Asia Pac Allergy.
2011 Oct;1(3):138-144. 10.5415/apallergy.2011.1.3.138.
Investigation of the antiallergic activity of olopatadine on rhinitis induced by intranasal instillation of antigen in sensitized rats using thermography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Pharmacological Research Laboratories, Research Division, Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd., Shizuoka 411-8731, Japan. tadafumi.tamura@kyowa-kirin.co.jp
- KMID: 2397432
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5415/apallergy.2011.1.3.138
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The main symptoms of allergic rhinitis (AR) are sneezing, rhinorrhea and nasal obstruction. It was reported that the nasal skin temperature after intranasal administration of histamine or grass pollen rose. In patients with AR, the levels of nerve growth factor (NGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) have increased in nasal fluids and mucosa.
OBJECTIVE
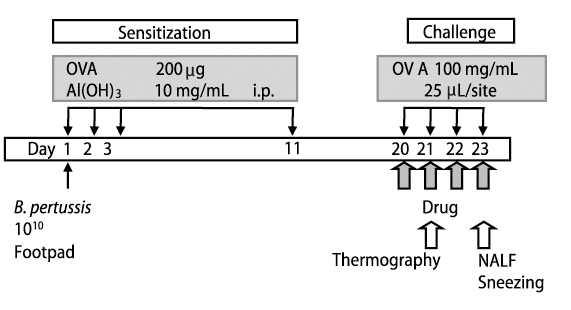
The present study were to determine the temperature changes of the nose in rat allergic rhinitis model, and if olopatadine, an antiallergic agent with histamine H1 receptor antagonistic action, proved to be effective, were studied the productions of NGF and VEGF in nasal lavage fluids (NALF). In the present study, we used ovalbumin (OVA)-sensitized rats as an animal model of nasal allergy and examined the effects of olopatadine on the skin temperature of the nose area, and the productions of NGF and VEGF in NALF.
METHODS
The temperature changes of the nose area were carried out with thermo tracer in rat passively sensitized with OVA antiserum. The numbers of sneezing episodes were counted and, NGF and VEGF levels in NALF were examined using the specific ELISA.
RESULTS
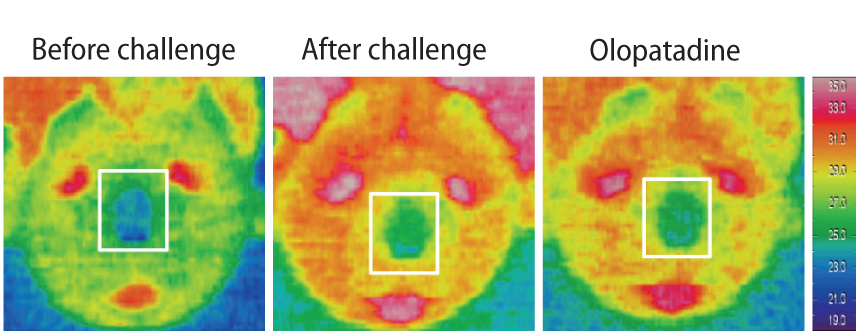
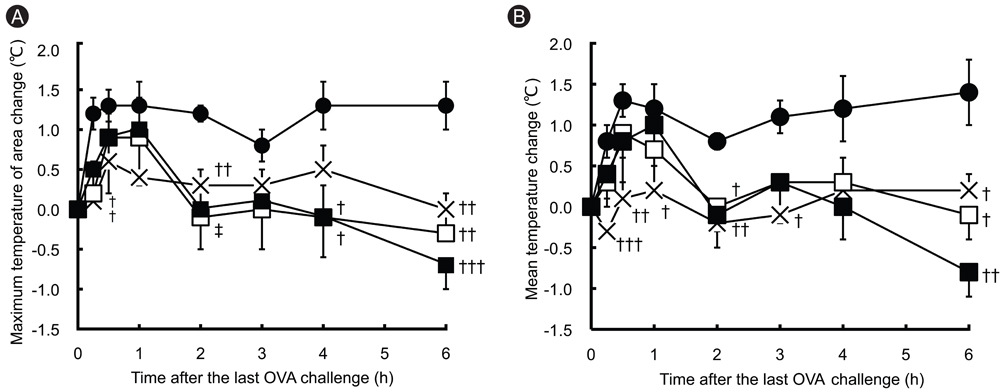
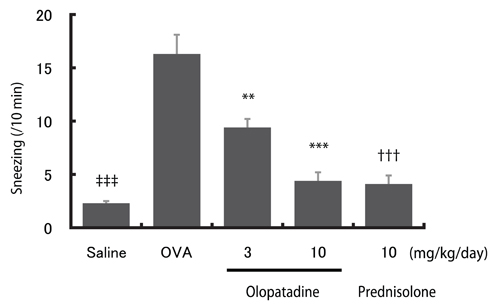
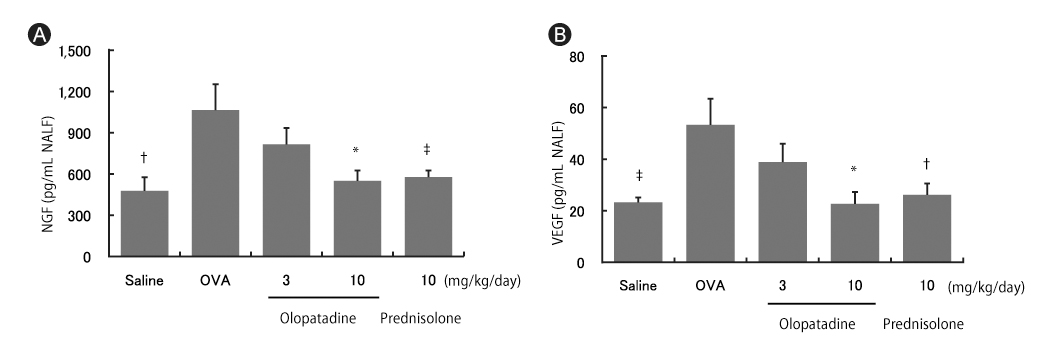
In OVA-sensitized rats, the number of sneezing episodes increase and the nasal skin temperature rise were provoked after OVA challenge. The levels of NGF and VEGF in NALF also were increased. Olopatadine reduced the increased frequency of sneezing and the nasal skin temperature rise. It also inhibited the increased NGF and VEGF productions in NALF.
