CT and MRI: a Case Report and Literature Review
- Xanthogranulomatous Pancreatitis Mimicking Pancreatic Cancer
- A Case of Pancreatic Head Carcinoma Mimicking Chronic Pancreatitis
- A Case of Branch Duct Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm Mimicking Pseudocysts Complicated by Recurrent Pancreatitis
- A Case of Xanthogranulomatous Sialadenitis with Facial Palsy Mimicking Malignancy