Asia Pac Allergy.
2014 Jan;4(1):68-72. 10.5415/apallergy.2014.4.1.68.
Rapid onset of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis after ingestion of acetaminophen
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul 138-736, Korea. allergy@medimail.co.kr
- KMID: 2397128
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5415/apallergy.2014.4.1.68
Abstract
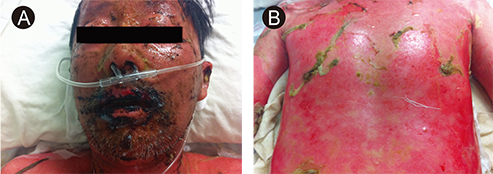
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) are rare, but life-threatening, severe cutaneous adverse reactions most frequently caused by exposure to drugs. Several reports have associated the use of acetaminophen with the risk of SJS or TEN. A typical interval from the beginning of drug therapy to the onset of an adverse reaction is 1-3 weeks. A 43-year-old woman and a 60-year-old man developed skin lesions within 3 days after administration of acetaminophen for a 3-day period. Rapid identification of the symptoms of SJS and TEN caused by ingestion of acetaminophen enabled prompt withdrawal of the culprit drug. After administration of intravenous immunoglobulin G, both patients recovered fully and were discharged. These two cases of rapidly developed SJS/TEN after ingestion of acetaminophen highlight the possibility that these complications can develop within only a few days following ingestion of over-the-counter medications such as acetaminophen.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Stevens–Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Associated with Acetaminophen Use during Viral Infections
Ga-Young Ban, Seun-Joo Ahn, Hye-Soo Yoo, Hae-Sim Park, Young-Min Ye
Immune Netw. 2016;16(4):256-260. doi: 10.4110/in.2016.16.4.256.Asia Pacific, and beyond
Yoon-Seok Chang, Sang-Il Lee
Asia Pac Allergy. 2014;4(1):1-2. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2014.4.1.1.Ibuprofen induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome - toxic epidermal necrolysis in Nepal
Siddheshwar S Angadi, Abhishek Karn
Asia Pac Allergy. 2016;6(1):70-73. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2016.6.1.70.
Reference
-
1. Kvedariene V, Bencherioua AM, Messaad D, Godard P, Bousquet J, Demoly P. The accuracy of the diagnosis of suspected paracetamol (acetaminophen) hypersensitivity: results of a single-blinded trial. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002; 32:1366–1369.
Article2. Vidal C, Pérez-Carral C, González-Quintela A. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) hypersensitivity. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1997; 79:320–321.3. Barvaliya M, Sanmukhani J, Patel T, Paliwal N, Shah H, Tripathi C. Drug-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and SJS-TEN overlap: a multicentric retrospective study. J Postgrad Med. 2011; 57:115–119.
Article4. Levi N, Bastuji-Garin S, Mockenhaupt M, Roujeau JC, Flahault A, Kelly JP, Martin E, Kaufman DW, Maison P. Medications as risk factors of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in children: a pooled analysis. Pediatrics. 2009; 123:e297–e304.
Article5. Lee T, Bae YJ, Park SK, Park HJ, Kim SH, Cho YS, Moon HB, Lee SO, Kim TB. Severe pneumonia caused by combined infection with Pneumocystis jiroveci, parainfluenza virus type 3, cytomegalovirus, and Aspergillus fumigatus in a patient with Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2010; 90:625–629.6. Roujeau JC, Kelly JP, Naldi L, Rzany B, Stern RS, Anderson T, Auquier A, Bastuji-Garin S, Correia O, Locati F, Mockenhaupt M, Paoletti C, Shapiro S, Shear N, Schöpf E, Kaufman DW. Medication use and the risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis. N Engl J Med. 1995; 333:1600–1607.
Article7. Roujeau JC, Stern RS. Severe adverse cutaneous reactions to drugs. N Engl J Med. 1994; 331:1272–1285.
Article8. Trujillo C, Gago C, Ramos S. Stevens-Jonhson syndrome after acetaminophen ingestion, confirmed by challenge test in an eleven-year-old patient. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2010; 38:99–100.
Article9. Halevi A, Ben-Amitai D, Garty BZ. Toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with acetaminophen ingestion. Ann Pharmacother. 2000; 34:32–34.
Article10. Mockenhaupt M. The current understanding of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2011; 7:803–813.
Article11. Harr T, French LE. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2010; 5:39.
Article12. Garcia-Doval I, LeCleach L, Bocquet H, Otero XL, Roujeau JC. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome: does early withdrawal of causative drugs decrease the risk of death? Arch Dermatol. 2000; 136:323–327.
Article13. Schneck J, Fagot JP, Sekula P, Sassolas B, Roujeau JC, Mockenhaupt M. Effects of treatments on the mortality of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: A retrospective study on patients included in the prospective EuroSCAR Study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008; 58:33–40.
Article14. Mangla K, Rastogi S, Goyal P, Solanki RB, Rawal RC. Efficacy of low dose intravenous immunoglobulins in children with toxic epidermal necrolysis: an open uncontrolled study. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2005; 71:398–400.
Article15. Tristani-Firouzi P, Petersen MJ, Saffle JR, Morris SE, Zone JJ. Treatment of toxic epidermal necrolysis with intravenous immunoglobulin in children. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002; 47:548–552.
Article16. French LE, Trent JT, Kerdel FA. Use of intravenous immunoglobulin in toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome: our current understanding. Int Immunopharmacol. 2006; 6:543–549.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- T Cell Mediated Drug Hypersensitivity: Stevens Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
- A Case of Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
- Stevens–Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Associated with Acetaminophen Use during Viral Infections
- A comparative clinical study of toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome
- Two Cases of HLA-B59(+) Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS)-Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN) Associated with Methazolamide Treatment