CONCLUSION
The nasal skin temperature after OVA challenge rose even in OVA-sensitized rats. These results suggest that the suppression of the increased NGF and VEGF levels might partially be involved in the improvement of allergy-like behavior (sneezing and nasal skin temperature rise) by the treatment of olopatadine.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Administration, Intranasal
Animals
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Histamine
Humans
Hypersensitivity
Models, Animal
Mucous Membrane
Nasal Lavage Fluid
Nasal Obstruction
Nerve Growth Factor
Nose
Olopatadine Hydrochloride*
Ovalbumin
Ovum
Poaceae
Pollen
Rats*
Receptors, Histamine H1
Rhinitis*
Rhinitis, Allergic
Skin Temperature
Sneezing
Thermography*
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
Histamine
Nerve Growth Factor
Olopatadine Hydrochloride
Ovalbumin
Receptors, Histamine H1
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Current trends in upper airways and ocular allergic inflammation
Ashok Shah
Asia Pac Allergy. 2011;1(3):105-107. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2011.1.3.105.
Reference
-
1. Takahashi H, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Iizuka H. Effects of bepotastine, cetirizine, fexofenadine, and olopatadine on histamine-induced wheal-and flare-response, sedation, and psychomotor performance. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2004. 29:526–532.
Article2. Takahashi H, Zhang Y, Morita E. Evaluation of the antihistamine effects of olopatadine, cetirizine and fexofenadine during a 24 h period: a double-blind, randomized, crossover, placebo-controlled comparison in skin responses induced by histamine iontophoresis. Arch Dermatol Res. 2008. 300:291–295.3. LaForce CF, Carr W, Tilles SA, Chipps BE, Storms W, Meltzer EO, Edwards M. Evaluation of olopatadine hydrochloride nasal spray, 0.6%, used in combination with an intranasal corticosteroid in seasonal allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2010. 31:132–140.
Article4. Segall N, Gawchik S, Georges G, Haeusler JM. Efficacy and safety of levocetirizine in improving symptoms and health-related quality of life in US adults with seasonal allergic rhinitis: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010. 104:259–267.
Article5. Seppey M, Hessler C, Bruchez M, Savary M, Pécoud A. Facial thermography during nasal provocation tests with histamine and allergen. Allergy. 1993. 48:314–318.
Article6. Larbig M, Burtin B, Martin L, Stamm H, Luettig B, Hohlfeld JM, Krug N. Facial thermography is a sensitive tool to determine antihistaminic activity: comparison of levocetirizine and fexofenadine. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2006. 62:158–164.
Article7. Sanico AM, Stanisz AM, Gleeson TD, Bora S, Proud D, Bienenstock J, Koliatsos VE, Togias A. Nerve growth factor expression and release in allergic inflammatory disease of the upper airways. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000. 161:1631–1635.
Article8. Mosimann BL, White MV, Hohman RJ, Goldrich MS, Kaulbach HC, Kaliner MA. Substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide, and vasoactive intestinal peptide increase in nasal secretions after allergen challenge in atopic patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1993. 92:95–104.
Article9. Shusterman D. Environmental nonallergic rhinitis. Clin Allergy Immunol. 2007. 19:249–266.10. Matsune S, Ohori J, Yoshifuku K, Kurono Y. Effect of vascular endothelial growth factor on nasal vascular permeability. Laryngoscope. 2010. 120:844–848.
Article11. Yamashita T, Terada N, Hamano N, Kishi H, Kobayashi N, Kotani Y, Miura M, Konno A. Involvement of vascular endothelial growth factor in nasal obstruction in patients with nasal allergy. Allergol Int. 2000. 49:183–188.
Article12. Ohmori K, Hasegawa K, Tamura T, Miyake K, Matsubara M, Masaki S, Karasawa A, Urayama N, Horikoshi K, Kajita J, Hasegawa M, Taniguchi K, Komada T, Kawamoto Y. Properties of olopatadine hydrochloride, a new antiallergic/antihistaminic drug. Arzneimittelforschung. 2004. 54:809–829.13. Yanni JM, Weimer LK, Sharif NA, Xu SX, Gamache DA, Spellman JM. Inhibition of histamine-induced human conjunctival epithelial cell responses by ocular allergy drugs. Arch Ophthalmol. 1999. 117:643–647.
Article14. Roland PS, Ryan MW, Wall GM. Olopatadine nasal spray for the treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis in patients aged 6 years and older. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2010. 11:1559–1567.
Article15. Tamura T, Komai M. Effect of olopatadine hydrochloride, an anti-histamine drug, on rhinitis induced by intranasal instillation of toluene-2,4-diisocyanate in rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 2008. 8:916–921.
Article16. Shimizu T, Hirano H, Majima Y, Sakakura Y. A mechanism of antigen-induced mucus production in nasal epithelium of sensitized rats. A comparison with lipopolysaccharide-induced mucus production. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000. 161:1648–1654.17. Enomoto T, Lu HQ, Yin M, Sakoda T, Dake Y, Enomoto K, Ide T, Cheng L. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of olopatadine and fexofenadine compared with placebo in Japanese cedar pollinosis using an environmental exposure unit. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2009. 19:299–305.18. Okubo K, Okuda M, Magara H, Kaneko K. Olopatadine hydrochloride in children: efficacy and safety for perennial allergic rhinitis. Curr Med Res Opin. 2010. 26:1657–1665.
Article19. Roland PS, Marple BF, Wall GM. Olopatadine nasal spray for the treatment of allergic rhinitis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2010. 6:197–204.
Article20. Tsumuro T, Alejandra Hossen M, Kishi Y, Fujii Y, Kamei C. Nasal congestion model in Brown Norway rats and the effects of some H1-antagonists. Int Immunopharmacol. 2006. 6:759–763.21. Kaise T, Ohmori K, Sakakura Y, Ukai K. The effect of KW-4679, an antiallergic drug, on experimental allergic rhinitis in guinea pigs: effects on nasal blockage. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1995. 69:435–438.
Article22. Hansen I, Klimek L, Mösges R, Hörmann K. Mediators of inflammation in the early and the late phase of allergic rhinitis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004. 4:159–163.
Article23. Rosenwasser L. New insights into the pathophysiology of allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2007. 28:10–15.
Article24. Sakai H, Enzaka J, Sakai-Oshita M, Chiba Y, Misawa M. Augmented venous responsiveness to leukotriene D4 in nasal septal mucosae of repeatedly antigen-challenged rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010. 644:215–219.25. Sanico AM, Atsuta S, Proud D, Togias A. Dose-dependent effects of capsaicin nasal challenge: in vivo evidence of human airway neurogenic inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997. 100:632–641.
Article26. Miyake K, Horikoshi K, Ikeda Y, Ishii A, Karasawa A. Effects of olopatadine hydrochloride on the increase of histamine and peptide-leukotrienes concentrations in nasal lavage fluid following the antigen-antibody reaction in actively sensitized guinea pigs. Jpn J Pharmacol. 2001. 85:453–456.
Article27. Kaise T, Akamatsu Y, Ikemura T, Ohmori K, Ishii A, Karasawa A. Involvement of neuropeptides in the allergic nasal obstruction in guinea pigs. Jpn J Pharmacol. 2001. 86:196–202.
Article28. Boesiger J, Tsai M, Maurer M, Yamaguchi M, Brown LF, Claffey KP, Dvorak HF, Galli SJ. Mast cells can secrete vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial cell growth factor and exhibit enhanced release after immunoglobulin E-dependent upregulation of Fcε receptor I expression. J Exp Med. 1998. 188:1135–1145.29. Sanico AM, Koliatsos VE, Stanisz AM, Bienenstock J, Togias A. Neural hyperresponsiveness and nerve growth factor in allergic rhinitis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1999. 118:154–158.
Article30. Heppt W, Dinh QT, Cryer A, Zweng M, Noga O, Peiser C, Melvan M, Witt C, Fischer A, Groneberg DA. Phenotypic alteration of neuropeptide-containing nerve fibres in seasonal intermittent allergic rhinitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004. 34:1105–1110.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Olopatadine ophthalmic solution suppresses substance P release in the conjunctivitis models
- Ciliary Activity of Upper Airway Epithelial Cells of Rats with Experimentally Induced Allergic Rhinitis
- The Effects of Intranasal Instillation of Stem Cell Factor in Mice with Experimentally-Induced Allergic Rhinitis
- House Dust Mite Allergic Rhinitis Model in C57BL/6 Mice
- The Change of Mast Cell and Smooth Muscle Contractility of Trachea, Intestine and Urinary Bladder in Sensitized Rats